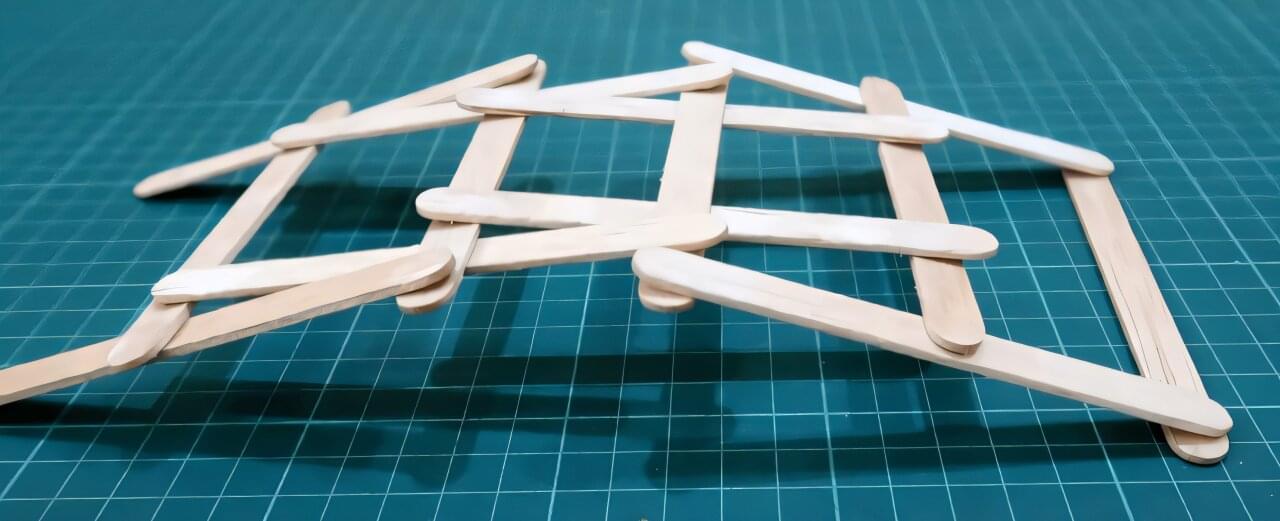
The concept of constructing a self-supporting structure made of rods—without the use of nails, ropes, or glue—dates back to Leonardo da Vinci. In the Codex Atlanticus, da Vinci illustrated a design for a self-supporting bridge across a river, which can be easily demonstrated using toothpicks, matches, or chopsticks. However, this design is fragile—pulling one of the rods or pushing the bridge from below can cause it to collapse.
In contrast, bird nests —which are also self-supporting structures consisting of rigid sticks and twigs—are remarkably stable despite continuous disturbances such as wind, ground vibrations, and the landing or takeoff of birds. What makes bird nests so sturdy?
This was the question at the center of a recent paper from L. Mahadevan and his team at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS). The research is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.