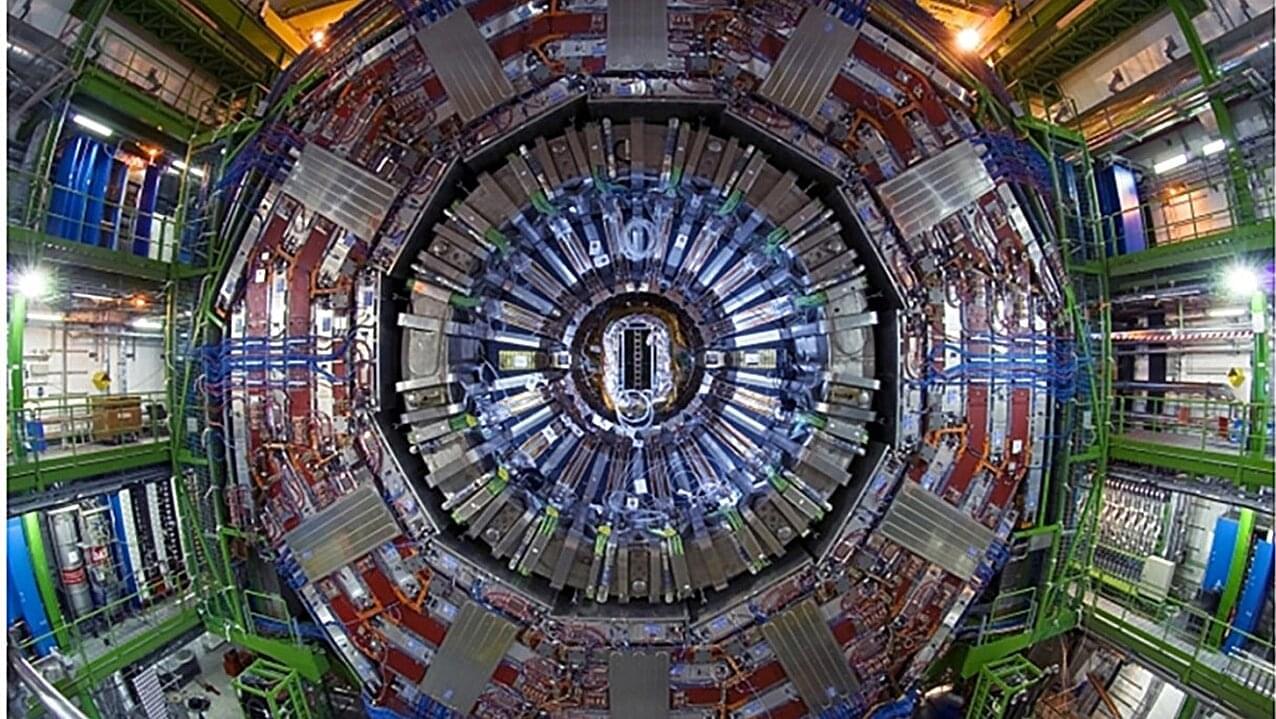
There is a limit to how big we can build particle colliders on Earth, whether that is because of limited space or limited economics. Since size is equivalent to energy output for particle colliders, that also means there’s a limit to how energetic we can make them. And again, since high energies are required to test theories that go beyond the standard model (BSM) of particle physics, that means we will be limited in our ability to validate those theories until we build a collider big enough.
But a team of scientists led by Yang Bai at the University of Wisconsin thinks they might have a better idea—use already existing neutrino detectors as a large scale particle collider that can reach energies way beyond what the LHC is capable of. The findings are published on the arXiv preprint server.
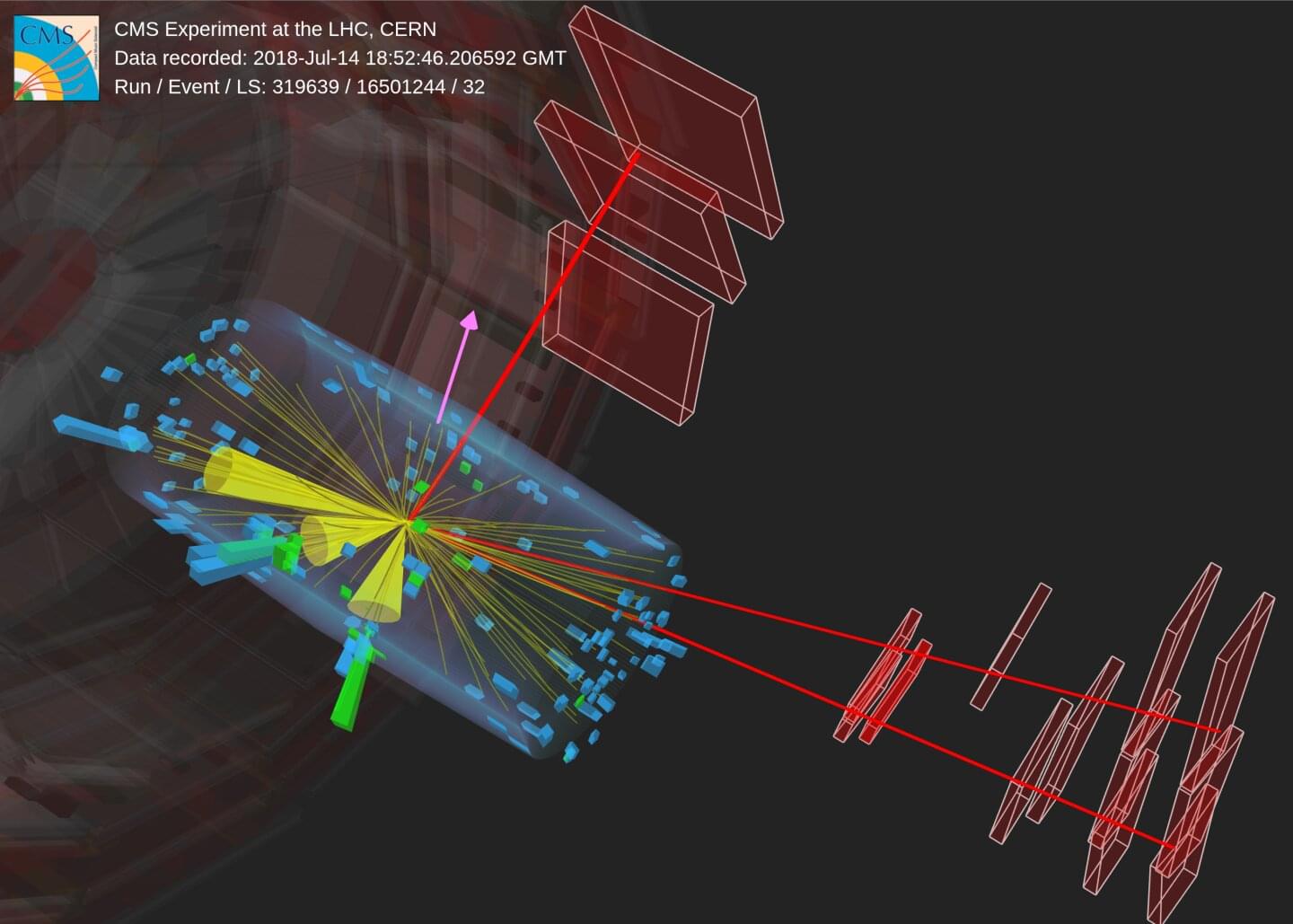
Neutrinos are notorious for very weakly interacting with things—there are trillions of them passing through you as you read this sentence. However, put enough matter in their way and eventually a special few will run directly into a proton or electron. The resulting particle spray, which is typically going faster than light in whatever medium the neutrino hits, creates a light known as Cherenkov radiation. But really what causes the Cherenkov radiation are the particles created by what is essentially a giant particle collider.