HighlyCitedPapers.
📝 — Schulze, et al.
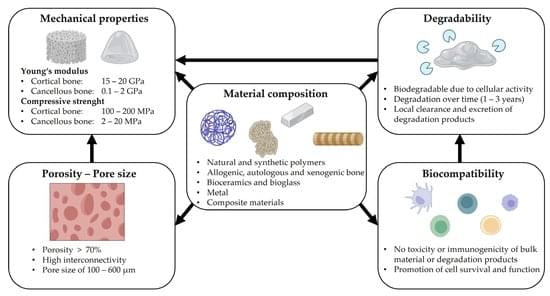
The present work reviews the strategies and technical approaches used to overcome the multilayered problems associated with large bone defect healing in long bones, with emphasis on research rooted in scaffold-guided tissue regeneration.
Full text is available 👇
Bone generally displays a high intrinsic capacity to regenerate. Nonetheless, large osseous defects sometimes fail to heal. The treatment of such large segmental defects still represents a considerable clinical challenge. The regeneration of large bone defects often proves difficult, since it relies on the formation of large amounts of bone within an environment impedimental to osteogenesis, characterized by soft tissue damage and hampered vascularization. Consequently, research efforts have concentrated on tissue engineering and regenerative medical strategies to resolve this multifaceted challenge. In this review, we summarize, critically evaluate, and discuss present approaches in light of their clinical relevance; we also present future advanced techniques for bone tissue engineering, outlining the steps to realize for their translation from bench to bedside.