Better technologies to stably monitor cell populations over long periods of time make it possible to study neural coding and dynamics in the human brain.

If we were living in a computer simulation, would we be able to tell we were living in a computer simulation? It’s a question that’s difficult to answer, but physicist Melvin Vopson of the University of Portsmouth in the UK believes that he may have found a clue.
According to his latest study, gravity could be a product of computational processes within the Universe, a by-product of the Universe’s attempt to keep information and matter neatly organized in space and time.
“My findings in this study fit with the thought that the Universe might work like a giant computer, or our reality is a simulated construct,” Vopson says.
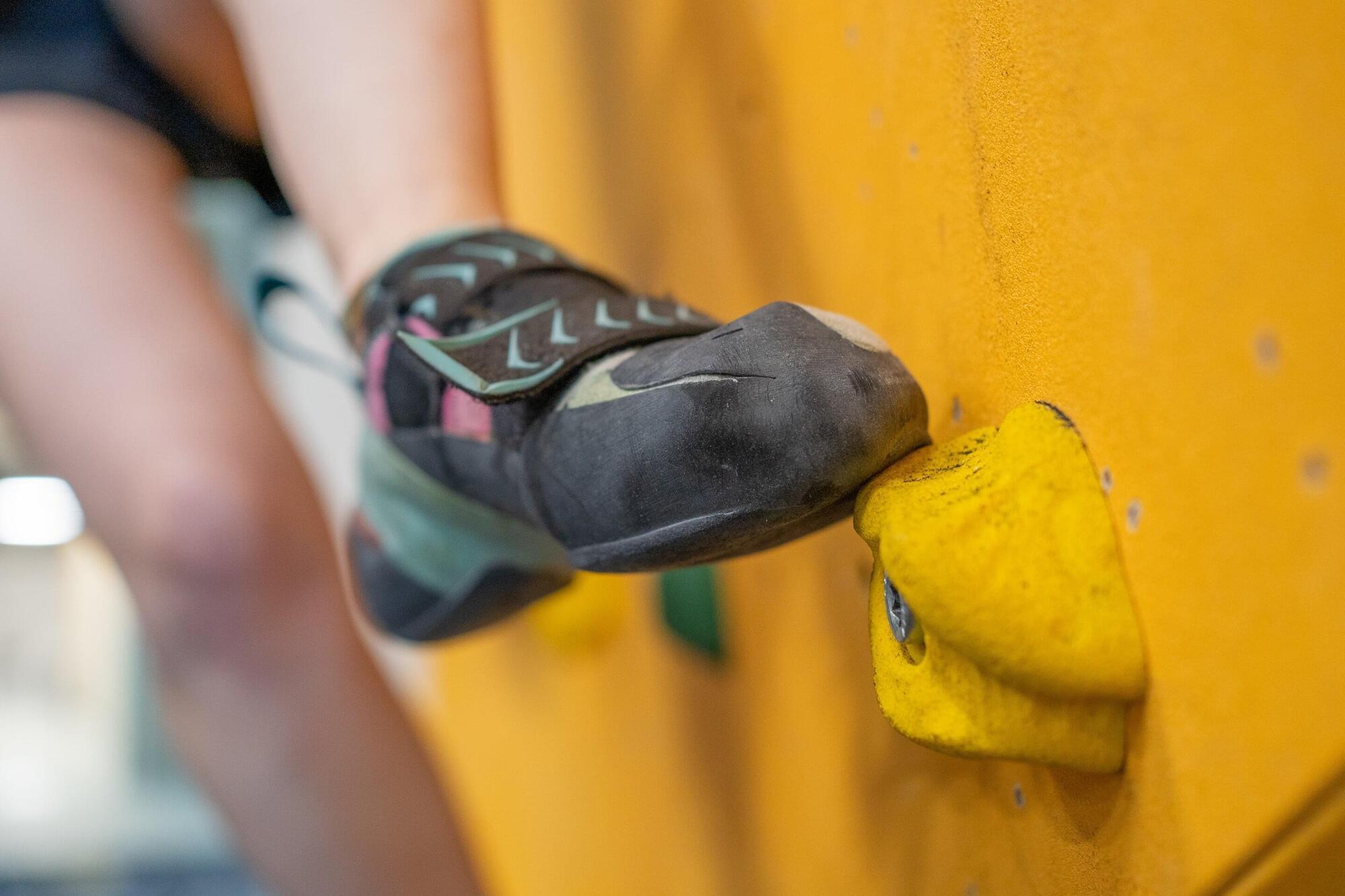



Those who climb indoors are doing something for their health. But climbing shoes contain chemicals of concern that can enter the lungs of climbers through the abrasion of the soles.
In a recent study, researchers from the University of Vienna and EPFL Lausanne have shown for the first time that high concentrations of potentially harmful chemicals from climbing shoe soles can be found in the air of bouldering gyms. In some cases they are higher than on a busy street. The results have been published in the journal ACS ES&T Air.
A climbing hall is filled with a variety of smells: sweat, chalk dust and a hint of rubber. A research group led by environmental scientist Thilo Hofmann at the University of Vienna has now discovered that rubber abrasion from climbing shoes can enter the lungs of athletes. The shoes contain rubber compounds similar to those used in car tires—including additives suspected of being harmful to humans and the environment.

Psilocybin, a natural compound found in certain mushrooms, has shown promise in treating depression and anxiety. UC San Francisco researchers wanted to know if it could be used to help Parkinson’s patients who often experience debilitating mood dysfunction in addition to their motor symptoms and don’t respond well to antidepressants or other medications.
The results were surprising.
Not only did participants tolerate the drug without serious side effects or worsening symptoms, which is what the pilot study was designed to test, they also experienced clinically significant improvements in mood, cognition, and motor function that lasted for weeks after the drug was out of their systems.
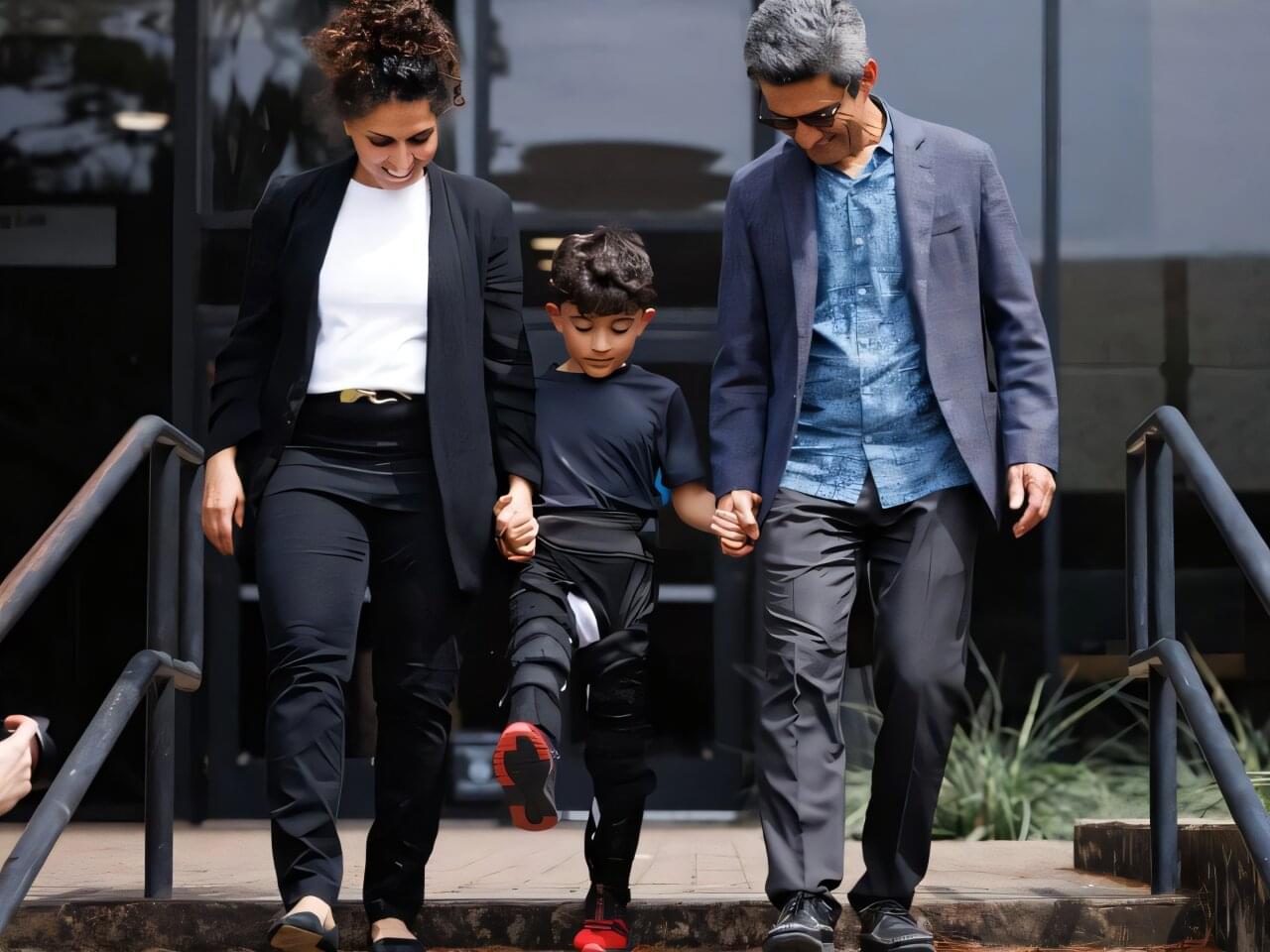



Just one look at the next-generation lightweight, soft exoskeleton for children with cerebral palsy reveals the powerful role technology can play in solving global challenges and improving lives.
Built to help children walk, MyoStep addresses motor impairments that severely restrict children’s participation in physical activities, self-care and academic pursuits, leading to developmental delays, social isolation and reduced self-esteem. It is lightweight, discreet, made of smart materials and wearable technology, and tailored to fit seamlessly into the lives of children and their families.
The MyoStep soft exoskeleton is introduced in IEEE Electron Devices Magazine by a team from the NSF UH Building Reliable Advances and Innovation in Neurotechnology (BRAIN) Center, an Industry–University Cooperative Research Center (IUCRC) and TIRR Memorial Hermann.