Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative condition characterized by the progressive deterioration of brain cells, which prompts memory loss, a decline in mental functions and behavioral changes. Estimates suggest that this disease affects approximately 1 in 14 people who are more than 65 years old and over 35% of people who are over 85 years old.
Due to its prevalence and debilitating nature, AD has become the focus of numerous neuroscience and medical studies. Most of these studies examined brain regions and neurogenetic processes that appear to be different in people diagnosed with AD.
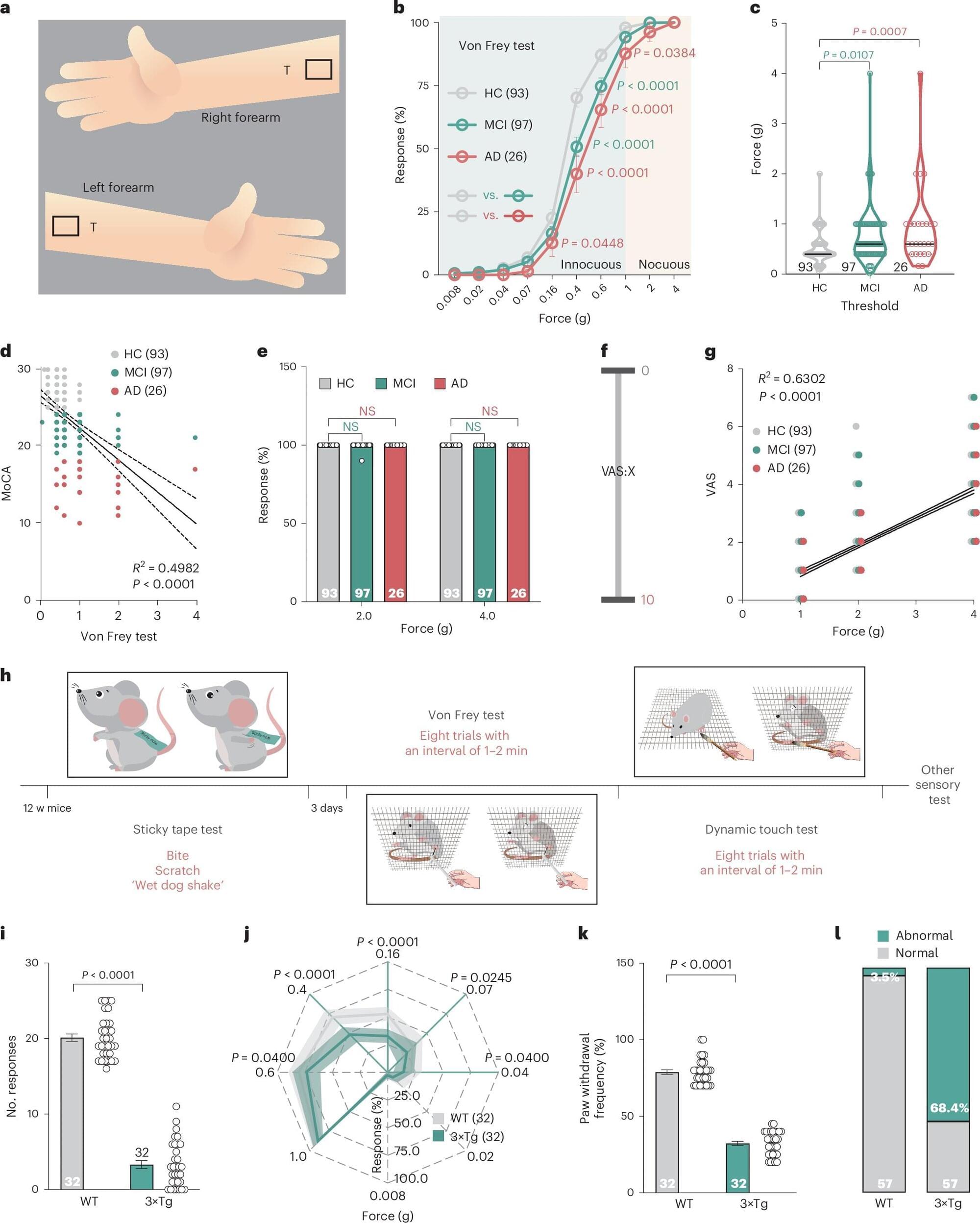
Recently, some neuroscientists gathered evidence suggesting that parts of the brain that support somatosensory processing (i.e., the interpretation of tactile stimuli, pressure and the body’s position in space), are also affected in individuals with AD. Yet the extent to which these tactile sensation-related deficits play a role in the cognitive decline typical of AD has not yet been determined.