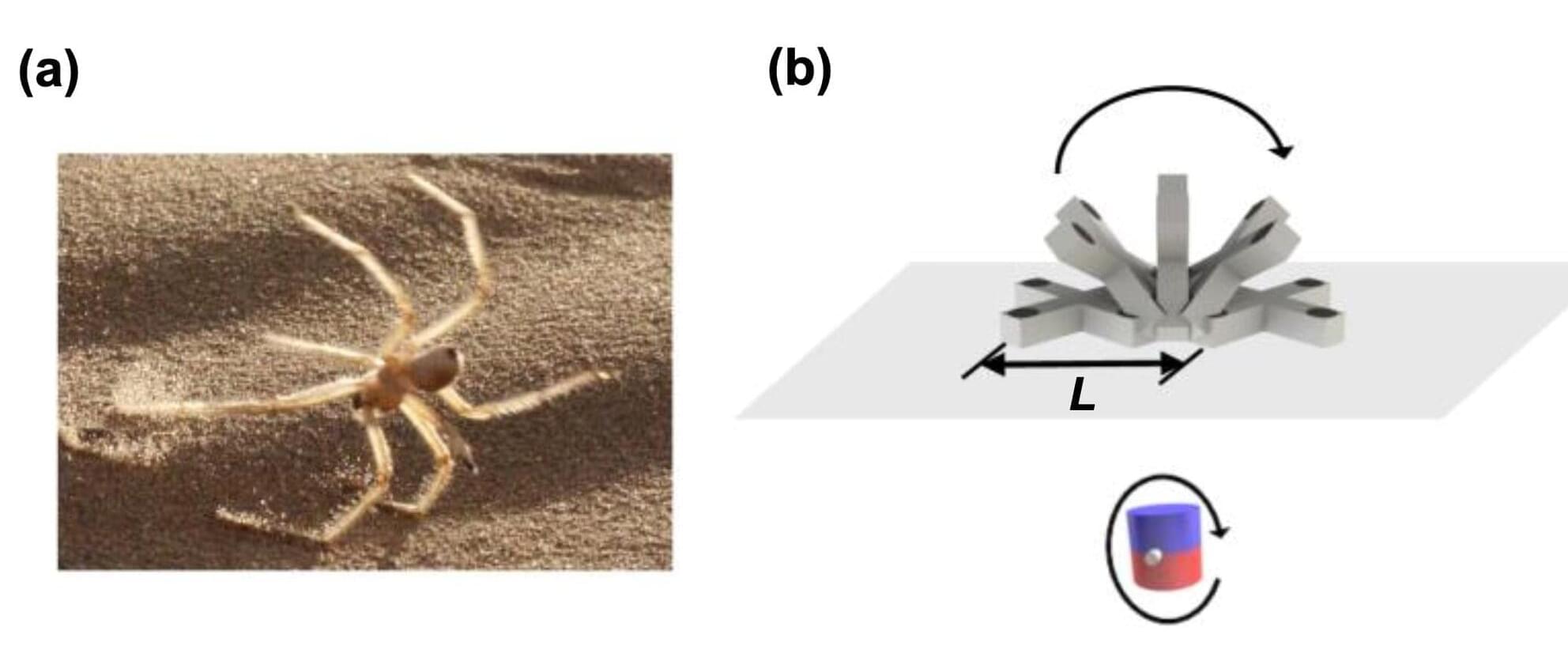
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is a collection of organs and structures inside the bodies of humans and other animals that is responsible for the digestion of food, the absorption of nutrients and the expulsion of waste. Its underlying parts include the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, rectum and anus.
Over the past decades, the incidence of cancer in the GI tract and some other conditions affecting the digestive system has risen substantially. Existing approaches to diagnose and treat GI cancers rely on endoscopy, a medical procedure that entails the inspection of internal organs via a flexible tube with an embedded camera (i.e., endoscope), which is inserted into the body through the anus, mouth or a small incision.
In addition to being highly uncomfortable for patients, endoscopy often fails to reach regions that are deep into the GI tract or are difficult to access due to the body’s natural configuration. Some biomedical engineers have thus been trying to devise alternative systems that could inspect parts of the digestive system more effectively, while causing patients minimal discomfort.