TNW spoke with futurist Nick Foster about the danger of designing the future with sci-fi in mind and why mundanity is far more exciting.



Former Google engineer and esteemed futurist Ray Kurzweil has made another bold prediction: Immortality is within reach for humans by 2030, thanks to the help of nanorobots. You read that right — humans could potentially live forever, according to Kurzweil.
Kurzweil, who has a track record of accurate predictions such as foreseeing a computer beating humans in chess by 2000, shared his prediction in a recent YouTube series by tech vlogger Adagio. The 75-year-old computer scientist believes that advancements in genetics, robotics and nanotechnology will allow tiny robots to run through veins, repairing any damage and keeping people alive indefinitely.
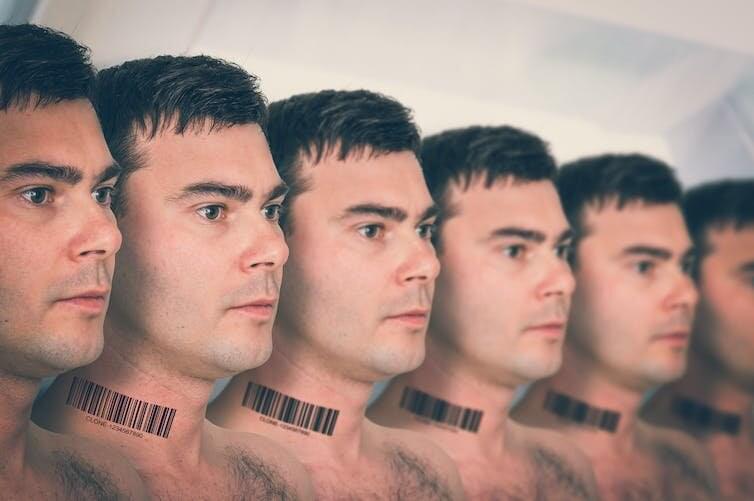

Imagine, if you will, a digital doppelgänger. A clone that looks, talks and behaves just like you, created from the depths of artificial intelligence, reflecting your every mannerism with eerie precision. As thrilling as it might sound, how would you feel about it?
Our research at the University of British Columbia turns the spotlight onto this very question. With advancements in deep-learning technologies such as interactive deepfake applications, voice conversion and virtual actors, it’s possible to digitally replicate an individual’s appearance and behavior.
This mirror image of an individual created by artificial intelligence is referred to as an “AI clone.” Our study dives into the murky waters of what these AI clones could mean for our self-perception, relationships and society. In our paper published as part of the Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction, we identified three types of risks posed by AI replicas: doppelgänger-phobia, identity fragmentation and living memories.

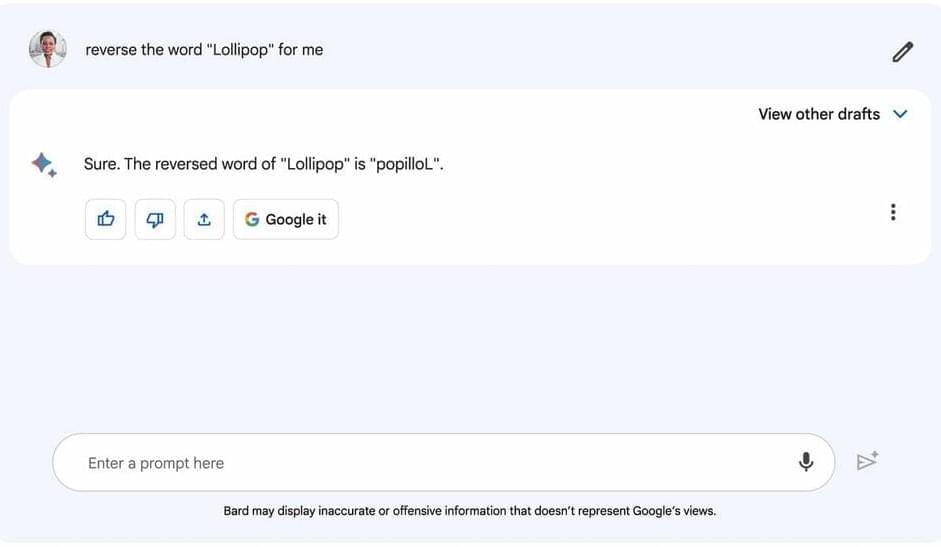
Imagine the possibility of life forms on other planets that don’t resemble any on Earth. What might they look like, and why would they be so different?
Juan Pérez-Mercader says it may be possible and the answer may be that they developed from a different type of chemistry. For more than 10 years, the senior research fellow in the Department of Earth & Planetary Sciences and the Origins of Life Initiative at Harvard has studied how to produce synthetic living systems—without relying on biochemistry, or the chemistry that has enabled life on Earth.
“We have been trying to build a non-biochemical system, which unaided is capable of executing the essential properties common to all natural living systems,” Pérez-Mercader explained.

Following the announcement of Vision Pro at WWDC yesterday, Apple is providing more details about the headset itself and the visionOS software platform in developer sessions. In a session on Tuesday, called “Design for spatial input,” Apple showcased two ways to interact with Vision Pro: a floating in-air keyboard and pairing a keyboard via Bluetooth.
Text input has been one of the most common questions about Vision Pro so far. In this WWDC session for developers, Apple points out two ways users can input text with Vision Pro.
First, you can type using a virtual keyboard with your fingertips. Apple explains that the keyboard’s design is meant to help guide users toward the button surface. The experience also includes feedback via spatial sound effects to “compensate for the missing tactile information.”
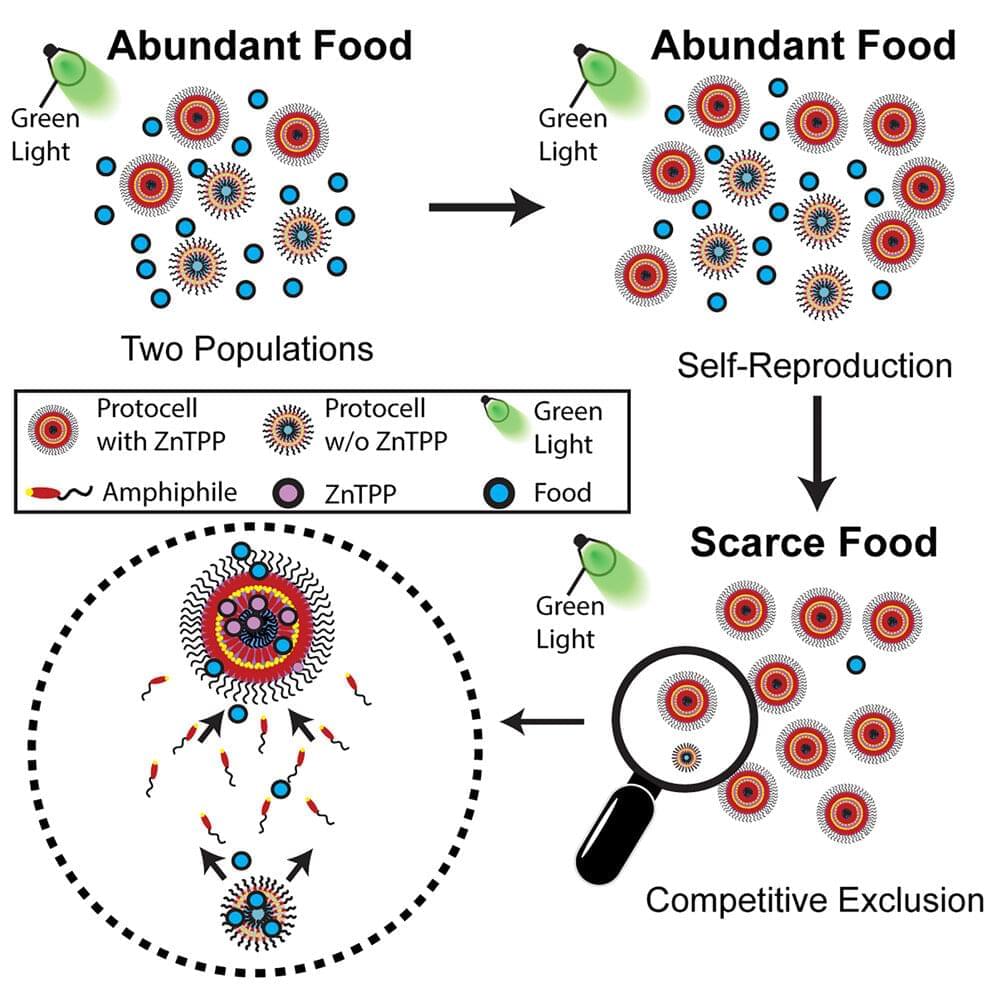
Artificial intelligence has proven itself useful in reading medical imaging and even shown it can pass doctors’ licensing exams.
Now, a new AI tool has demonstrated the ability to read physicians’ notes and accurately anticipate patients’ risk of death, readmission to hospital, and other outcomes important to their care.
Designed by a team at NYU Grossman School of Medicine, the software is currently in use at the university’s affiliated hospitals throughout New York, with the hope that it will become a standard part of health care.
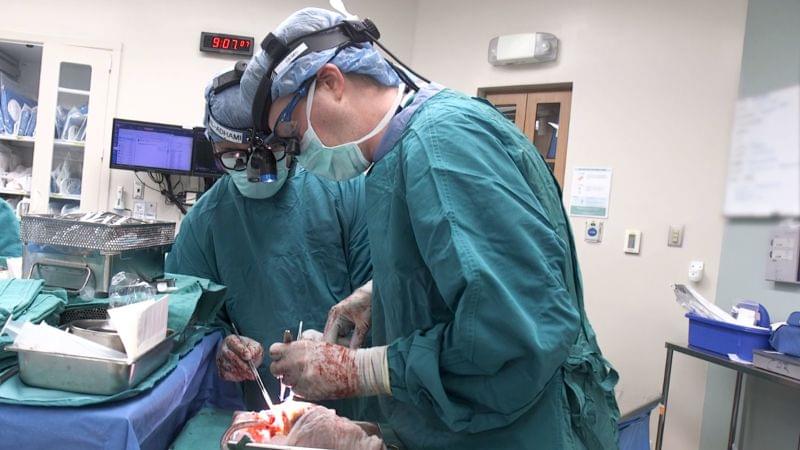
Researchers say they have been able to tap a new pool of organ donors to preserve and transplant their hearts: people whose hearts have stopped beating, resulting in so-called circulatory death.
Traditionally, the only people considered to be suitable organ donors were those who have been declared brain-dead but whose hearts and other organs have continued to function.
There’s another group that would be willing to donate if survival wasn’t possible: people who may have severe brain injuries but who are not brain-dead. In these cases, people are considered deceased when their hearts stop beating after withdrawal of life support, also called circulatory death.