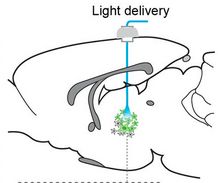
Optogenetic laser light stimulation of the thalamus (credit: Jia Liu et al./eLife)
By flashing high-frequency (40 to 100 pulses per second) optogenetic lasers at the brain’s thalamus, scientists were able to wake up sleeping rats and cause widespread brain activity. In contrast, flashing the laser at 10 pulses per second suppressed the activity of the brain’s sensory cortex and caused rats to enter a seizure-like state of unconsciousness.
“We hope to use this knowledge to develop better treatments for brain injuries and other neurological disorders,” said Jin Hyung Lee, Ph.D., assistant professor of neurology, neurosurgery, and bioengineering at Stanford University, and a senior author of the study, published in the open-access journal eLIFE.








 By not having to answer to industry or academia, OpenAI hopes to focus not just on developing digital intelligence, but also guide research along an ethical route that, according to
By not having to answer to industry or academia, OpenAI hopes to focus not just on developing digital intelligence, but also guide research along an ethical route that, according to 