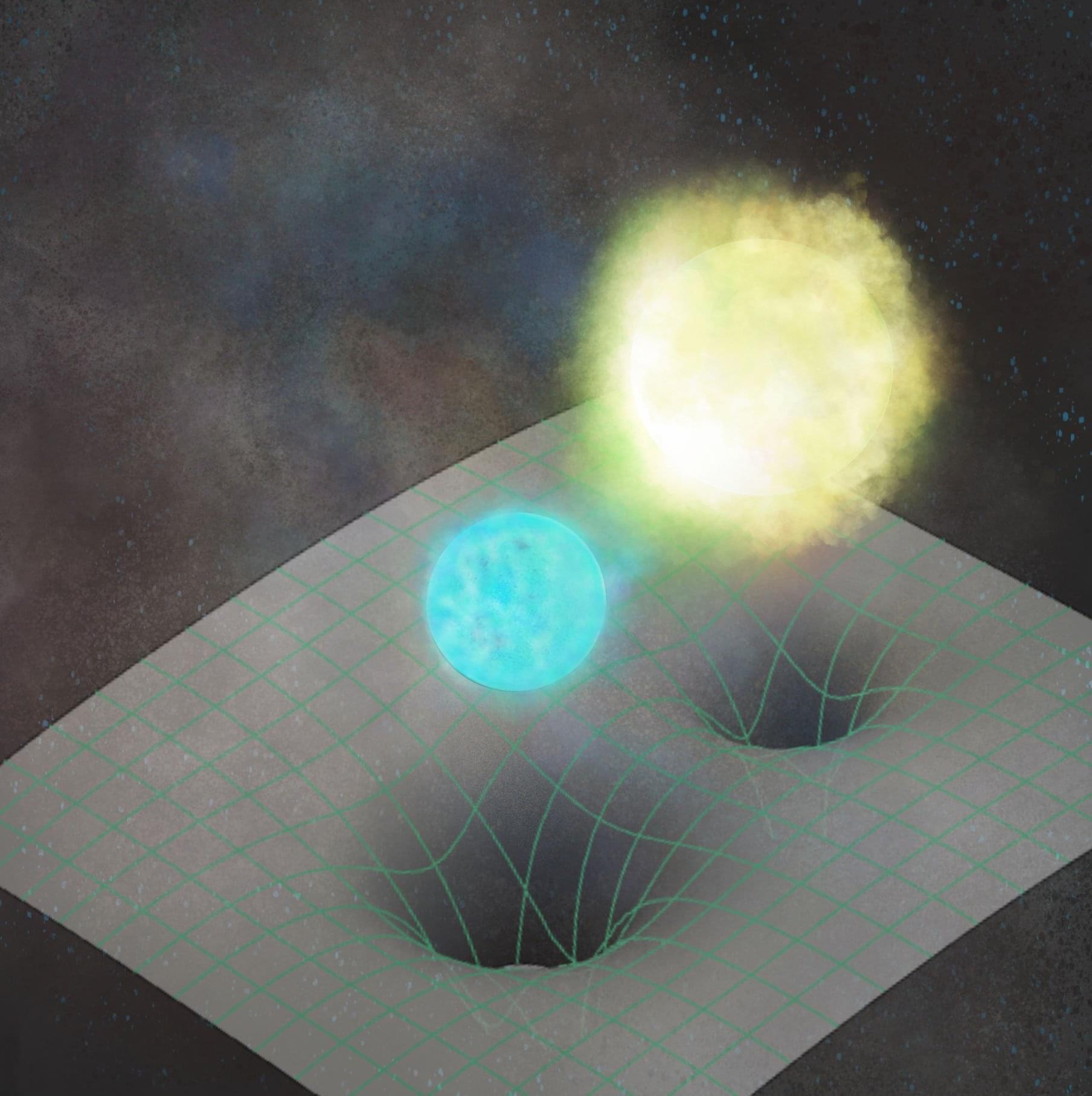
White dwarfs are the dense, compact remains left behind when stars exhaust their nuclear fuel, a process that will one day occur to our own Sun. These stellar remnants are known as degenerate stars because their internal physics defy normal expectations: as they gain mass, they actually become smaller in size.
Many white dwarfs exist in pairs, forming what are known as binary systems, where two stars orbit each other. Most of these systems are ancient by galactic standards and have cooled over time to surface temperatures near 4,000 Kelvin.
Yet, astronomers have recently identified a remarkable group of short-period binary systems in which the stars complete an orbit in less than an hour. Surprisingly, these white dwarfs appear to be about twice as large as models predict, with much higher surface temperatures ranging from 10,000 to 30,000 Kelvin.