The man filed a complaint against OpenAI.
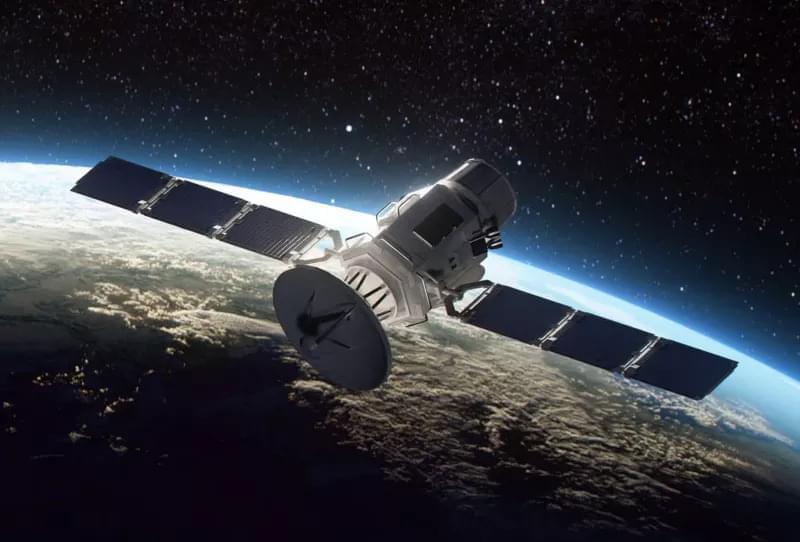



The Los Alamos National Laboratory has introduced the “Spacecraft Speedometer,” a novel technology for tracking satellites in low Earth orbit. This compact, resource-efficient device can precisely measure a satellite’s speed as it orbits the planet. Researchers believe it could also serve as a tracking solution for deep-space missions.
Designed to provide onboard, real-time velocity measurements, the Spacecraft Speedometer enables space agencies and commercial operators to predict satellite positions and execute orbital maneuvers to avoid collisions with other satellites or space debris.
Los Alamos developed the system in response to increasing congestion in LEO, where the number of active satellites surged from 2,287 in 2019 to over 10,000 in 2024. With the rise of mega-constellations, traffic management challenges are expected to grow even more severe.

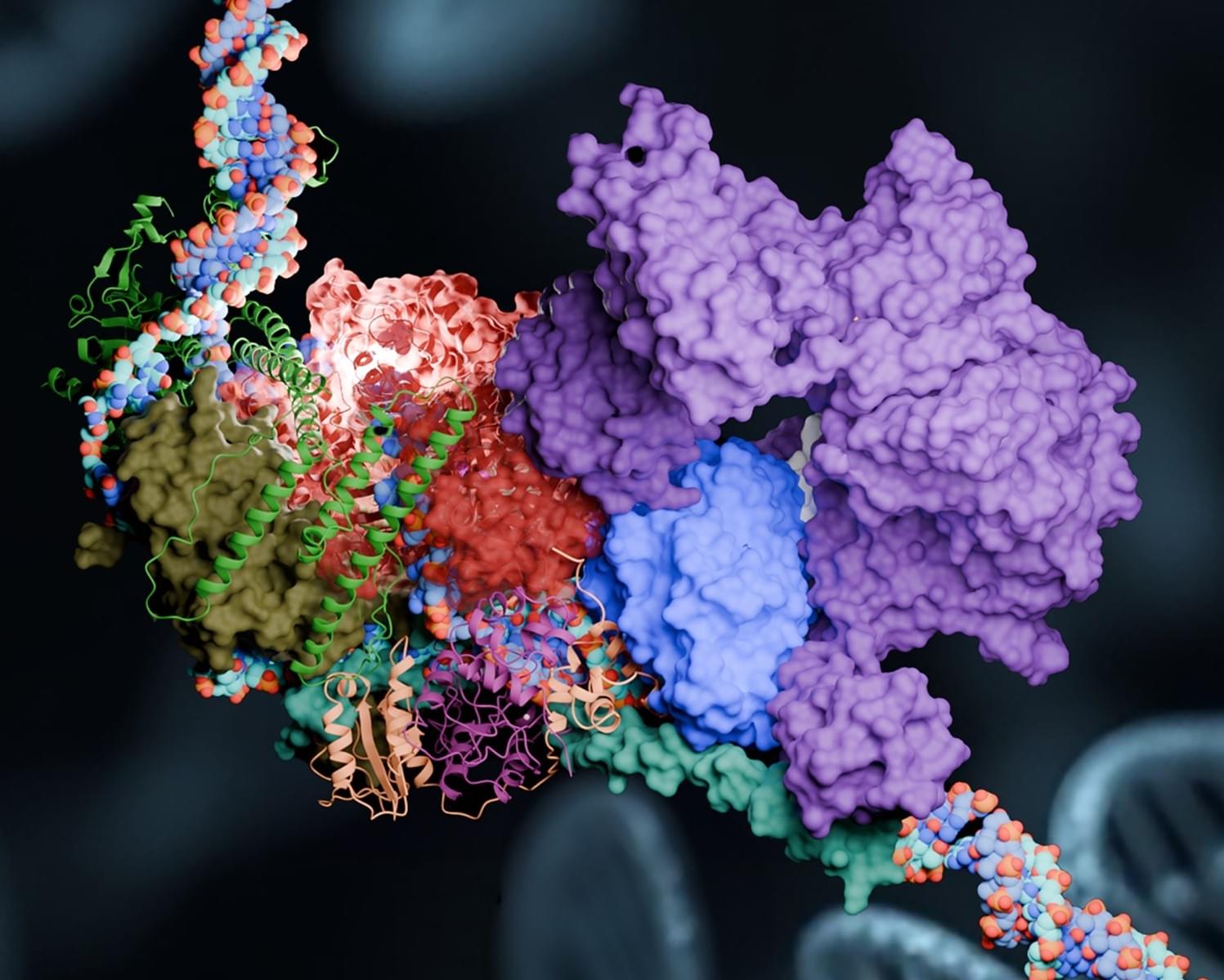
Sunburns and aging skin are obvious effects of exposure to harmful UV rays, tobacco smoke and other carcinogens. But the effects aren’t just skin deep. Inside the body, DNA is literally being torn apart.
Understanding how the body heals and protects itself from DNA damage is vital for treating genetic disorders and life-threatening diseases such as cancer. But despite numerous studies and medical advances, much about the molecular mechanisms of DNA repair remains a mystery.
For the past several years, researchers at Georgia State University tapped into the Summit supercomputer at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory to study an elaborate molecular pathway called nucleotide excision repair, or NER relies on an array of highly dynamic protein complexes to cut out, or excise, damaged DNA with surgical precision.
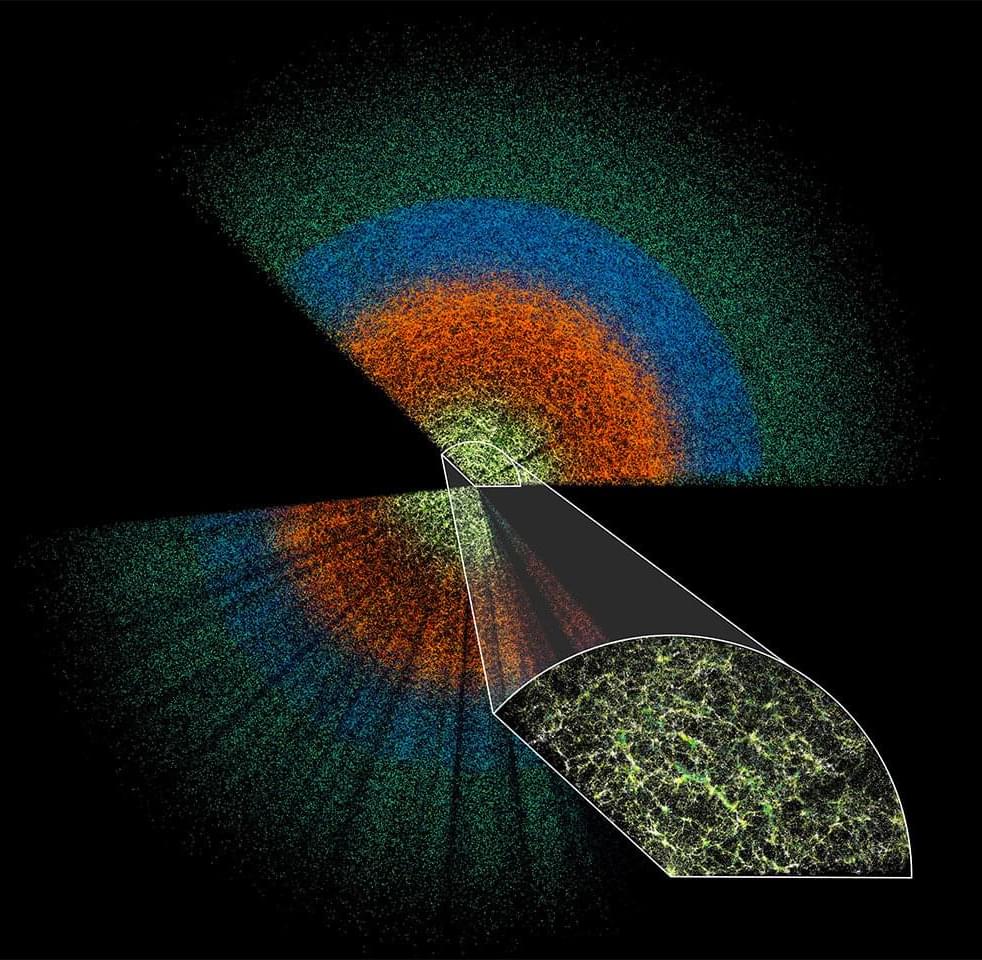
This week, ALMA researchers reported the discovery of oxygen in the most distant known galaxy. Geologists believe unusual structures in rock in the desert regions of Namibia, Oman and Saudia Arabia may be evidence of an unknown microorganism. And a group of physicists may have generated a tiny charge of electricity using the Earth’s rotational energy. But the biggest story by far is the second release of data from the DESI survey of the universe, which could upend the standard model:
An emerging generation of cosmological surveys launched this week with the second release of data from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument at Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona, which is mapping an unprecedentedly huge number of galaxies spanning 11 billion years of cosmic history in order to better understand dark energy.
Astronomers have known for many decades that the universe is expanding; in the 1990s, the first image of the cosmic microwave background—the echo of the big bang—revealed that this expansion is accelerating for unknown reasons. Astronomers call this expansion “dark energy,” which translates to “we don’t understand what this energy is.”
Joscha Bach, Cognitive Scientist and AI researcher, as well as Anthony Aguirre, UCSC Professor of Physics, join us to explore the world through the lens of computation and the difficulties we face on the way to beneficial futures.
Topics discussed in this episode include:
-Understanding the universe through digital physics.
–How human consciousness operates and is structured.
–The path to aligned AGI and bottlenecks to beneficial futures.
–Incentive structures and collective coordination.
Find the page for this podcast here: https://futureoflife.org/2021/03/31/j… to be the FLI Podcast Producer here: https://futureoflife.org/job-postings/ Follow the podcast on: Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/show/2Op1WO3… Apple Podcasts: https://podcasts.apple.com/us/podcast… SoundCloud: / futureoflife Have any feedback about the podcast? You can share your thoughts here: www.surveymonkey.com/r/DRBFZCT Timestamps: 0:00 Intro 1:58 What is truth and knowledge? 11:39 What is subjectivity and objectivity? 15:13 What is the universe ultimately? 20:32 Is the universe a cellular automaton? Is the universe ultimately digital or analogue? 25:59 Hilbert’s hotel from the point of view of computation 39:14 Seeing the world as a fractal 43:00 Describing human consciousness 57:46 Meaning, purpose, and harvesting negentropy 1:02:30 The path to aligned AGI 1:05:13 Bottlenecks to beneficial futures and existential security 1:16:01 A future with one, several, or many AGI systems? How do we maintain appropriate incentive structures? 1:30:39 Non-duality and collective coordination 1:34:16 What difficulties are there for an idealist worldview that involves computation? 1:37:19 Which features of mind and consciousness are necessarily coupled and which aren’t? 1:47:47 Joscha’s final thoughts on AGI This podcast is possible because of the support of listeners like you. If you found this conversation to be meaningful or valuable, consider supporting it directly by donating at: https://futureoflife.org/donate Contributions like yours make these conversations possible.
Apply to be the FLI Podcast Producer here: https://futureoflife.org/job-postings/
Follow the podcast on:
Joscha Bach is a cognitive scientist focusing on cognitive architectures, consciousness, models of mental representation, emotion, motivation and sociality.
Patreon: / curtjaimungal.
Crypto: https://tinyurl.com/cryptoTOE
PayPal: https://tinyurl.com/paypalTOE
Twitter: / toewithcurt.
Discord Invite: / discord.
iTunes: https://podcasts.apple.com/ca/podcast… https://pdora.co/33b9lfP Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/show/4gL14b9… Subreddit r/TheoriesOfEverything: / theoriesofeverything Merch: https://tinyurl.com/TOEmerch 0:00:00 Introduction 0:00:17 Bach’s work ethic / daily routine 0:01:35 What is your definition of truth? 0:04:41 Nature’s substratum is a “quantum graph”? 0:06:25 Mathematics as the descriptor of all language 0:13:52 Why is constructivist mathematics “real”? What’s the definition of “real”? 0:17:06 What does it mean to “exist”? Does “pi” exist? 0:20:14 The mystery of something vs. nothing. Existence is the default. 0:21:11 Bach’s model vs. the multiverse 0:26:51 Is the universe deterministic 0:28:23 What determines the initial conditions, as well as the rules? 0:30:55 What is time? Is time fundamental? 0:34:21 What’s the optimal algorithm for finding truth? 0:40:40 Are the fundamental laws of physics ultimately “simple”? 0:50:17 The relationship between art and the artist’s cost function 0:54:02 Ideas are stories, being directed by intuitions 0:58:00 Society has a minimal role in training your intuitions 0:59:24 Why does art benefit from a repressive government? 1:04:01 A market case for civil rights 1:06:40 Fascism vs communism 1:10:50 Bach’s “control / attention / reflective recall” model 1:13:32 What’s more fundamental… Consciousness or attention? 1:16:02 The Chinese Room Experiment 1:25:22 Is understanding predicated on consciousness? 1:26:22 Integrated Information Theory of consciousness (IIT) 1:30:15 Donald Hoffman’s theory of consciousness 1:32:40 Douglas Hofstadter’s “strange loop” theory of consciousness 1:34:10 Holonomic Brain theory of consciousness 1:34:42 Daniel Dennett’s theory of consciousness 1:36:57 Sensorimotor theory of consciousness (embodied cognition) 1:44:39 What is intelligence? 1:45:08 Intelligence vs. consciousness 1:46:36 Where does Free Will come into play, in Bach’s model? 1:48:46 The opposite of free will can lead to, or feel like, addiction 1:51:48 Changing your identity to effectively live forever 1:59:13 Depersonalization disorder as a result of conceiving of your “self” as illusory 2:02:25 Dealing with a fear of loss of control 2:05:00 What about heart and conscience? 2:07:28 How to test / falsify Bach’s model of consciousness 2:13:46 How has Bach’s model changed in the past few years? 2:14:41 Why Bach doesn’t practice Lucid Dreaming anymore 2:15:33 Dreams and GAN’s (a machine learning framework) 2:18:08 If dreams are for helping us learn, why don’t we consciously remember our dreams 2:19:58 Are dreams “real”? Is all of reality a dream? 2:20:39 How do you practically change your experience to be most positive / helpful? 2:23:56 What’s more important than survival? What’s worth dying for? 2:28:27 Bach’s identity 2:29:44 Is there anything objectively wrong with hating humanity? 2:30:31 Practical Platonism 2:33:00 What “God” is 2:36:24 Gods are as real as you, Bach claims 2:37:44 What “prayer” is, and why it works 2:41:06 Our society has lost its future and thus our culture 2:43:24 What does Bach disagree with Jordan Peterson about? 2:47:16 The millennials are the first generation that’s authoritarian since WW2 2:48:31 Bach’s views on the “social justice” movement 2:51:29 Universal Basic Income as an answer to social inequality, or General Artificial Intelligence? 2:57:39 Nested hierarchy of “I“s (the conflicts within ourselves) 2:59:22 In the USA, innovation is “cheating” (for the most part) 3:02:27 Activists are usually operating on false information 3:03:04 Bach’s Marxist roots and lessons to his former self 3:08:45 BONUS BIT: On societies problems.
Pandora: https://pdora.co/33b9lfP
Spotify: https://open.spotify.com/show/4gL14b9…
Subreddit r/TheoriesOfEverything: / theoriesofeverything.
Merch: https://tinyurl.com/TOEmerch.
0:00:00 Introduction.
0:00:17 Bach’s work ethic / daily routine.
0:01:35 What is your definition of truth?
0:04:41 Nature’s substratum is a \.

The IoT world is a big world that everybody is talking about. IoT products nowadays come in different forms — some are labelled as IoT, but in fact they represent only a small portion of what an IoT product really entails. A fully fledged IoT project not only requires programming and hardware expertise but also expertise on a broad range of domains from energy to smart home and even automotive.
The purpose of this article is to highlight the significant differences among the Internet of Things (IoT) and Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), and while walking through the listed considerations, the reader will have the chance to learn about their ecosystems and the particularities of their applications. Moreover, the gaps in the standardization of the technologies related to the IoT are presented along with the current initiatives from various institutions for mitigating these gaps.
Before talking about the differences between the IoT and IIoT, let’s look first at the similarities of the two. Both have the same fundamental layer on top of which they are built. With IIoT being a subset of the larger IoT, they automatically share common technologies like sensors, cloud platforms, connectivity and analytics.
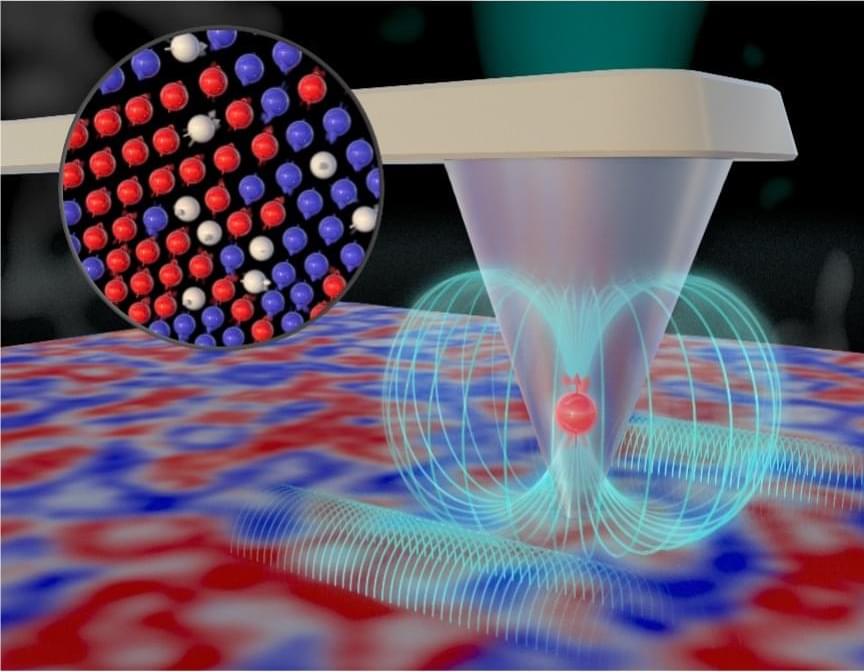
Working at nanoscale dimensions, billionths of a meter in size, a team of scientists led by the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory revealed a new way to measure high-speed fluctuations in magnetic materials. Knowledge obtained by these new measurements, published in Nano Letters, could be used to advance technologies ranging from traditional computing to the emerging field of quantum computing.
Many materials undergo phase transitions characterized by temperature-dependent stepwise changes of important fundamental properties. Understanding materials’ behavior near a critical transition temperature is key to developing new technologies that take advantage of unique physical properties. In this study, the team used a nanoscale quantum sensor to measure spin fluctuations near a phase transition in a magnetic thin film. Thin films with magnetic properties at room temperature are essential for data storage, sensors and electronic devices because their magnetic properties can be precisely controlled and manipulated.
The team used a specialized instrument called a scanning nitrogen-vacancy center microscope at the Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, a DOE Office of Science user facility at ORNL. A nitrogen-vacancy center is an atomic-scale defect in diamond where a nitrogen atom takes the place of a carbon atom, and a neighboring carbon atom is missing, creating a special configuration of quantum spin states. In a nitrogen-vacancy center microscope, the defect reacts to static and fluctuating magnetic fields, allowing scientists to detect signals on a single spin level to examine nanoscale structures.