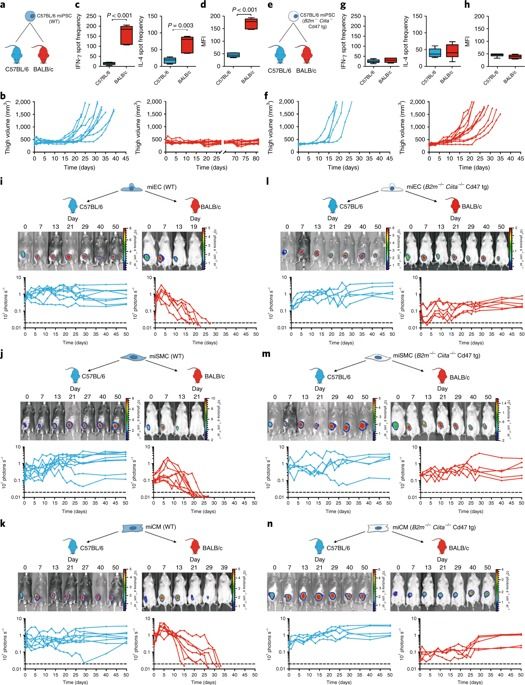
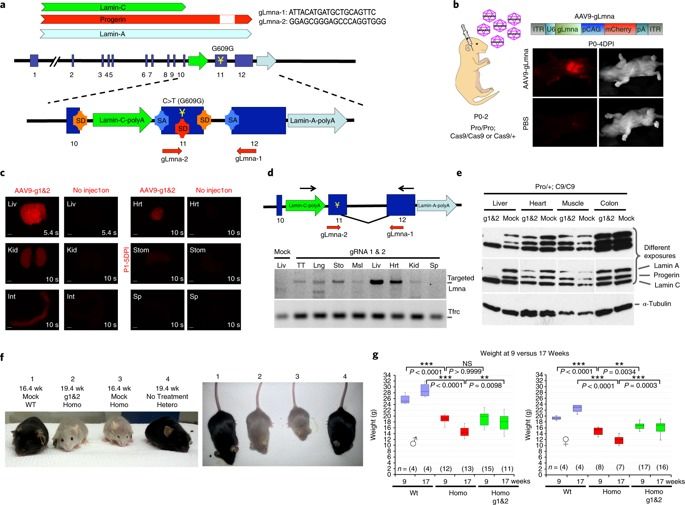
Autologous induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) constitute an unlimited cell source for patient-specific cell-based organ repair strategies. However, their generation and subsequent differentiation into specific cells or tissues entail cell line-specific manufacturing challenges and form a lengthy process that precludes acute treatment modalities. These shortcomings could be overcome by using prefabricated allogeneic cell or tissue products, but the vigorous immune response against histo-incompatible cells has prevented the successful implementation of this approach. Here we show that both mouse and human iPSCs lose their immunogenicity when major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and II genes are inactivated and CD47 is over-expressed. These hypoimmunogenic iPSCs retain their pluripotent stem cell potential and differentiation capacity. Endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and cardiomyocytes derived from hypoimmunogenic mouse or human iPSCs reliably evade immune rejection in fully MHC-mismatched allogeneic recipients and survive long-term without the use of immunosuppression. These findings suggest that hypoimmunogenic cell grafts can be engineered for universal transplantation.