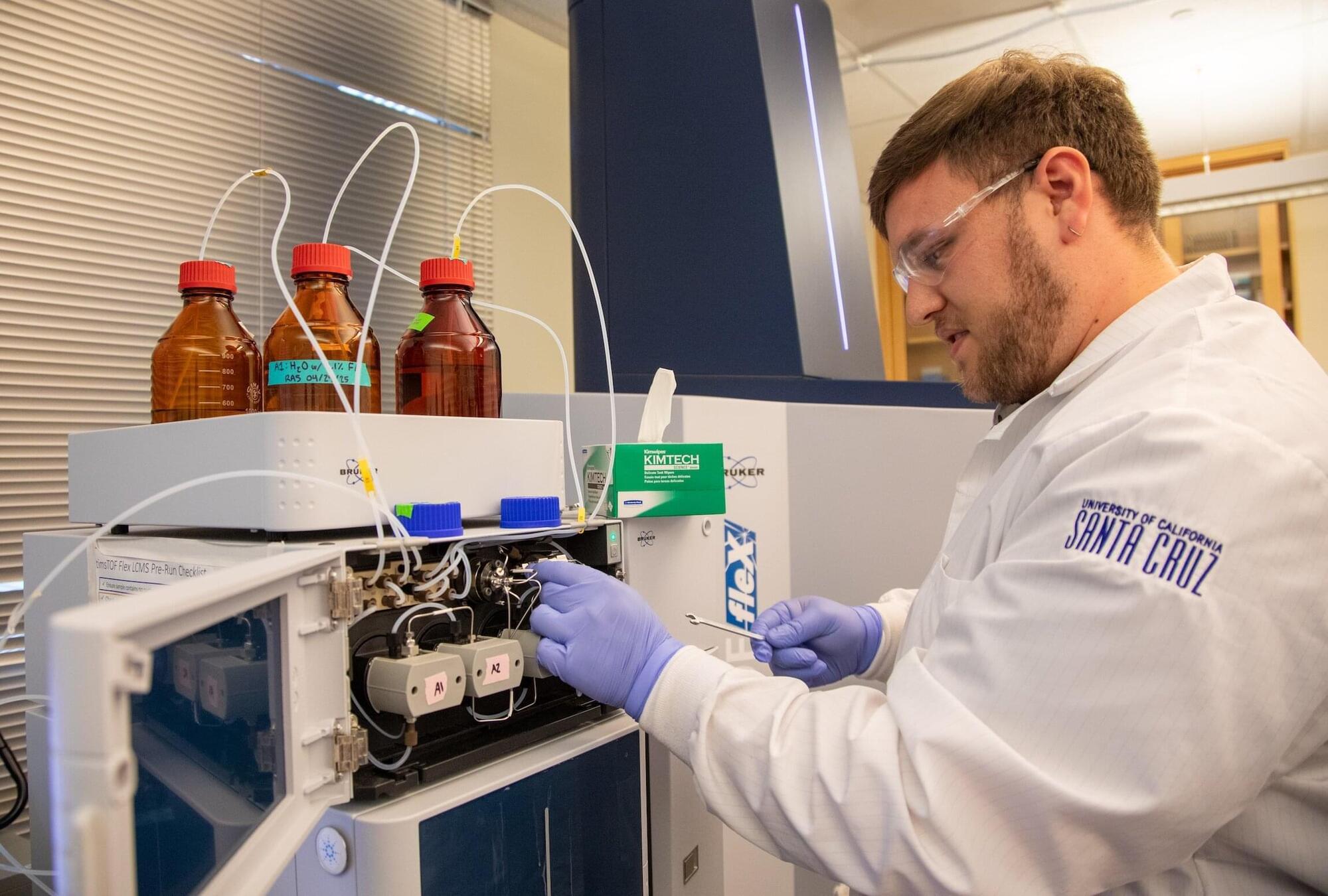
A team of biochemists at the University of California, Santa Cruz, has developed a faster way to identify molecules in the lab that could lead to more effective pharmaceuticals. The discovery advances the rapidly growing field of biocatalysis, which depends on generating large, genetically diverse libraries of enzymes, and then screening those variants to find ones that perform a desired chemical task best.
This strategy has attracted major investment, particularly from drugmakers, because it promises quicker routes to complex, high-value molecules. However, traditional approaches to finding new biologically beneficial molecules often require “lots of shots on goal,” where researchers test enormous numbers of candidates through slow and inefficient workflows.
The method developed by the UC Santa Cruz team aims to significantly shorten that process by introducing smarter and faster decision-making tools that help researchers identify promising enzyme variants much earlier. The researchers detail their new approach in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science.