Artificial intelligence will have a significant and lasting impact on the ways we live and work.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are predicted to be part of the next industrial revolution and could help business and industry save billions of dollars by the next decade.
The tech giants Google, Facebook, Apple, IBM and others are applying artificial intelligence to all sorts of data.
Machine learning methods are being used in areas such as translating language almost in real time, and even to identify images of cats on the internet.
Some of the biggest names in the business are teaming up to secure the future of virtual reality.
Google, Sony, Oculus, Samsung, Acer and HTC have combined their efforts in order to create a healthy and equal industry for virtual reality hardware and software to develop and expand. The result is the Global Virtual Reality Association, a nonprofit organization dedicated to promoting the growth of the virtual reality industry by providing educational resources, connecting developers with necessary resources and much more.
“The organization will foster dialogue between public and private stakeholders in VR around the world and make education and training material available to the public. Working groups will be organized around important topics for the industry, enabling us to produce relevant research and guidance. We will also host and participate in international discussions on important topics in VR to shape the public discussion on the technology. Ultimately, the group will develop best practices and share them openly.”
Wild.
The expression “once bitten, twice shy” is an illustration of how a bad experience can induce fear and caution. How to effectively reduce the memory of aversive events is a fundamental question in neuroscience. Scientists in China are reporting that by transplanting mouse embryonic interneurons into the brains of mice and combining that procedure with training to lessen fear, they can help to reduce the fear response. The study is being published December 8 in Neuron.
“Anxiety and fear-related disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder [PTSD] cause great suffering and impose high costs to society,” says Yong-Chun Yu, a professor at the Institutes of Brain Science at Fudan University in Shanghai and the study’s senior author. “Pharmacological and behavioral treatments of PTSD can reduce symptoms, but many people tend to relapse. There’s a pressing need for new strategies to treat these refractory cases.”
In the study, the researchers used traditional conditioning to instill fear in the mice. They exposed them to a sound as a neutral stimulus, followed by a mild shock to the foot. To determine the level of fear, they measured the amount of time the mice exhibited freezing behavior–the natural sympathetic fear response in prey animals that is indicated by crouching. They then conducted fear extinction training, in which the mice were exposed to the sound but not the shock. After a few rounds, the freezing response times were significantly reduced.
Those “sell by” or “best by” dates that you see on food packaging? They’re so last century. In the future, built-in sensors in food labels will not only tell you when a product is going bad but also if you’re storing it correctly. Some might even be able to give you a breakdown of its nutritional data. All this is thanks to developments in the burgeoning world of printable electronics. Now researchers at MIT have invented a printing process that could turn a lot of the potential breakthroughs, such as electricity-generating clothing and smart sutures we’ve been seeing in this space, into an inexpensive reality.
“There is a huge need for printing of electronic devices that are extremely inexpensive but provide simple computations and interactive functions,” says A. John Hart, an associate professor in contemporary technology and mechanical engineering.
While some researchers have been studying the possibility of using inkjet printing and rubber stamping, these techniques have produced mixed results at best, often resulting in fuzzy, coffee-ring patterns or incomplete circuits due to the difficulty of controlling ink flow at such small scales.
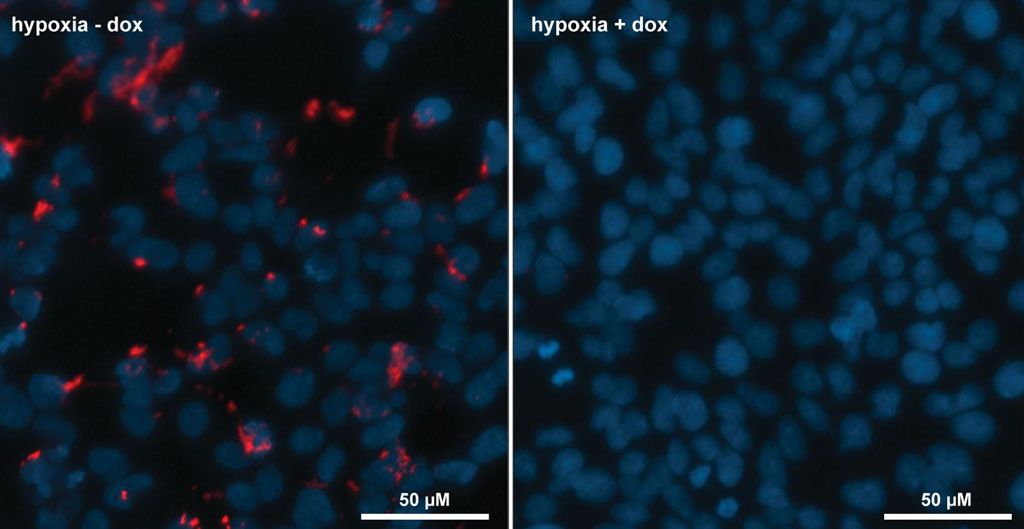
Gene therapy techniques were used to insert a peptide into cultures of human cancer cells that blocked their ability to use the enzyme Hypoxia-inducible factor-1, a heterodimeric transcription factor that enables cell survival under low oxygen conditions by altering the transcription of over 300 genes.
Hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) is a heterodimeric transcription factor that acts as the master regulator of cellular response to reduced oxygen levels, thus playing a key role in the adaptation, survival, and progression of tumors. There is significant evidence that inhibition of HIF-1 would be beneficial for cancer therapy, since tumor cells must thrive in a microenvironment characterized by lack of oxygen. In previous work, investigators at the University of Southampton (United Kingdom) discovered a cyclic hexapeptide (cyclo-CLLFVY) that inhibited the HIF-1alpha/HIF-1beta protein–protein interaction in vitro and prevented HIF-1-mediated hypoxia-response signaling in cells. This cyclic peptide was identified by screening a library that contained more than 3.2 million compounds.
With a view to demonstrating the potential for encoding the production of a therapeutic agent in response to a disease marker, the investigators engineered human cells with an additional chromosomal control circuit that conditionally encoded the production of the cyclic peptide HIF-1 inhibitor. They then demonstrated the conditional production of the HIF-1 inhibitor in response to hypoxia, and its inhibitory effect on HIF-1 dimerization and downstream hypoxia-response signaling.
Counting Cells
Posted in biological, computing
Scientists from MIT and Boston University have developed biological cells that can count and ‘remember’ cellular events by creating simple circuits through a series of genes that are activated in a precise order. These circuits, which the scientists say simulate computer chips, could be employed to tally the number of times a cell divides or to track a cycle of developmental stages. Such counting cells could also be used as biosensors to count the number of toxin exposures present in an environment.
Synthetic Biology Diabetes mellitus affects hundreds of millions of people worldwide. Blood glucose levels are chronically deregulated in diabetics, and this can lead to many serious disorders, including cardiovascular disease and renal failure. Xie et al. engineered a synthetic circuit into human.