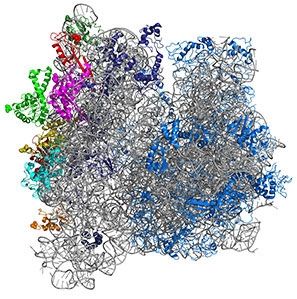
Over the past several years, Northwestern Engineering’s Michael Jewett did the seemingly impossible. He overcame the critical barrier to making mutant ribosomes, the core catalyst in cells that are responsible for life.
Now, with funding from the Department of Defense’s Multidisciplinary University Research Initiatives (MURI) program, Jewett is ready to take this research to the next level. Along with a multi-school team, he plans to use engineer and repurpose the ribosome to make new kinds of polymers for flow batteries.
“We are in a new era of biomaterial design,” Jewett said. “So far, the ribosome has been this untouchable biomolecular machine — one that we couldn’t engineer or modify. Now, armed with recent advances in our ability to construct new versions, new applications may only be limited by our imagination.”
The MURI grant joins researchers from Northwestern, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, University of Texas at Austin, and Georgia Institute of Technology who will work together to develop new types of electrical materials for battery storage. By using biological catalysts, the team aims to produce materials for sustainable, rechargeable batteries that are currently impossible to make chemically.
Read more