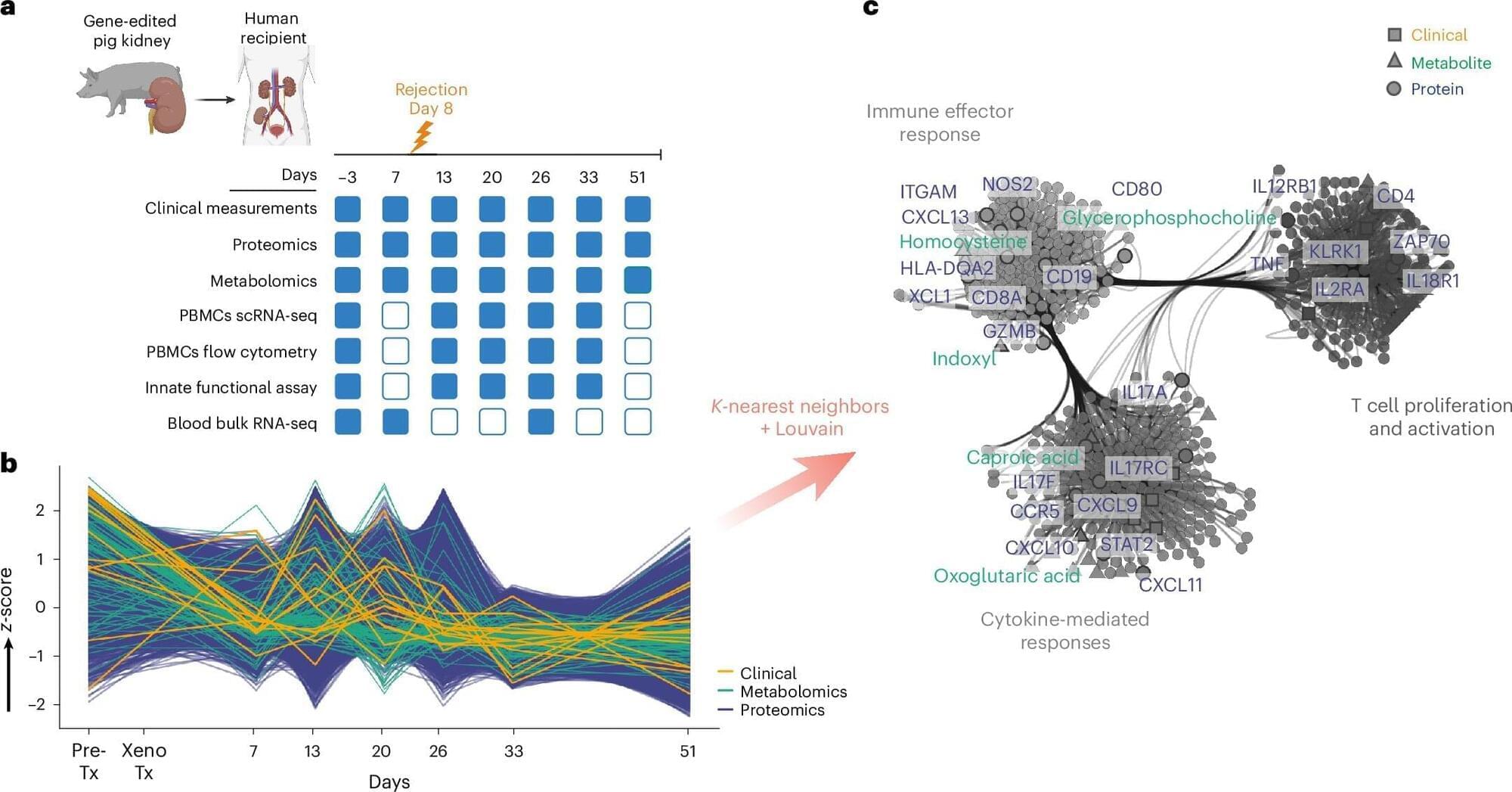
Novel research led by Brazilian scientists describes the immune system’s reactions in detail in the first living patient to receive a genetically modified pig kidney transplant. This paves the way for the search for therapies that can prevent organ rejection.
The study demonstrates the feasibility of this type of graft but indicates that controlling initial rejection alone is insufficient. This is because even with immunosuppressants, continuous activation of innate immunity—the body’s first line of defense, especially macrophages, which react to any threat—can compromise long-term survival.
Through transcriptomic, proteomic, metabolomic, and spatial analyses, the scientists have determined that new strategies are necessary to achieve long-term survival and favorable clinical outcomes. They recommend combining therapies that target innate immunity with advanced genetic engineering in donor pigs. They also suggest preventing early T lymphocyte-mediated rejection and implementing more sensitive monitoring approaches.