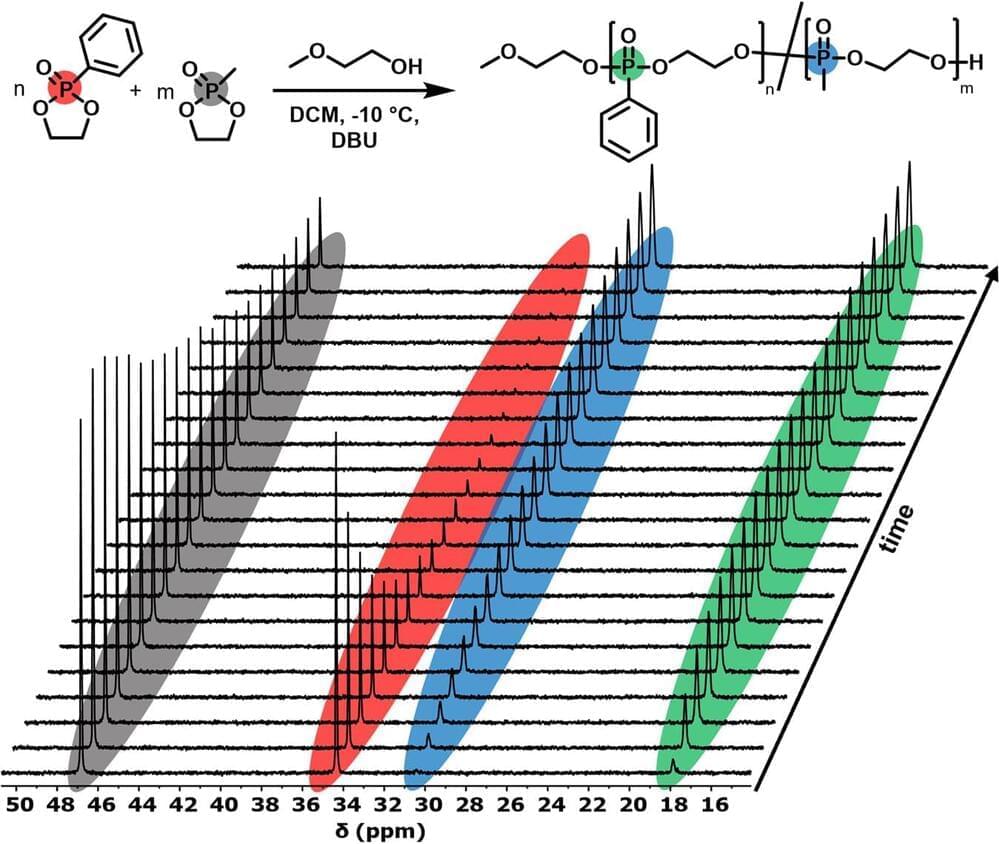
Polyphosphoesters, molecules containing phosphorus as the central element, are easily traceable without the need for contrast agents, thanks to developments by researchers from the University of Twente (UT). Normally, these molecules display a similar molecular composition to our DNA, leading to considerable “noise” in the image.
The UT researchers provided a solution and developed unique polymers that are traceable with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Dr. Olga Koshkina, Project Leader in the Sustainable Polymer Chemistry Group, published this new concept of traceable polymers in Communications Chemistry.
The researchers adjusted the properties of polyphosphoesters (special polymers with a molecular structure inspired by DNA and RNA). As a result, the polymers acquired a different “MRI color,” making them more distinguishable from the natural background. Additionally, they exhibit other physical MRI characteristics suitable for imaging.