Experiments on soft granular materials have allowed researchers to derive a rheological description for these materials by extending an established framework valid for hard granular materials.



Researchers at the University of Texas have developed an AI that predicted 70% of earthquakes during a trial in China, indicating potential for future quake risk mitigation.
The AI, trained on seismic data, also ranked first in an international competition, underscoring its effectiveness and opening doors for further enhancements in regions like California and Texas.
AI Earthquake Prediction Breakthrough

Superconductors, known for enabling lossless electrical conductivity and even magnetic levitation, typically function only at extremely low temperatures. Recent research has identified electron pairing, a core superconductor behavior, in materials at higher-than-expected temperatures, such as an antiferromagnetic insulator.
This discovery by SLAC and Stanford researchers could lead to new ways to develop superconductors that operate closer to room temperature, potentially revolutionizing technology in many fields including quantum computing and transportation.
Exploring the Enigma of Superconductors.



The progress of science in the last 400 years is mind-blowing. Who would have thought we’d be able to trace the history of our universe to its origins 14 billion years ago? Science has increased the length and the quality of our lives, and the technology that is commonplace in the modern world would have seemed like magic to our ancestors.
For all of these reasons and more, science is rightly celebrated and revered. However, a healthy pro-science attitude is not the same thing as “scientism”, which is the view that the scientific method is the only way to establish truth. As the problem of consciousness is revealing, there may be a limit to what we can learn through science alone.
Perhaps the most worked out form of scientism was the early 20th century movement knows as logical positivism. The logical positivists signed up to the “verification principle”, according to which a sentence whose truth can’t be tested through observation and experiments was either logically trivial or meaningless gibberish. With this weapon, they hoped to dismiss all metaphysical questions as not merely false but nonsense.
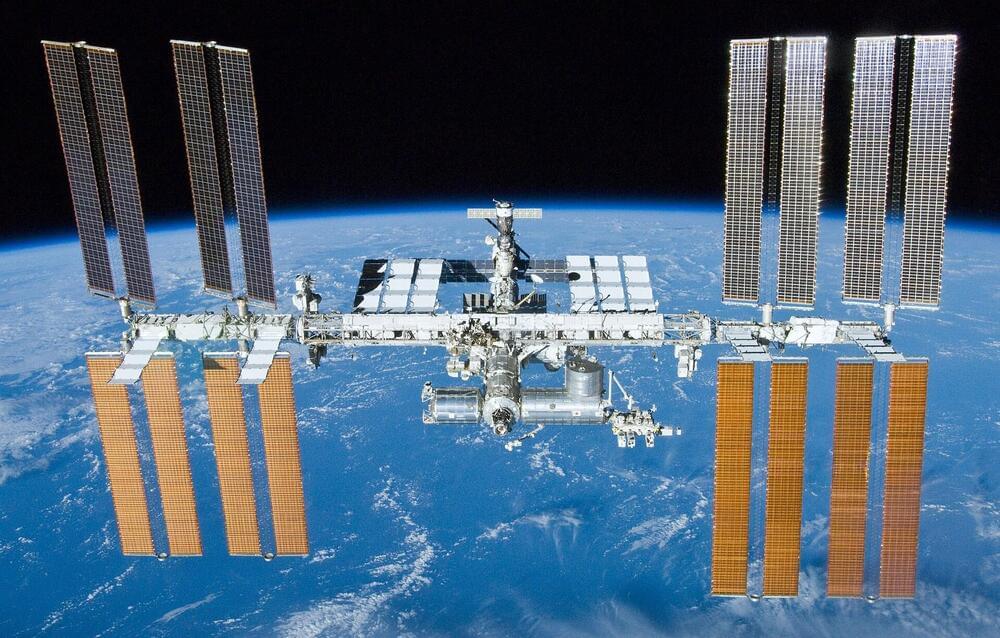
“Space-based research has a long history of contributing to advancements on Earth,” said Dr. Lisa Carnell.
The International Space Station (ISS) has been a beacon of scientific and medical research ever since the station’s first module was launched in 1999, as astronauts continue to push the boundaries regarding microgravity research that has contributed to advancing science and medical knowledge back on Earth. To continue this, NASA and the ISS National Laboratory recently announced a partnership through the ISS National Lab Research Announcement (NLRA) 2024-09: Igniting Innovation: Science in Space to Cure Disease on Earth that will provide up to $4 million with the goal of helping to advance disease diagnosis and treatment back on Earth.
Through collaboration between government agencies, industry, and academia, the NLRA hopes to accomplish several objectives pertaining to developing medical technologies on Earth, including disease mechanism models, population and disease diversity, drug discovery & development, drug delivery, and drug resistance. This announcement comes after the ISS National Laboratory announced in July 2024 that five projects were selected for the Cancer Research in Space for Life on Earth with the goal of providing $7 million in grants to advance cancer research in microgravity onboard the ISS.

Dr. Caroline Dorn: “The larger the planet and the greater its mass, the more the water tends to go with the iron droplets and become integrated in the core.”
Do certain exoplanets mirror Earth regarding their distribution of iron and water? This is what a recent study published in Nature Astronomy hopes to address as an international team of researchers investigated the evolution of exoplanets and how they form their iron core with water residing either beneath or above the surface, and whether as a liquid or gas. This study holds the potential to help researchers better understand the formation and evolution of exoplanets, which will enable scientists to provide better targets for identifying Earth-like worlds throughout the cosmos.
For the study, the researchers use computer models to simulate the formation of planetary interiors on super-Earth and sub-Neptune exoplanets, specifically with a focus on the distribution of water within a planet’s interior in relation to the additional iron and metallic composition. In the end, the researchers found that longstanding hypotheses about the formation and evolution of water worlds are challenged given the model’s results that 95 percent or more of water on an exoplanet is stored within the planet’s interior, as opposed to the surface.