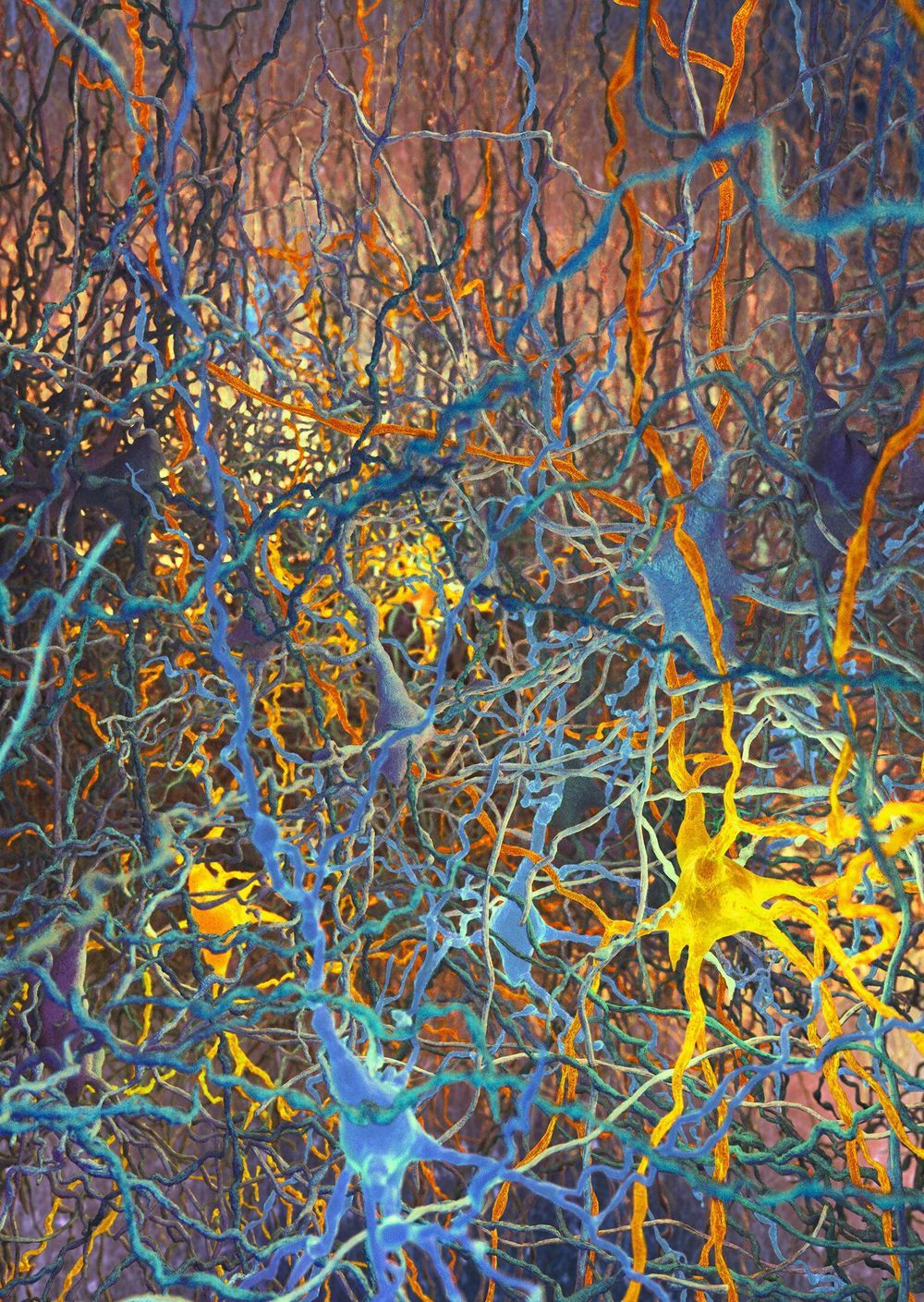
A team led by Lida Kanari now reports a new system for distinguishing cell types in the brain, an algorithmic classification method that the researchers say will benefit the entire field of neuroscience. Blue Brain founder Professor Henry Markram says, “For nearly 100 years, scientists have been trying to name cells. They have been describing them in the same way that Darwin described animals and trees. Now, the Blue Brain Project has developed a mathematical algorithm to objectively classify the shapes of the neurons in the brain. This will allow the development of a standardized taxonomy [classification of cells into distinct groups] of all cells in the brain, which will help researchers compare their data in a more reliable manner.”
The team developed an algorithm to distinguish the shapes of the most common type of neuron in the neocortex, the pyramidal cells. Pyramidal cells are distinctively tree-like cells that make up 80 percent of the neurons in the neocortex, and like antennas, collect information from other neurons in the brain. Basically, they are the redwoods of the brain forest. They are excitatory, sending waves of electrical activity through the network, as people perceive, act, and feel.
The father of modern neuroscience, Ramón y Cajal, first drew pyramidal cells over 100 years ago, observing them under a microscope. Yet up until now, scientists have not reached a consensus on the types of pyramidal neurons. Anatomists have been assigning names and debating the different types for the past century, while neuroscience has been unable to tell for sure which types of neurons are subjectively characterized. Even for visibly distinguishable neurons, there is no common ground to consistently define morphological types.