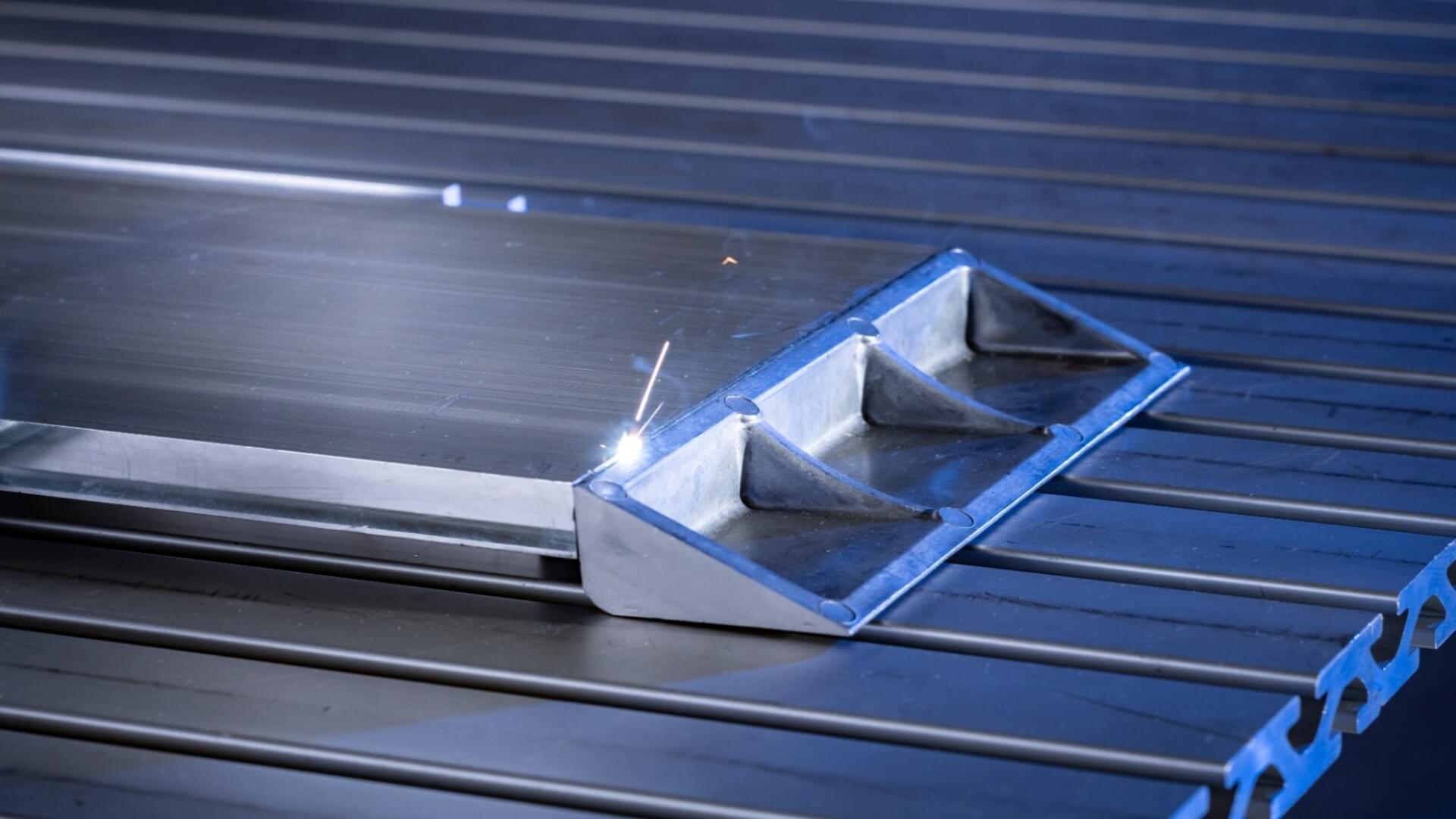
Laser welding tech enables crack-free EV battery housings without filler wire.
Researchers in Germany have recently unveiled a novel laser welding technology that eliminates the need for filler wire and delivers stronger, crack-free joints for electric vehicles, aerospace tanks, and heavy steel structures.
Developed by the Fraunhofer Institute for Material and Beam Technology IWS in Dresden, the process uses dynamic beam shaping to control the melt pool, reduce pores, and stabilize welds.