Very interesting discussion (with interactive animations) of how diffusion and criticality can model real-world processes and give us insight into why things happen.
Learn how things spread with playable simulations.
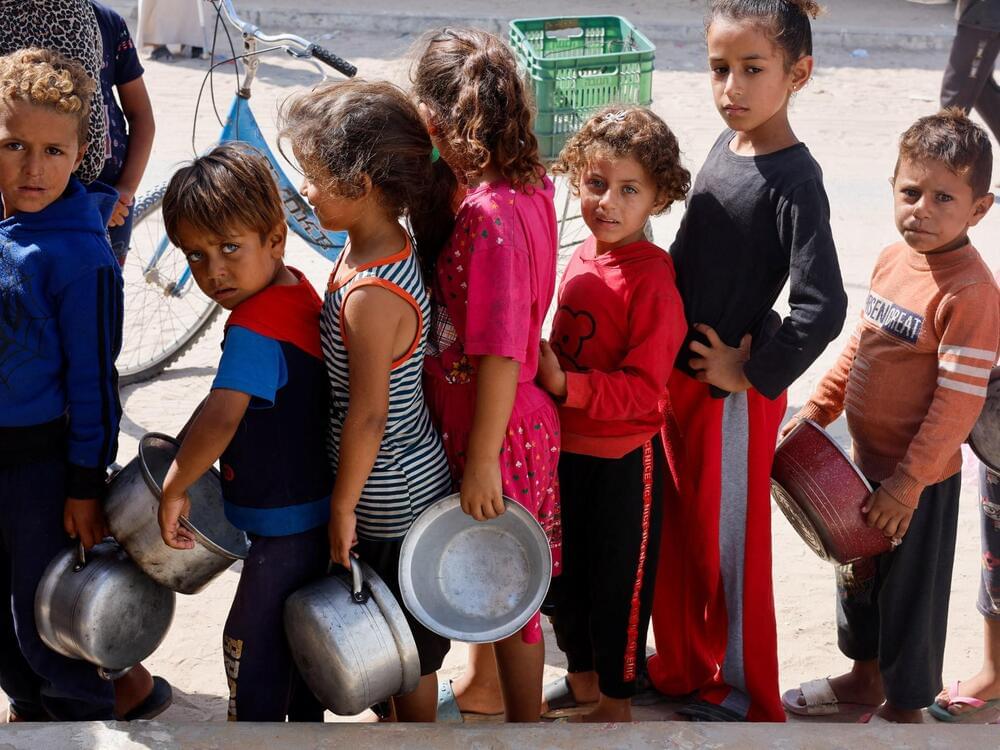


Child mortality in conflict settings was 8 percent, compared with 1.1 percent in peaceful countries.
It also said that 83.2 percent of the world’s poorest people live in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia.
The index, compiled jointly with the Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative (OPHI), used indicators such as a lack of adequate housing, sanitation, electricity, cooking fuel, nutrition and school attendance to assess levels of “multidimensional poverty”

I believe that vertical farming will be able to meet the demand of 9.7 billion people by 2050 or even be able to feed eventually the entire globe or even space stations. The leading vertical farming company I like is aero farms:3.
By 2050, we’ll need to produce 70% more food to feed over 9 billion mouths. Luckily, a wide range of vertical farming companies are developing innovative solutions to redefine production, expand urban agriculture and transform consumers into green-fingered growers.


World renowned neurophysiologist and computational neuroscientist Christof Koch joins Brian Greene to discuss how decades of experimental and theoretical investigation have shaped his understanding of consciousness and the brain — and how recent psychedelic experiences have profoundly reshaped his perspective on life and death.
This program is part of the Big Ideas series, supported by the John Templeton Foundation.
Participant: Christof Koch.
Moderator: Brian Greene.
00:00 — Introduction.
00:34 — Participant Introduction.
03:19 — Examining The Mystery Of Consciousness.
09:00 — Approaching Consciousness As A Physicist.
17:54 — Crafting Theories About Consciousness.
26:19 — A Brief Look Into The Causal Powers Of Consciousness.
43:12 — The Question Of Free Will.
51:46 — Introspection As A Tool For Examining The Mind.
01:22:52 — Credits.
SUBSCRIBE to our youtube channel and \.


Just as humans can use the taps of Morse Code or the patterns of smoke signals to communicate precise messages, infants show a remarkable flexibility to interpret nonlinguistic signals to aid their learning.
But what conditions are required for babies to elevate new nonlinguistic signals in this way? And how early can they do so?
Sandra Waxman, the study’s senior author, and her colleagues discovered that infants as young as six months old were able to harness nonlinguistic signals for learning, a surprising finding because at this age, babies are just beginning to acquire their own language.
The evidence revealed the conditions under which babies conferred communicative status to the novel tone signals and then recruited them to successfully complete a learning task. Infants’ success did not depend on whether the signals were produced by humans, or in a give-and-take interchange between individuals. Instead, what mattered was cross-modal temporal synchrony, in other words, if the method of signal delivery included synchronized sound and movement.
Six-month-old infants use cross-modal synchrony to identify novel communicative signals. Sci Rep 14, 27859 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-78801-9
DDW Editor Reece Armstrong speaks to Ellie Mahjubi, Vice President, Protein and cell analysis at Thermo Fisher Scientific, about how spatial biology is impacting drug discovery and development research.
RA: What’s the future and potential for spatial biology?
EM: Technological advancements in spatial biology are providing unprecedented insights into single cells within their spatial context, facilitating the analysis of cell types, functional states, cell interaction networks, as well as tissue microenvironments and architecture. These innovations promise to significantly advance basic research and enhance our understanding of human health and disease.