Quantum sensing is a rapidly developing field that utilizes the quantum states of particles, such as superposition, entanglement, and spin states, to detect changes in physical, chemical, or biological systems. A promising type of quantum nanosensor is nanodiamonds (NDs) equipped with nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers. These centers are created by replacing a carbon atom with nitrogen near a lattice vacancy in a diamond structure.
When excited by light, the NV centers emit photons that maintain stable spin information and are sensitive to external influences like magnetic fields, electric fields, and temperature. Changes in these spin states can be detected using optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR), which measures fluorescence changes under microwave radiation.
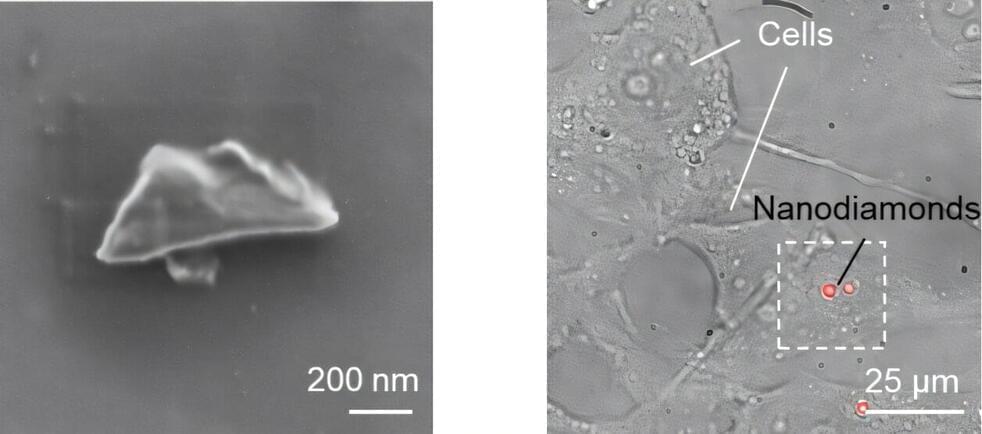
In a recent breakthrough, scientists from Okayama University in Japan developed nanodiamond sensors bright enough for bioimaging, with spin properties comparable to those of bulk diamonds. The study, published in ACS Nano, on 16 December 2024, was led by Research Professor Masazumi Fujiwara from Okayama University, in collaboration with Sumitomo Electric Company and the National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology.