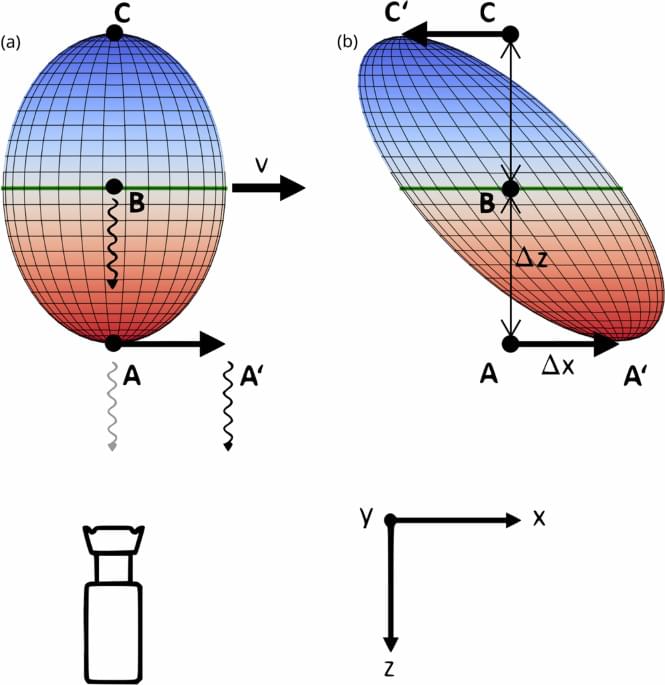
Not exactly a brain chip per se by a bit of nanotech.
While companies like Elon Musk’s Neuralink are hard at work on brain-computer interfaces that require surgery to cut open the skull and insert a complex array of wires into a person’s head, a team of researchers at MIT have been researching a wireless electronic brain implant that they say could provide a non-invasive alternative that makes the technology far easier to access.
They describe the system, called Circulatronics, as more of a treatment platform than a one-off brain chip. Working with researchers from Wellesley College and Harvard University, the MIT team recently released a paper on the new technology, which they describe as an autonomous bioelectronic implant.
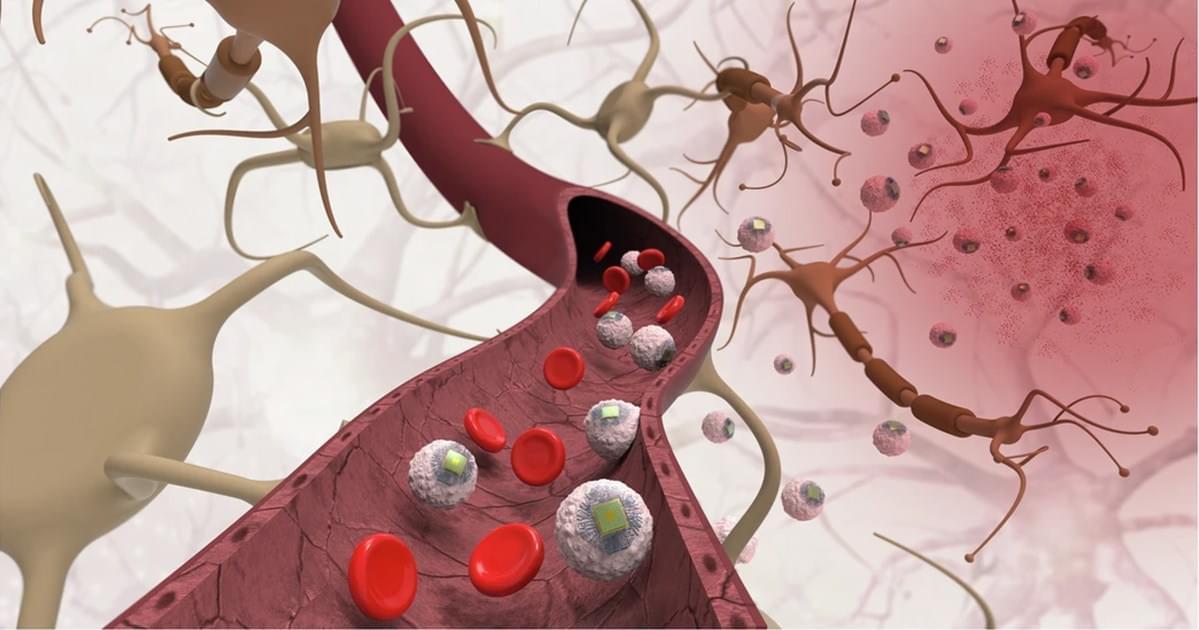
As New Atlas points out, the Circulatronics platform starts with an injectable swarm of sub-cellular sized wireless electronic devices, or “SWEDs,” which can travel into inflamed regions of the patient’s brain after being injected into the bloodstream. They do so by fusing with living immune cells, called monocytes, forming a sort of cellular cyborg.