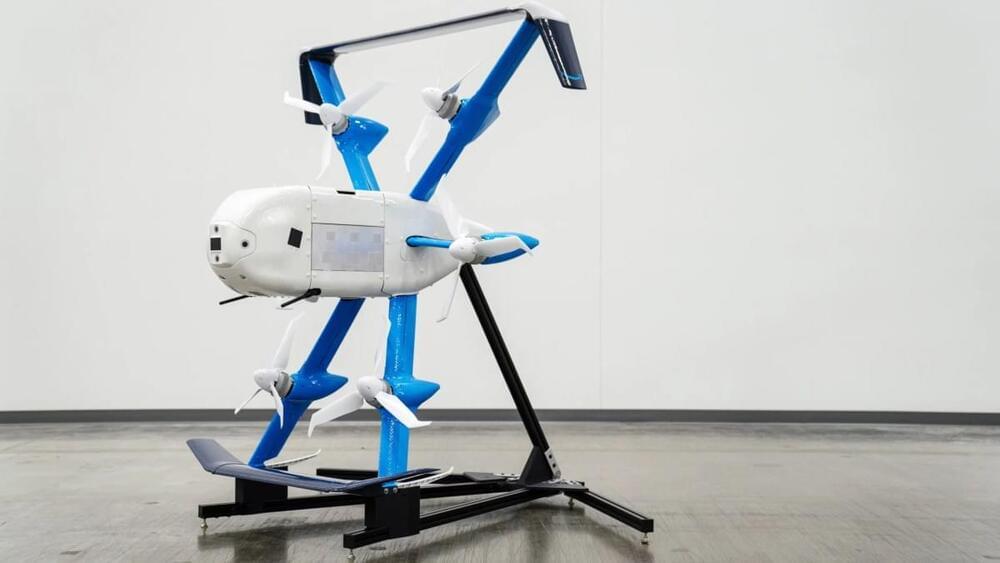
Amazon confirmed it is ending Prime Air drone delivery operations in Lockeford, California. The Central California town of 3,500 was the company’s second U.S. drone delivery site, after College Station, Texas. Operations were announced in June 2022.
The retail giant is not offering details around the setback, only noting, “We’ll offer all current employees opportunities at other sites, and will continue to serve customers in Lockeford with other delivery methods. We want to thank the community for all their support and feedback over the past few years.”
College Station deliveries will continue, along with a forthcoming site in Tolleson, Arizona set to kick off deliveries later this year. Tolleson, a city of just over 7,000, is located in Maricopa County, in the western portion of the Phoenix metropolitan area.