Discover Japan’s renewable energy breakthrough with the first titanium solar panel—1000 times more powerful than conventional cells.



Despite its uniquely rich inventory of organic molecules, Saturn’s largest moon, Titan, may be able to support only a minuscule amount of biomass, if life exists on the moon, according to a study using bioenergetic modeling.
Titan, Saturn’s largest moon, is a strange, alien world. Covered in rivers and lakes of liquid methane, icy boulders and dunes of soot-like “sand,” its topography has long fascinated scientists and invited speculation on whether lifeforms might lurk beneath the moon’s thick, hazy atmosphere.
An international team of researchers co-led by Antonin Affholder at the U of A Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology and Peter Higgins at Harvard University’s Department of Earth and Planetary sciences set out to develop a realistic scenario of what life on Titan might look like if it does exist, where it is most likely to occur and how much of it might be present.
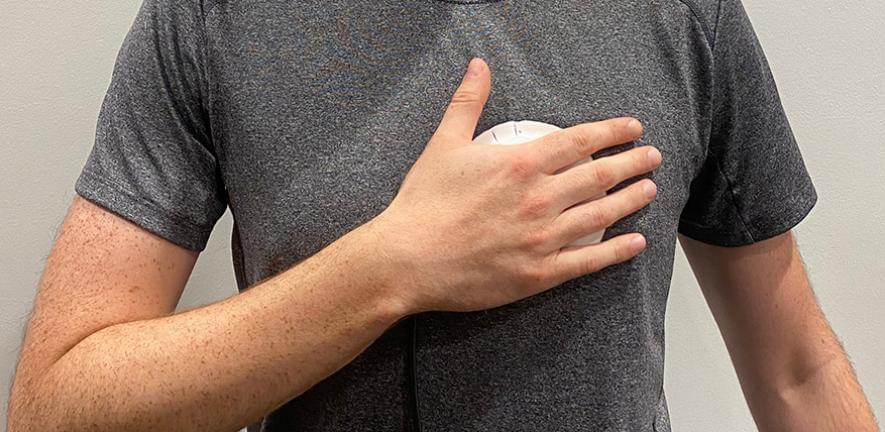

Researchers have developed a handheld device that could potentially replace stethoscopes as a tool for detecting certain types of heart disease.
The researchers, from the University of Cambridge, developed a device that makes it easy for people with or without medical training to record heart sounds accurately. Unlike a stethoscope, the device works well even if it’s not placed precisely on the chest: its larger, flexible sensing area helps capture clearer heart sounds than traditional stethoscopes.
The device can also be used over clothing, making it more comfortable for patients – especially women – during routine check-ups or community heart health screening programmes.
THX 1138 movie clips: http://j.mp/1x59pYDBUY THE MOVIE: http://j.mp/RcXMHzDon’t miss the HOTTEST NEW TRAILERS: http://bit.ly/1u2y6prCLIP DESCRIPTION:THX (Rob…
Amazing track by electro-industrial american band Velvet Acid Christ (Bryan Erickson): http://www.velvetacidchrist.com
Dismantled’s “Purity” (Vocal Edit) off of their Dystopia CDM (2002)
Feedback surge.
Probe injected.
Data flood overloading neural circuitry.
Trodes on.
Pulse is racing.
Neon grid expanding into binary grey.
We trace our pathways, dissolve in beams.
We breach through cores on static wings.
Pressure starts.
Ice below you.
Shockwaves tumble, pulling.
down the consciousness.
below the circuits.
Noise sets in.
Nervous system failing.
Locked into eternity.
forever looped in frames.
We run through wires, disguise in screens.
We blend in patterns of input streams.
It can be hard to hear a signal 100 miles away—so what does it take to build a beacon loud enough to be heard 100,000 light years away? In this episode, we explore galactic beacons: powerful transmissions that may teach, warn, or outlast the minds that made them.
Watch my exclusive video The End of Science https://nebula.tv/videos/isaacarthur–… Nebula using my link for 40% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur Get a Lifetime Membership to Nebula for only $300: https://go.nebula.tv/lifetime?ref=isa… Use the link gift.nebula.tv/isaacarthur to give a year of Nebula to a friend for just $30. Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a… Facebook Group:
/ 1,583,992,725,237,264 Reddit:
/ isaacarthur Twitter:
/ isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content. SFIA Discord Server:
/ discord Credits: Galactic Beacons Episode 440b; April 1, 2024 Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur Graphics: Darth Biomech, Jeremy Jozwik, Ken York YD Visual, Sergio Botero Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator.
Get Nebula using my link for 40% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Get a Lifetime Membership to Nebula for only $300: https://go.nebula.tv/lifetime?ref=isa…
Use the link gift.nebula.tv/isaacarthur to give a year of Nebula to a friend for just $30.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Credits:
Galactic Beacons.
Episode 440b; April 1, 2024
Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur.
Graphics: Darth Biomech, Jeremy Jozwik, Ken York YD Visual, Sergio Botero.
Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images.
Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator
In the previous excerpt from my conversation with Stephen Wolfram, I asked him how I can remain a single, coherent, persistent consciousness in a branching universe.
In this excerpt, we went deeper into this question. As a conscious observer, I have a single thread of experience. So if the universe branches into many timelines, why don’t I branch into many versions of me?
Stephen’s answer touched on many profound aspects of the Wolfram model.
He started with the failure of the Many Worlds interpretation of quantum mechanics to consider the possibility that different branches of history can merge, in other words, come back together again. This failure is rooted in assumption that the universe is continuous; as soon as we start thinking of the universe as discrete, such merging seems not only possible, but inevitable.
He went on to consider the concept of causal invariance, the idea that it doesn’t matter which of countless similar paths you take through the multiway graph, you end up in the same place. In the Ruliad, he said, causal invariance is inevitable.
Then we got to the core of the concept of the observer. According to Stephen Wolfram, an observer equivalences many different states and experiences the aggregate of these states.
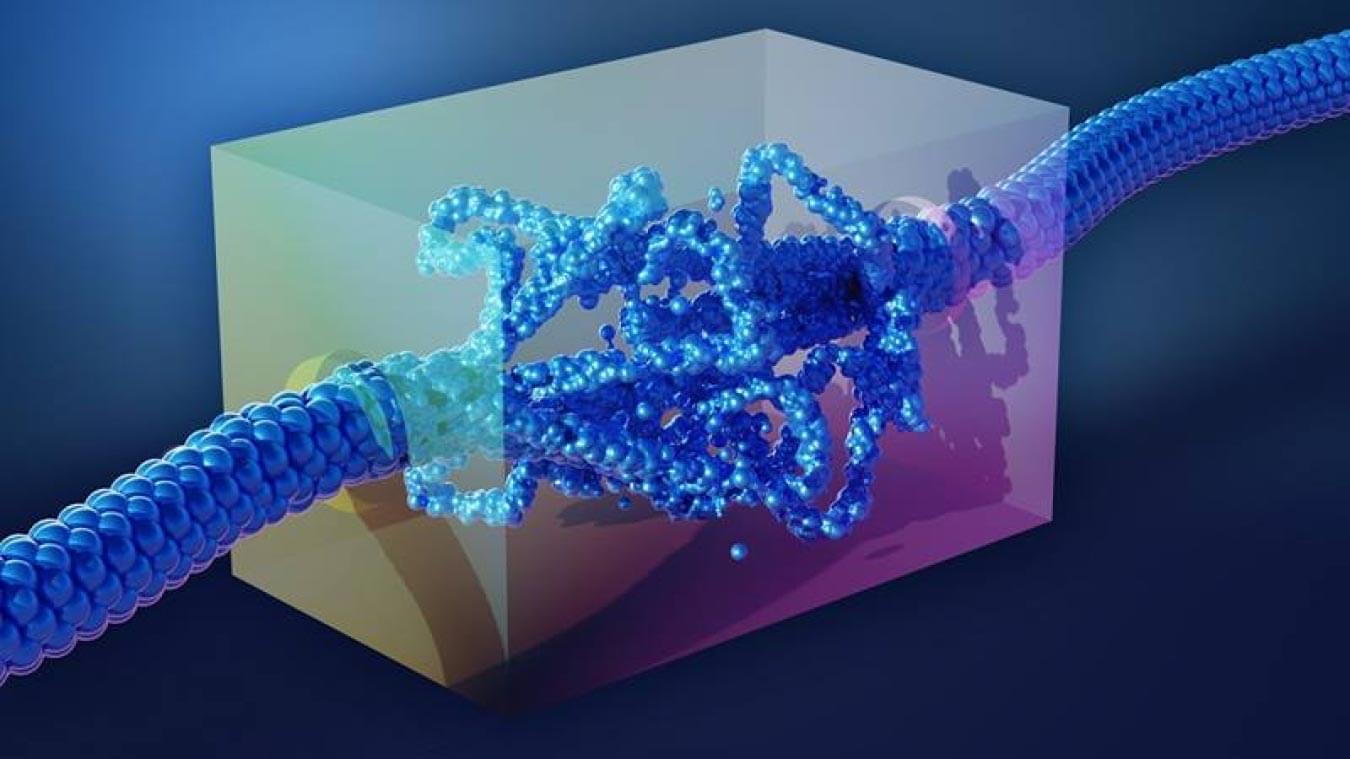

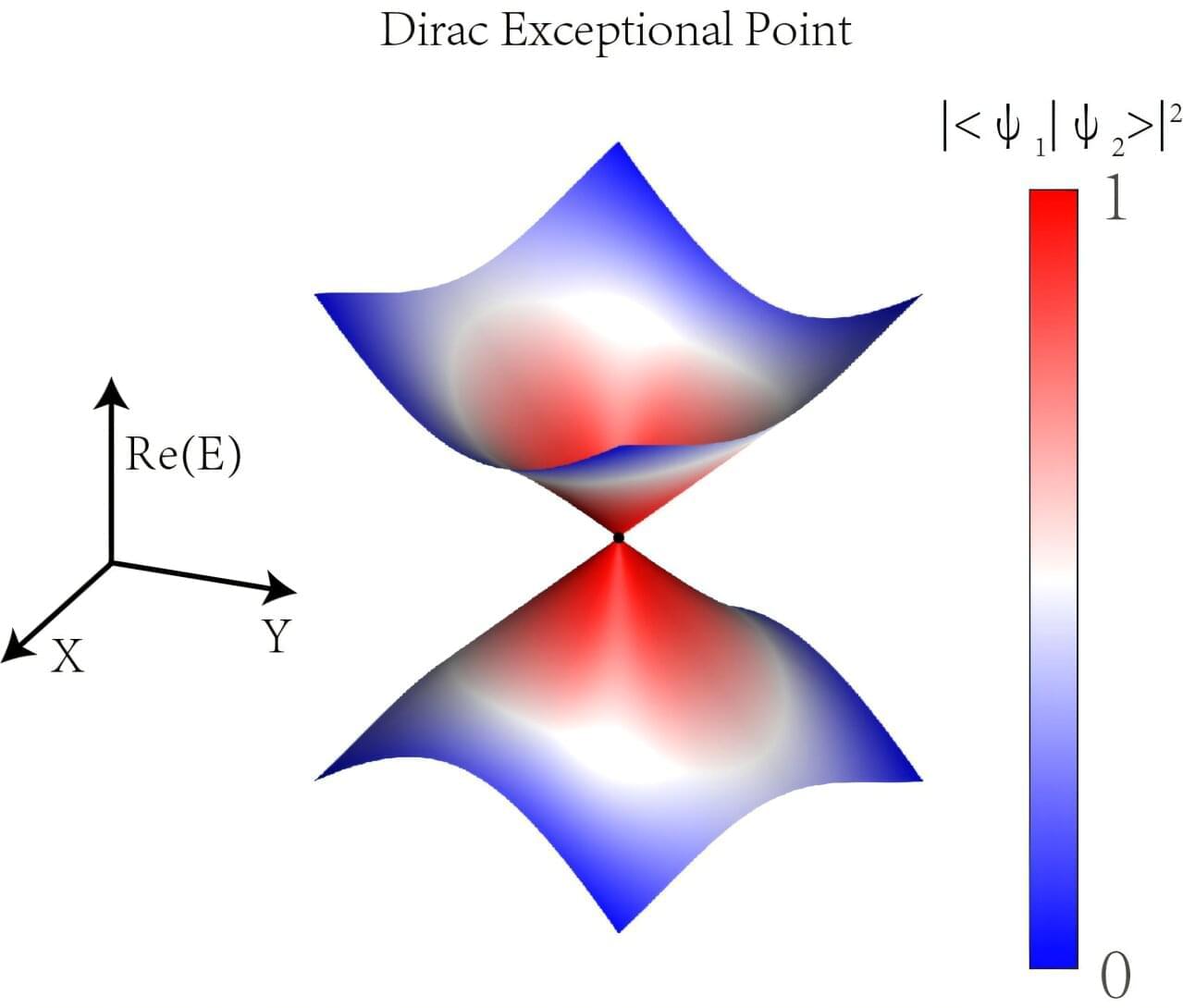
Exceptional points (EPs) are unique types of energy-level degeneracies that occur in non-Hermitian systems. Since their existence was first proposed more than a century ago, physicists have only been able to experimentally observe two types of EPs, both of which were found to give rise to exotic phases of matter in various materials, including Dirac and Weyl semimetals.
Building on recent theoretical studies, researchers at the University of Science and Technology of China recently set out to experimentally observe a new class of EPs, known as Dirac EPs. Their paper, published in Physical Review Letters, could open new exciting possibilities for the study of non-Hermitian dynamics and for the development of protocols to reliably control quantum systems.
“Our inspiration stemmed from a prior theoretical study that proposed a type of exceptional point (EP) termed Dirac EPs,” Xing Rong, senior author of the paper, told Phys.org. “We realized that this novel type of EP is distinct from all experimentally observed EPs over the past half-century. Our work aimed to transform this theoretical prediction into experimental reality.”