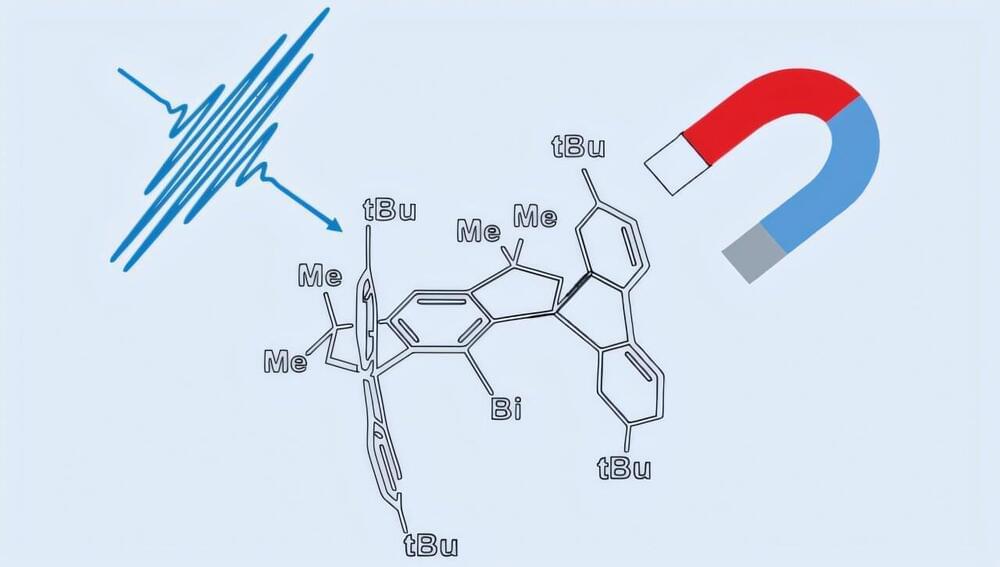
At the Berlin synchrotron radiation source BESSY II, the largest magnetic anisotropy of a single molecule ever measured experimentally has been determined. The larger a molecule’s anisotropy is, the better suited it is as a molecular nanomagnet. Such nanomagnets have a wide range of potential applications, for example, in energy-efficient data storage.
Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Kohlenforschung (MPI KOFO), the Joint Lab EPR4Energy of the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Energy Conversion (MPI CEC) and the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin were involved in the study.
The research involved a bismuth complex synthesized in the group of Josep Cornella (MPI KOFO). This molecule has unique magnetic properties that a team led by Frank Neese (MPI KOFO) recently predicted in theoretical studies. So far, however, all attempts to measure the magnetic properties of the bismuth complex and thus experimentally confirm the theoretical predictions have failed.