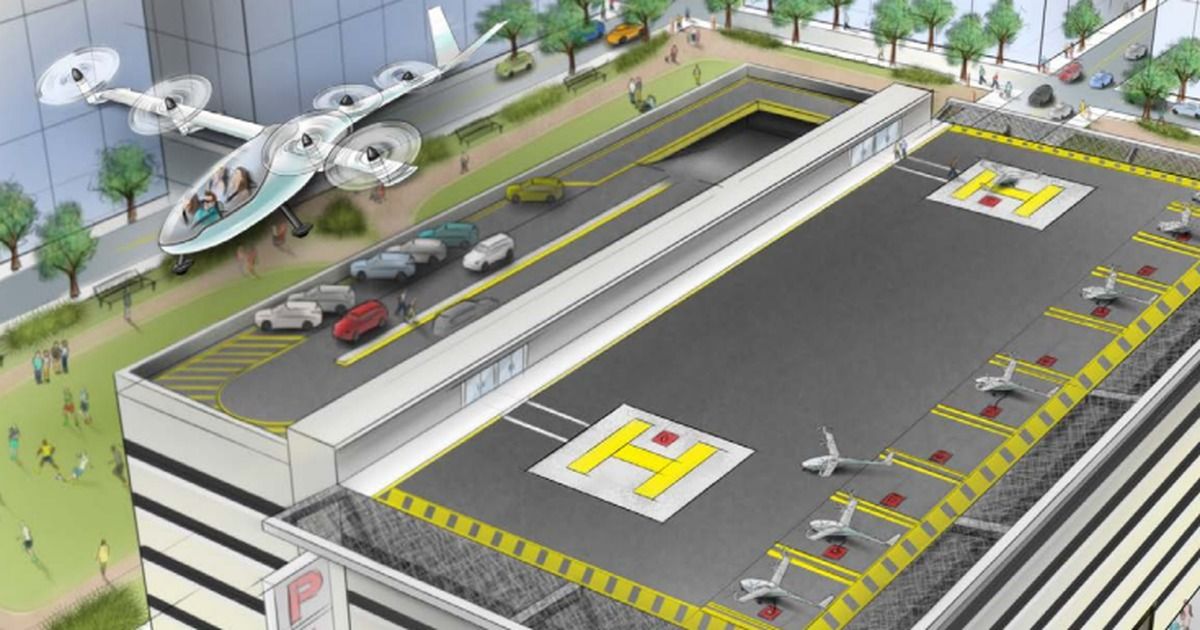
Uber is preparing for on-demand aviation.
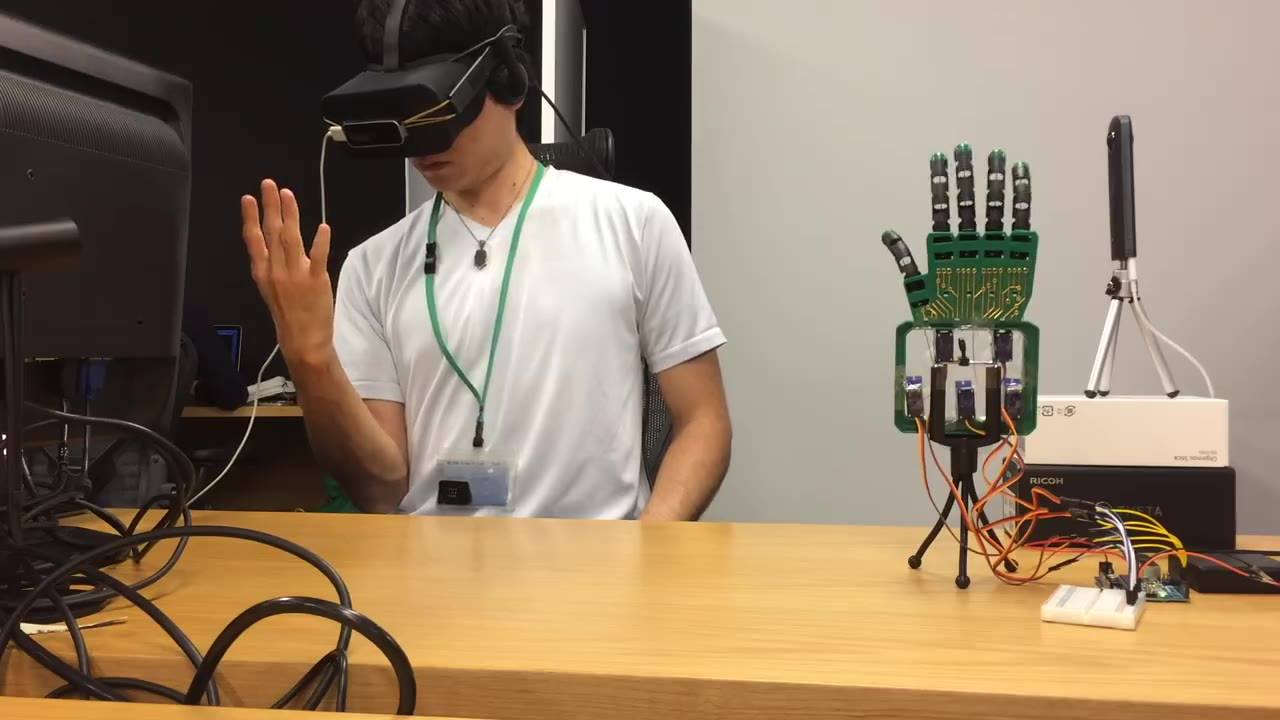
There have been significant advances in developing new prostheses with a simple sense of touch, but researchers are looking to go further. Scientists and engineers are working on a way to provide prosthetic users and those suffering from spinal cord injuries with the ability to both feel and control their limbs or robotic replacements by means of directly stimulating the cortex of the brain.
For decades, a major goal of neuroscientists has been to develop new technologies to create more advanced prostheses or ways to help people who have suffered spinal cord injuries to regain the use of their limbs. Part of this has involved creating a means of sending brain signals to disconnected nerves in damaged limbs or to robotic prostheses, so they can be moved by thought, so control is simple and natural.
However, all this had only limited application because as well as being able to tell a robotic or natural limb to move, a sense of touch was also required, so the patient would know if something has been grasped properly or if the hand or arm is in the right position. Without this feedback, it’s very difficult to control an artificial limb properly even with constant concentration or computer assistance.
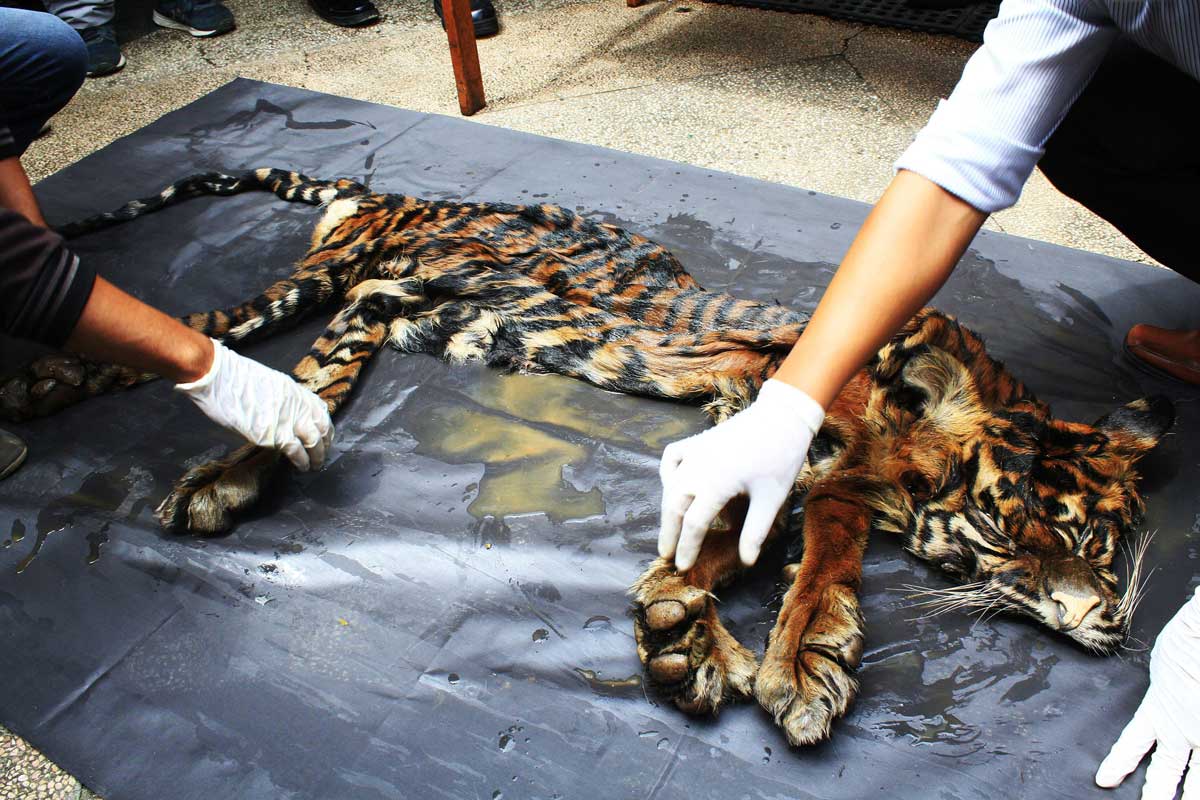
Nearly three-fifths of all animals with a backbone — fish, birds, amphibians, reptiles and mammals — have been wiped out since 1970 by human appetites and activity, according to a grim study released Thursday.
On current trends, stocks of global wildlife could plunge two-thirds by 2020, an annual decline of two per cent, conservation group WWF and the Zoological Society of London warned in their joint biennial Living Planet report.
Tough times lay ahead for human workers. With the advent of automation comes a much smaller job market and an ever-shrinking work force. Jobs traditionally held by humans are now being taken over by robots and computer software. Now, another job sector is being threatened by automation: the public sector.
A study conducted by Oxford University and Deloitte, a business advisory firm, found that 850,000 public sector jobs in the UK are at risk of being lost by 2030 due to automation. The report also mentions how more than 1.3 million administrative jobs in the public sector have a 77% probability of being automated. These jobs include highly repetitive jobs like clerical work and transportation work.
–This report comes as good news to fiscal policy makers who wish to cut costs. It shows the government can save up to £12 billion in public sector wages by 2030.
Within 20 years nearly all jobs will be automated and will lead to a human revolution, claims top futurist philosopher.
Futurist and architect Jacque Fresco speaks in parables. If he goes on too long with a story, his 40-year partner Roxanne Meadows interjects facts to keep him on track. Fresco recently turned 100 years old, and is the oldest celebrity futurist in the world. His magnum opus is The Venus Project, a 21-acre Central Florida Eden with white dome-shaped buildings that Meadows and he hand built over three and a half decades. The sanctuary and research center is where Fresco still leads weekly seminars, which includes a tour of 10 buildings—some filled with hundreds of future city models inside them—that highlight the promise of a future world where equality and technology abound.
It might be a blue pill that makes you hallucinate in an entertaining way – and then another white pill that brings you back to normality, Reed Hastings said…
The future of TV might everyone taking hallucinogenic drugs, according to the head of Netflix.
The threats to the streaming TV company might not be Amazon or other streaming services, but instead “pharmacological” ways of entertaining people, Reed Hastings has said.
And just as films and TV shows are a supposedly improved version of other entertainments, those same things might eventually become defunct, he said. In the same way that the cinema and TV screen made “the opera and the novel” much smaller, something else might be on the way to do the same thing, the Netflix boss said at a Wall Street Journal event.
Not all things future are for the best😑.
The world is facing the biggest extinction since the dinosaurs, with seven in 10 mammals, birds, fish, amphibians and reptiles wiped out in just 50 years, a new report warns.
The latest Living Planet report by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and the Zoological Society of London (ZSL) estimates that by 2020 populations of vertebrates will have fallen by 67 per cent since 1970.
Extinction rates are now running at 100 times their natural level because of deforestation, hunting, pollution, overfishing and climate change.
Something needed to replace antibacterial soaps.
Whether they’re hand soap, shampoo, dish-washing liquid or laundry detergent, the majority of commonly-used soaps contain petroleum-based cleansing agents. Obtaining that petroleum isn’t exactly an eco-friendly process, plus it becomes a source of pollution once it goes down the drain. While there are petroleum-free soaps out there, they often don’t perform that well. Now, however, scientists have developed one that is claimed to actually work better than mainstream products.
The new soap was developed by a consortium led by the University of Minnesota. It combines renewable biodegradable ingredients such as fatty acids from soybeans or coconut, along with sugar from corn, to form a soap molecule known as oleo-furan-surfactant (OFS).
According to the university, relatively low concentrations of OFS are required to form soap particles, so less soap is needed to do the same amount of cleaning.