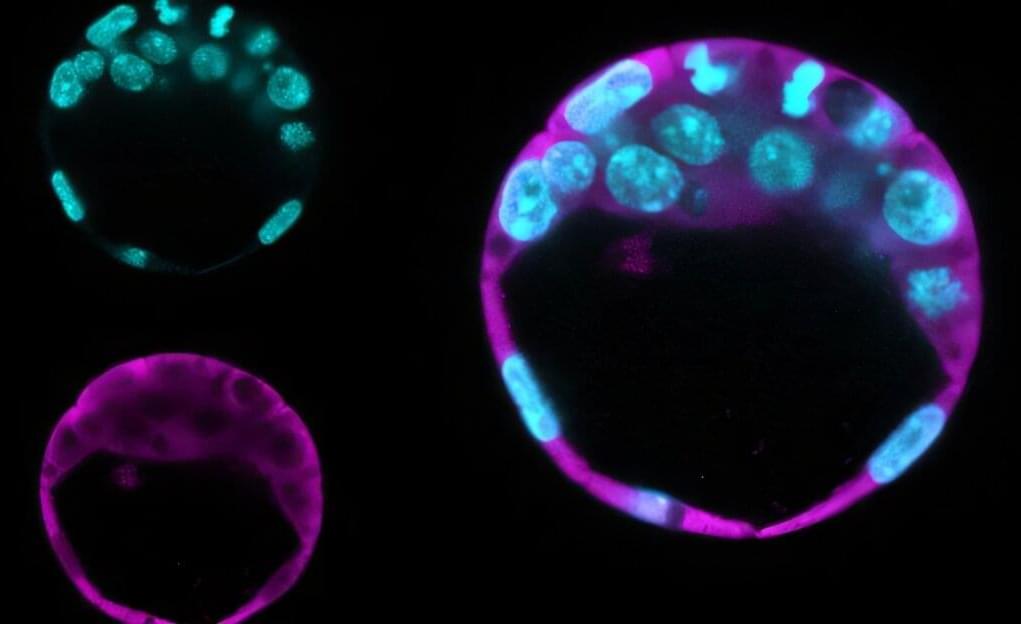
Two recently published studies led by Brazilian scientists reveal the key roles of multifunctional proteins, STIP1 and Maspin, in vital cellular processes.
The results demonstrate new protein functions that help clarify how cells maintain their shape, communicate, and renew themselves. These findings contribute to new studies on cancer, embryogenesis, and potential applications in regenerative medicine.
According to one of the studies, STIP1 plays a central role in embryonic development and maintaining pluripotency, or the ability of cells to multiply and give rise to other cell types.