UMass Amherst physicists believe such an explosion could occur within the next decade, potentially “revolutionizing physics and rewriting the history of the universe.” Physicists have long thought that black holes end their lives in rare explosions that occur, at most, once every 100,000 years. N
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

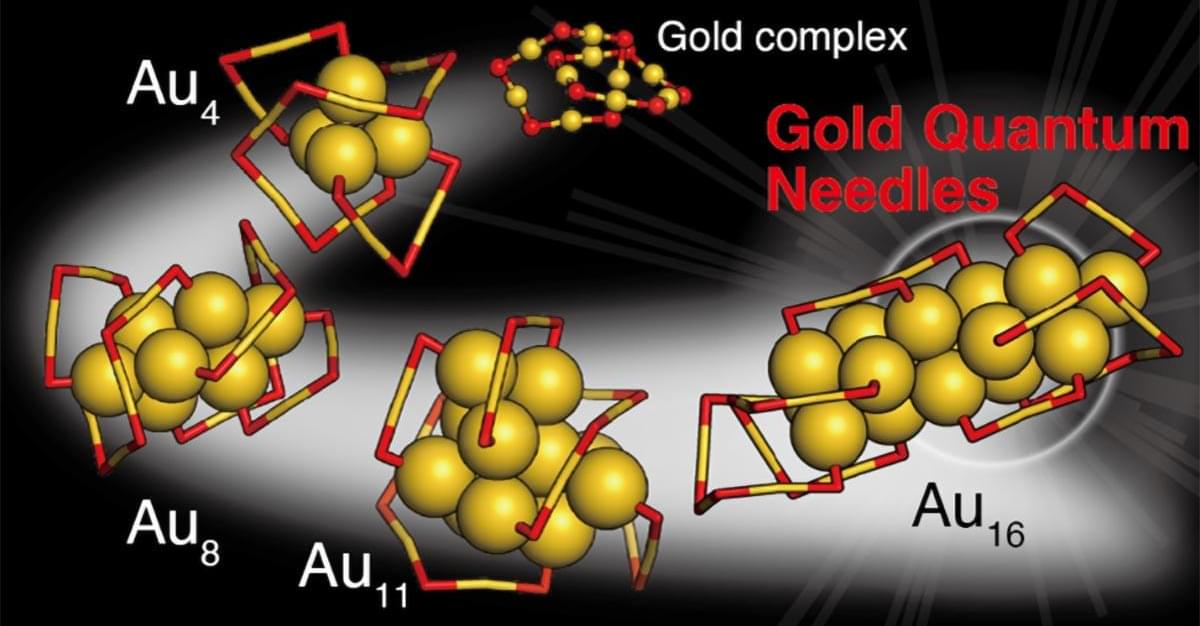

Rice research team on quest to engineer computing systems from living cells
Rice University biosciences professor Matthew Bennett has received a $1.99 million grant from the National Science Foundation to lead research on engineered bacterial consortia that could form the basis of biological computing systems. The four-year project will also involve co-principal investigators Kirstin Matthews, Caroline Ajo-Franklin and Anastasios Kyrillidis from Rice along with Krešimir Josić from the University of Houston. The research team aims to develop platforms that integrate microbial sensing and communication with electronic networks, paving the way for computing systems constructed from living cells instead of traditional silicon-based hardware.
The project highlights the growing potential of synthetic biology, where microbes are examined not just as living organisms but as processors of information. If successful, Bennett’s research could accelerate medical diagnostics, environmental monitoring and the development of next-generation computing applications.
“Microbes are remarkable information processors, and we want to understand how to connect them into networks that behave intelligently,” Bennett said. “By integrating biology with electronics, we hope to create a new class of computing platforms that can adapt, learn and respond to their environments.”
Analog optical computer for AI inference and combinatorial optimization
An analog optical computer that combines analog electronics, three-dimensional optics, and an iterative architecture accelerates artificial intelligence inference and combinatorial optimization in a single platform, paving a promising path for faster and sustainable computing.

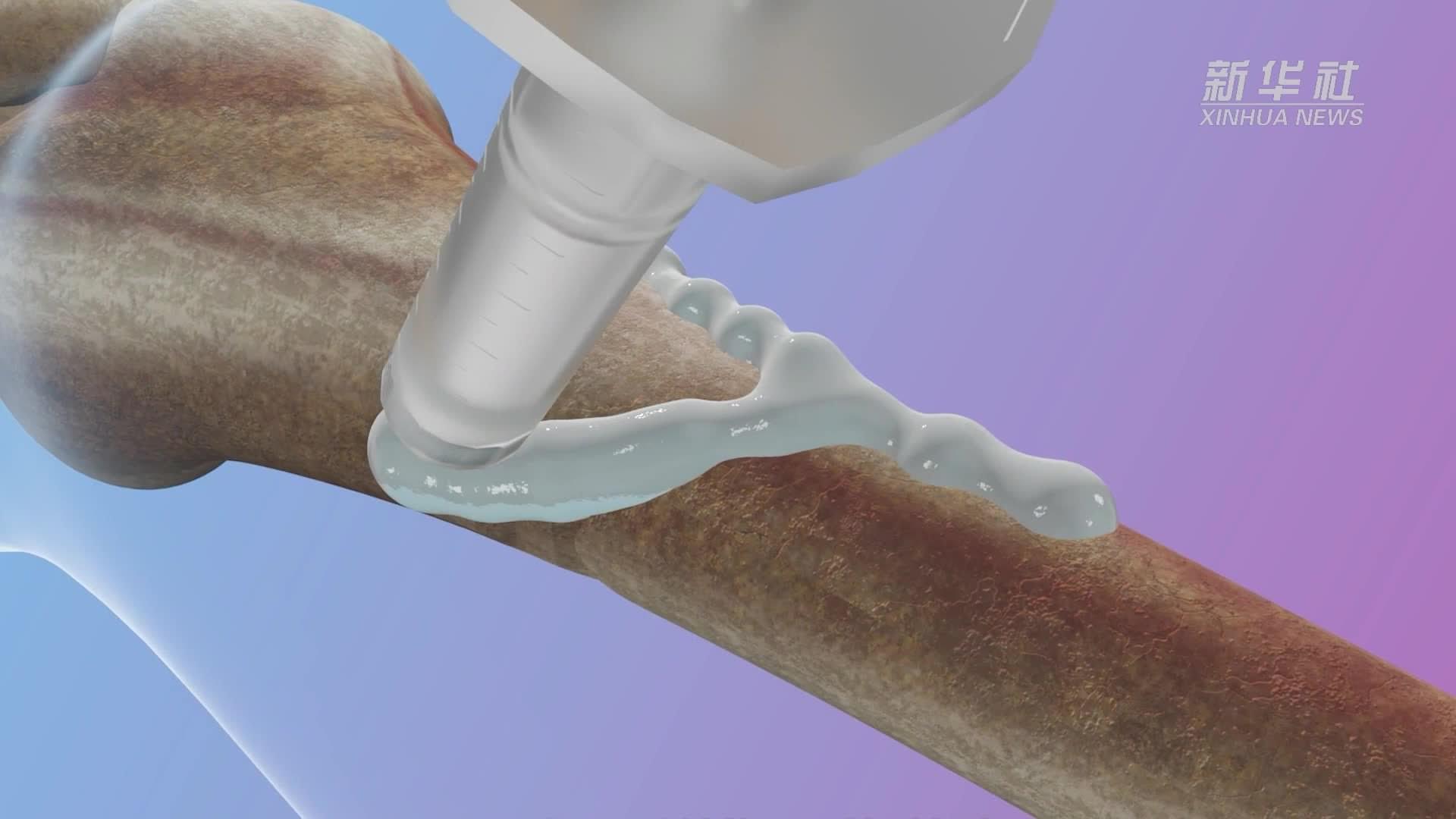
Chinese researchers on Tuesday unveiled their self-developed world’s first “bone glue”
Material capable of securely bonding fractured bone fragments within 2–3 minutes in a blood-rich environment.
Chinese researchers on Tuesday unveiled their self-developed world’s first “bone glue” material capable of securely bonding fractured bone fragments within 2–3 minutes in a blood-rich environment.
Inspired by oysters, this new biomaterial, with a maximum adhesion strength of over… pic.twitter.com/7ozvRrQBP0— China Science (@ChinaScience) September 10, 2025
ในช่วงไม่กี่ปีที่ผ่านมา จีนได้แสดงศักยภาพด้านวิทยาศาสตร์การแพทย์อย่างต่อเนื่อง หนึ่งในผลงานที่ได้รับความสนใจระดับโลกคือการพัฒนาวัสดุชีวภาพชนิดใหม่ที่เรียกว่ากาวกระดูก (Bine Glue) ที่สามารถเชื่อมกระดูกที่หักให้ติดกันได้ภายในระยะเวลาเพียง 3 นาที
Chemists Create Next-Gen Rocket Fuel Compound That Packs 150% More Energy
Chemists at the University at Albany have developed a high-energy compound that could transform rocket fuel and make space travel more efficient. When ignited, this compound produces significantly more energy per unit of weight and volume than current propellants.
For rockets, this means that less fuel would be needed to achieve the same mission duration or payload capacity, leaving more space for essential equipment and supplies. The research was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
“In rocket ships, space is at a premium,” said Assistant Professor of Chemistry Michael Yeung, whose lab led the work. “Every inch must be packed efficiently, and everything onboard needs to be as light as possible. Creating more efficient fuel using our new compound would mean less space is needed for fuel storage, freeing up room for equipment, including instruments used for research. On the return voyage, this could mean more space is available to bring samples home.”

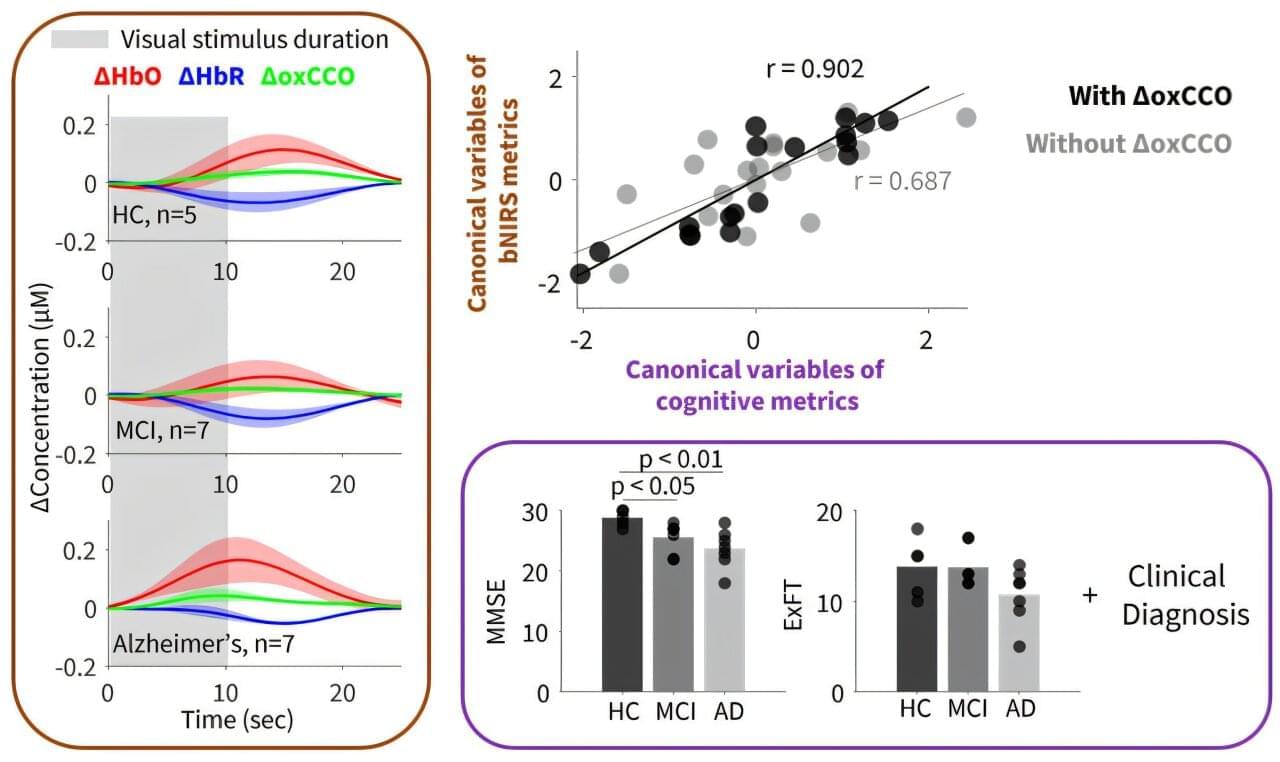
Portable light-based brain monitor shows promise for dementia diagnosis
Early and accurate diagnosis of dementia remains a major challenge. Standard approaches such as MRI and PET scans can provide valuable information about brain structure and function, but they are expensive, not always accessible, and often too expensive for repeated use.
A team of researchers in the UK has now demonstrated that a compact, noninvasive technology—broadband near-infrared spectroscopy (bNIRS)—may offer a new way to detect brain changes linked to Alzheimer’s disease, even in the early stages.
In this pilot study reported in the Journal of Biomedical Optics, scientists used bNIRS to monitor both blood oxygenation and brain metabolism in response to visual stimulation.