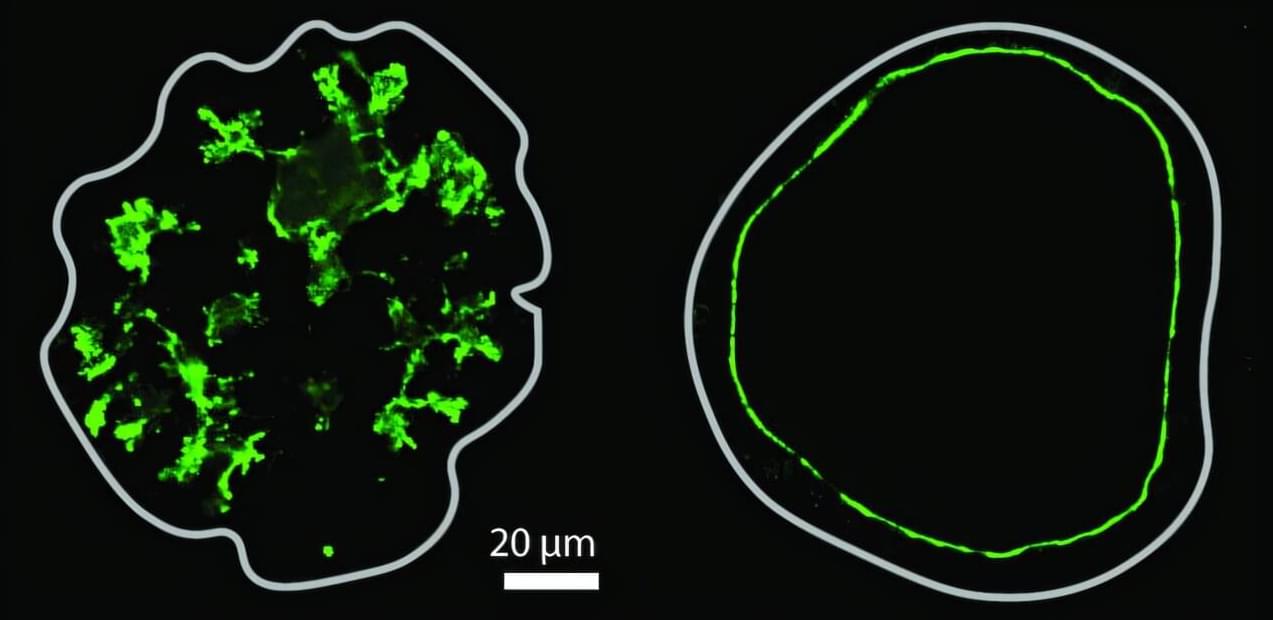
Organs often have fluid-filled spaces called lumens, which are crucial for organ function and serve as transport and delivery networks. Lumens in the pancreas form a complex ductal system, and its channels transport digestive enzymes to the small intestine. Understanding how this system forms in embryonic development is essential, both for normal organ formation and for diagnosing and treating pancreatic disorders.
Despite their importance, how lumens take certain shapes is not fully understood, as studies in other models have largely been limited to the formation of single, spherical lumens. Organoid models, which more closely mimic the physiological characteristics of real organs, can exhibit a range of lumen morphologies, such as complex networks of thin tubes.
Researchers in the group of Anne Grapin-Botton, director at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG) in Dresden, Germany, and also Honorary Professor at TU Dresden, teamed up with colleagues from the group of Masaki Sano at the University of Tokyo (Japan), Tetsuya Hiraiwa at the Institute of Physics of Academia Sinica (Taiwan), and with Daniel Rivéline at the Institut de Génétique et de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire (France) to explore the processes involved in complex lumen formation.