Google DeepMind has used its technology to identify parts of human DNA that might cause diseases.
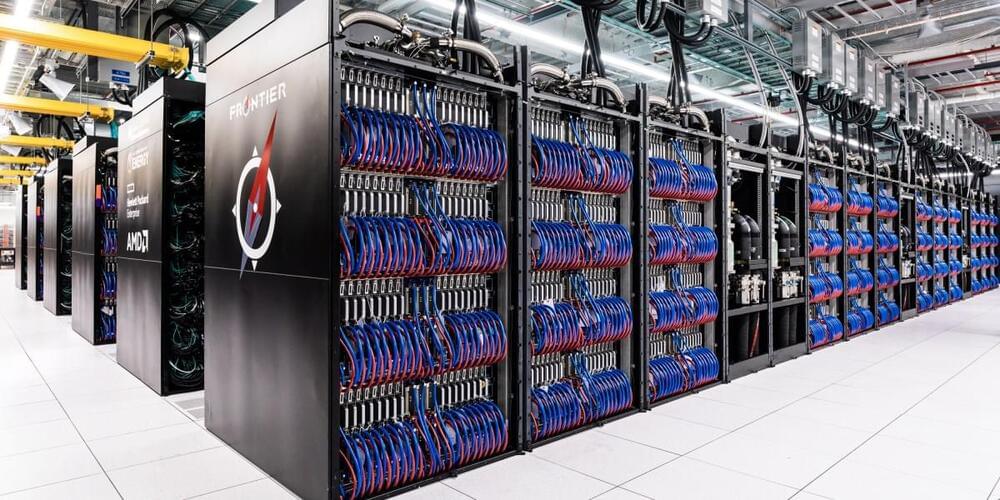



Here are some more specs: Frontier uses approximately 50,000 processors, compared with the most powerful laptop’s 16 or 24. It consumes 20 million watts, compared with a laptop’s 65 or so. It cost $600 million to build.
When Frontier came online, it marked the dawn of so-called exascale computing, with machines that can execute an exaflop—or a quintillion (1018) floating point operations a second. Since then, scientists have geared up to make more of these blazingly fast computers: several exascale machines are due to come online in the US and Europe in 2024.

From Iran to China to Russia, there’s an escalating ‘cat-and-mouse’ game between the censors and those trying to evade them.
I want to talk about the battle that’s raging every day between people who want to censor online content and those who want to protect access to a free and open internet.
It also relates to a recent scoop about a new Google product that’s designed to make it easier for developers to build censorship-resistant apps. I’ve said it before and I’ll say it again: this is a space worth paying attention to.
A virtual cell modeling system, powered by AI, will lead to breakthroughs in our understanding of diseases, argue the cofounders of the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative.
As the smallest living units, cells are key to understanding disease—and yet so much about them remains unknown. We do not know, for example, how billions of biomolecules—like DNA, proteins, and lipids—come together to act as one cell. Nor do we know how our many types of cells interact within our bodies. We have limited understanding of how cells, tissues, and organs become diseased and what it takes for them to be healthy.
AI can help us answer these questions and apply that knowledge to improve health and well-being worldwide—if… More.
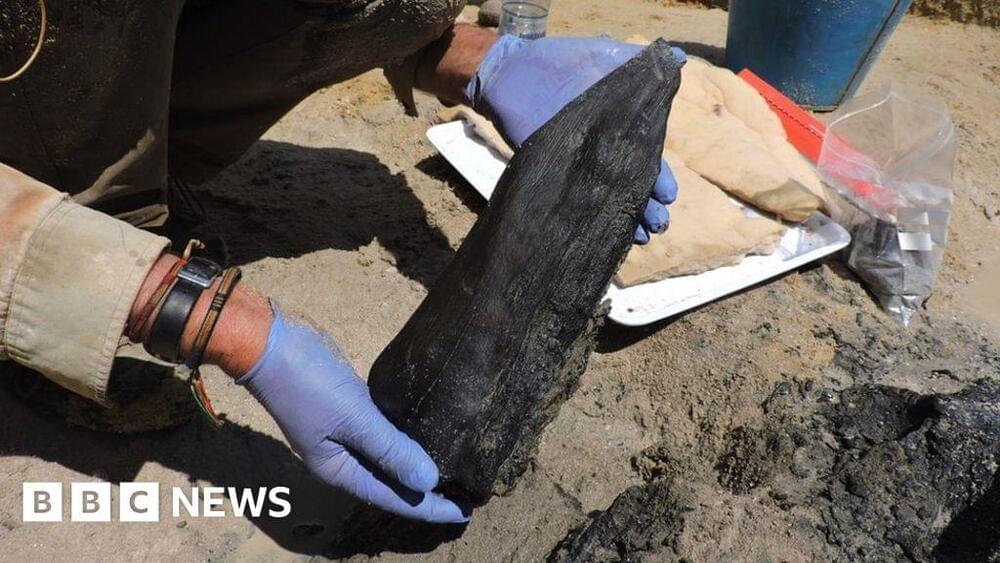
CHOP researchers established the feasibility of an artificial womb called the “Biobag” to nurture a premature lamb in 2017.
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will hold a meeting of independent advisors on September 19–20. The meeting’s agenda is to discuss the viability of clinical trials using artificial womb technology to improve the survival and health of extremely preterm newborns.
Reportedly, during this meeting, regulators and experts will delve into ethical concerns and evaluate various crucial aspects, including the potential steps and design of human trials for this technology.

Generative AI startup Writer has raised $100 million in a series B funding round, valuing it between $500 million and $750 million, the company announced Monday. Writer’s large language models produce content ranging from incident reports and emails to product descriptions and executive summaries, placing it squarely in competition with OpenAI’s ChatGPT Enterprise, which was launched last month, and other fast-growing unicorns like Typeface.
But despite the crowded generative AI space, Writer CEO and cofounder May Habib told Forbes that some enterprise customers are switching from Azure OpenAI over to Writer because the quality of outputs generated by ChatGPT wasn’t high enough. Her startup’s… More.
Firms like Spotify, Uber and Accenture use Writer’s generative AI tools to research, create and analyze content.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly a part of the world around us, and it’s rapidly changing our lives. It offers a hugely exciting opportunity, and sometimes, it can be more than a little scary. And without a doubt, the big development in AI making waves right now is generative AI.
Just like it sounds, it’s AI that can create, from words and images to videos, music, computer applications, and even entire virtual worlds.
What makes generative AI different and special is that it puts the power of machine intelligence in the hands of just about anyone.
Unlock the potential of generative AI and explore how this revolutionary technology is democratizing creativity and redefining the concept of originality.

Get my FREE guide 3 Steps to Reverse Aging when you sign up for my weekly health picks 👉 https://bit.ly/IncreaseHealthspan.
There is powerful science behind how our beliefs inform our genetic expression. It’s not our genes alone that dictate our health outcomes, rather it’s the biology of belief that determines our destiny.
Today on The Doctor’s Farmacy, I’m excited to talk to Dr. Bruce Lipton about how exactly our thoughts determine our genetic expression, and how we can influence our health using our minds.
Dr. Bruce Lipton is a stem cell biologist and author of the bestselling books, The Biology of Belief, Spontaneous Evolution, and The Honeymoon Effect. Dr. Lipton is the recipient of the prestigious Japanese Goi Peace Award and has been listed in the top 100 of “the world’s most spiritually influential people” by Briton’s Watkins Journal for the last 13 years.
This episode is brought to you by Rupa Health, BiOptimizers, LMNT, and Apollo.
Rupa Health is a place where Functional Medicine practitioners can access more than 3,000 specialty lab tests from over 35 labs like DUTCH, Vibrant America, Genova, and Great Plains. You can check out a free, live demo with a Q&A or create an account at https://RupaHealth.com.
