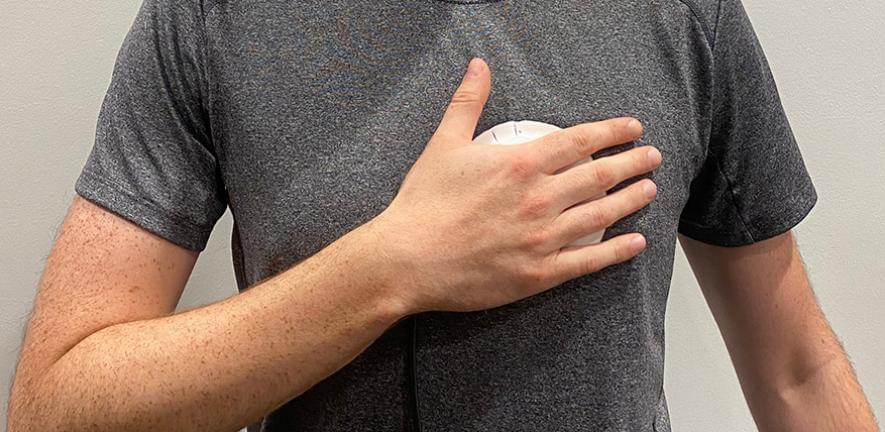
Researchers have developed a handheld device that could potentially replace stethoscopes as a tool for detecting certain types of heart disease.
The researchers, from the University of Cambridge, developed a device that makes it easy for people with or without medical training to record heart sounds accurately. Unlike a stethoscope, the device works well even if it’s not placed precisely on the chest: its larger, flexible sensing area helps capture clearer heart sounds than traditional stethoscopes.
The device can also be used over clothing, making it more comfortable for patients – especially women – during routine check-ups or community heart health screening programmes.