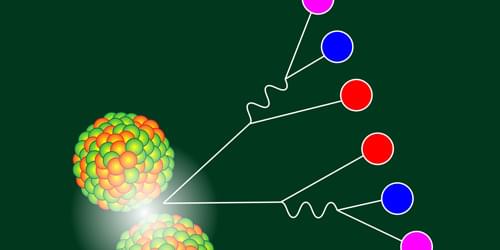
Top quarks and antiquarks have been detected in heavy-ion collisions at the Large Hadron Collider, showing that all six quark flavors were present in the Universe’s first moments.
Quarks, the fundamental building blocks of matter, are usually confined within hadrons, such as protons and neutrons, by the strong force. But in the first moments after the big bang, quarks and gluons moved freely in an extremely hot, dense state of matter called a quark–gluon plasma (QGP) [1]. This “primordial soup” was the Universe’s first form of matter, existing for roughly 10 microseconds after the big bang, until the Universe cooled sufficiently for quarks and gluons to combine [2]. Scientists recreate and study these early-Universe conditions by smashing together ultrarelativistic heavy nuclei at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN in Switzerland, and similar facilities.