Hydrogen peroxide is widely used in everyday life, from disinfectants and medical sterilization to environmental cleanup and manufacturing. Despite its importance, most hydrogen peroxide is still produced using large-scale industrial processes that require significant energy. Researchers are thus seeking cleaner alternatives.
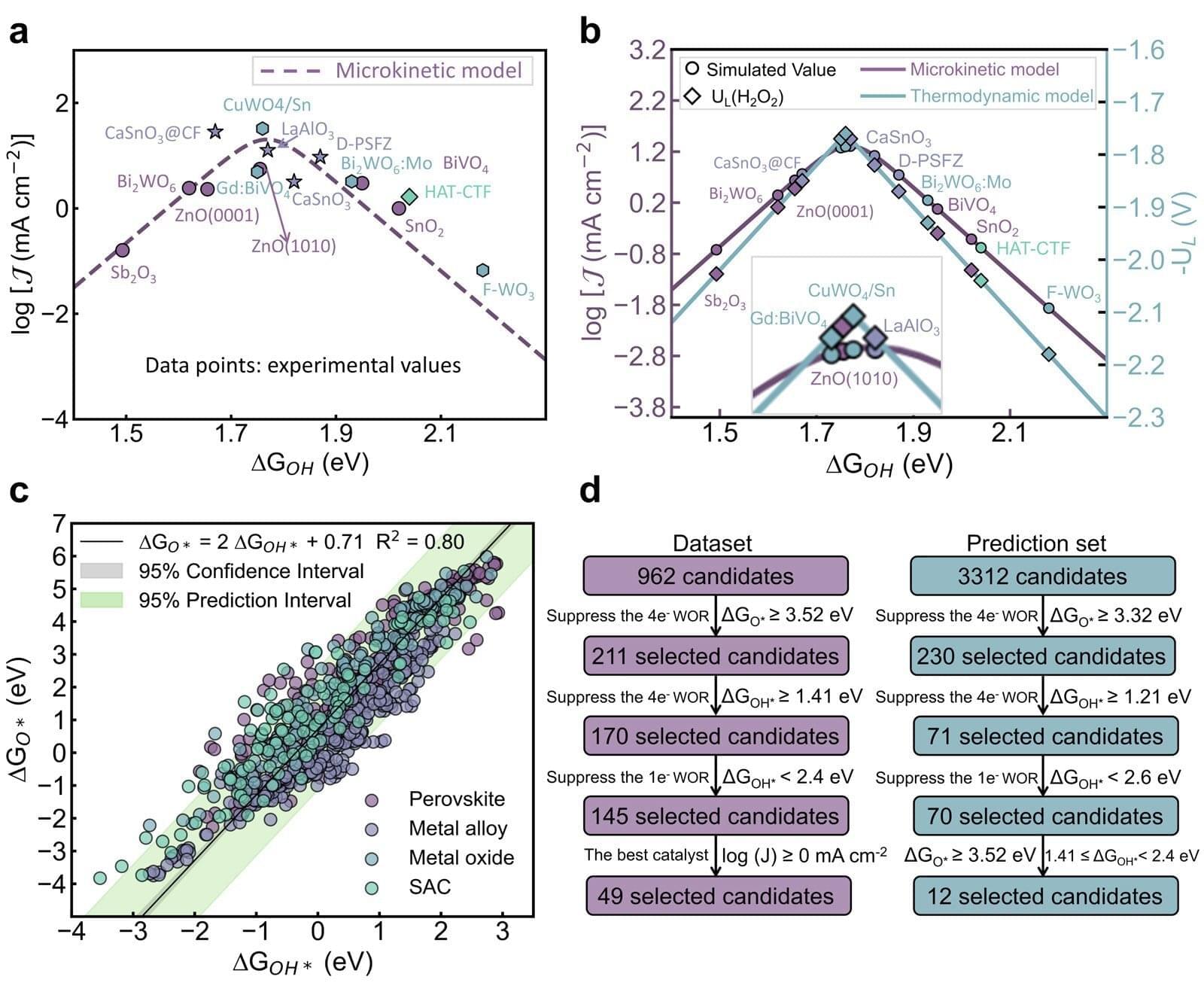
A team of researchers has made a breakthrough in this regard, developing a new computational framework that helps identify effective catalysts for producing hydrogen peroxide directly from water and electricity.
The work focuses on the two-electron water oxidation reaction, an electrochemical process that can generate hydrogen peroxide in a more localized and potentially sustainable way.