A new computational approach developed at the University of Chicago promises to shed light on some of the world’s most puzzling materials—from high-temperature superconductors to solar cell semiconductors—by uniting two long-divided scientific perspectives.
“For decades, chemists and physicists have used very different lenses to look at materials. What we’ve done now is create a rigorous way to bring those perspectives together,” said senior author Laura Gagliardi, Richard and Kathy Leventhal Professor in the Department of Chemistry and the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering. “This gives us a new toolkit to understand and eventually design materials with extraordinary properties.”
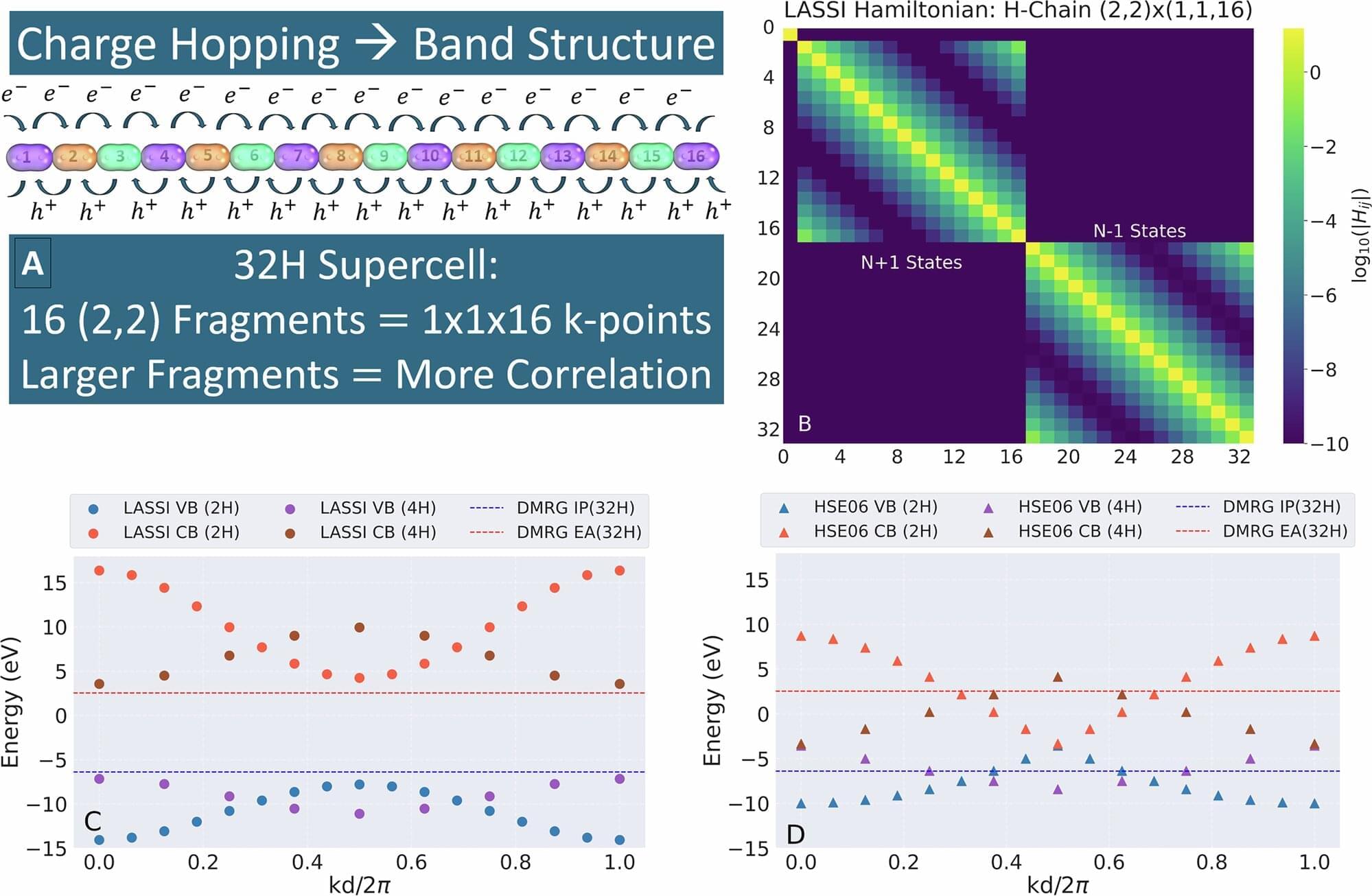
When it comes to solids, physicists usually think in terms of broad, repeating band structures, while chemists focus on the local behavior of electrons in specific molecules or fragments. But many important materials—such as organic semiconductors, metal–organic frameworks, and strongly correlated oxides—don’t fit neatly into either picture. In these materials, electrons are often thought of as hopping between repeating fragments rather than being distributed across the material.