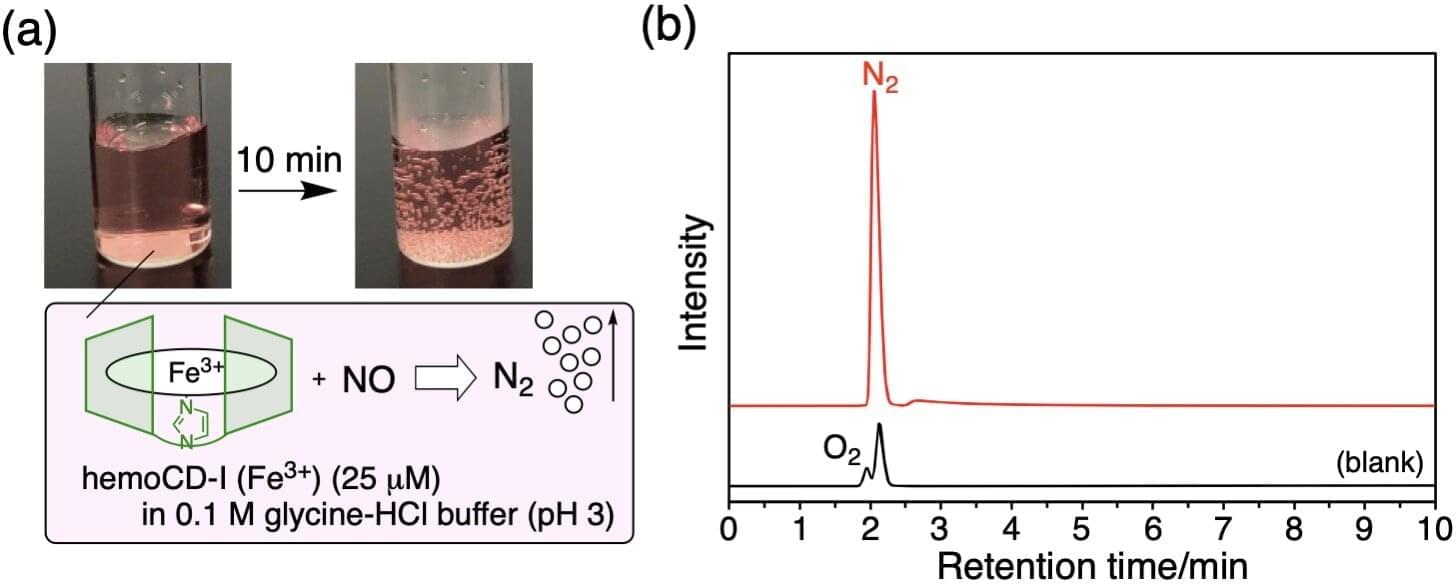
Nitrogen is a crucial component of proteins and nucleic acids, the fundamental building blocks of all living things, and thus is essential to life on Earth. Gaseous N2 from the atmosphere can be fixed by soil bacteria capable of converting N2 to ammonia or nitrates (NO3).
Nitrifying bacteria in the soil then convert ammonia into NO3, which plants utilize for growth. Animals that consume plants put the N2 back into the soil in the form of ammonia when they die or excrete waste.
The NO3 in the soil is converted back into N2 and released into the atmosphere by the activity of denitrifying microbes in the soil. This native nitrogen cycle regulates the N2 levels in the atmosphere and on Earth and is vital for sustaining life.