For better and worse, toys powered by AI are becoming an intimate part of kids’ lives.




In years to come, quantum computers and quantum networks might be able to tackle tasks that are inaccessible to traditional computer systems. For instance, they could be used to simulate complex matter or enable fundamentally secure communications.
The elementary building blocks of quantum information systems are known as qubits. For quantum technology to become a tangible reality, researchers will need to identify strategies to control many qubits with very high precision rates.
Spins of individual particles in solids, such as electrons and nuclei have recently shown great promise for the development of quantum networks. While some researchers were able to demonstrate an elementary control of these qubits, so far, no one has reported entangled quantum states containing more than three spins.
Researchers at the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology (Skoltech) in Russia have recently introduced a new strategy to enhance interactions between humans and robotic swarms, called SwarmTouch. This strategy, presented in a paper pre-published on arXiv, allows a human operator to communicate with a swarm of nano-quadrotor drones and guide their formation, while receiving tactile feedback in the form of vibrations.
“We are working in the field of swarm of drones and my previous research in the field of haptics was very helpful in introducing a new frontier of tactile human-swarm interactions,” Dzmitry Tsetserukou, Professor at Skoltech and head of Intelligent Space Robotics laboratory, told TechXplore. “During our experiments with the swarm, however, we understood that current interfaces are too unfriendly and difficult to operate.”
While conducting research investigating strategies for human-swarm interaction, Tsetserukou and his colleagues realised that there are currently no available interfaces that allow human operators to easily deploy a swarm of robots and control its movements in real time. At the moment, most swarms simply follow predefined trajectories, which have been set out by researchers before the robots start operating.
The cryptocurrency Bitcoin is limited by its astronomical electricity consumption and outsized carbon footprint. A nearly zero-energy alternative sounds too good to be true, but as School of Computer and Communication Sciences (IC) Professor Rachid Guerraoui explains, it all comes down to our understanding of what makes transactions secure.
To explain why the system developed in his Distributed Computing Lab (DCL) represents a paradigm shift in how we think about cryptocurrencies—and about digital trust in general—Professor Rachid Guerraoui uses a legal metaphor: all players in this new system are “innocent until proven guilty.”
This is in contrast to the traditional Bitcoin model first described in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto, which relies on solving a difficult problem called “consensus” to guarantee the security of transactions. In this model, everyone in a distributed system must agree on the validity of all transactions to prevent malicious players from cheating—for example, by spending the same digital tokens twice (double-spending). In order to prove their honesty and achieve consensus, players must execute complex—and energy-intensive—computing tasks that are then verified by the other players.
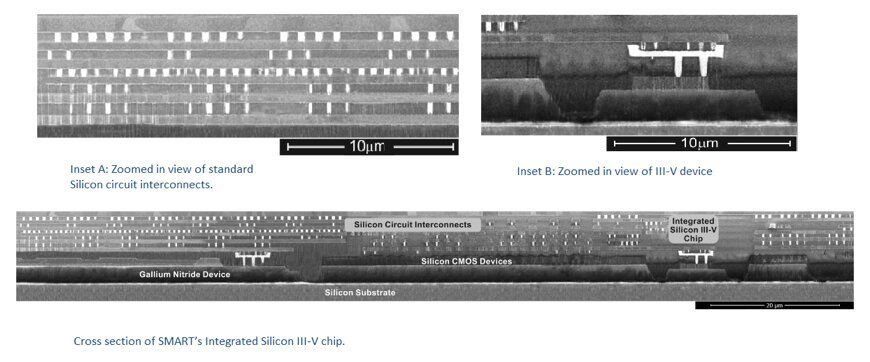
The Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART), MIT’s Research Enterprise in Singapore, has announced the successful development of a commercially viable way to manufacture integrated Silicon III-V Chips with high-performance III-V devices inserted into their design.
In most devices today, silicon-based CMOS chips are used for computing, but they are not efficient for illumination and communications, resulting in low efficiency and heat generation. This is why current 5G mobile devices on the market get very hot upon use and would shut down after a short time.
This is where III-V semiconductors are valuable. III-V chips are made from elements in the 3rd and 5th columns of the elemental periodic table such as Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Indium Gallium Arsenide (InGaAs). Due to their unique properties, they are exceptionally well suited for optoelectronics (LEDs) and communications (5G etc) — boosting efficiency substantially.


Time, as far as we know, moves only in one direction. But last year, researchers found events in some gamma-ray burst pulses that seemed to repeat themselves as though they were going backwards in time.
Now, new research suggests a potential answer for what might be causing this time reversibility effect. If waves within the relativistic jets that produce gamma-ray bursts travel faster than light — at ‘superluminal’ speeds — one of the effects could be time reversibility.
Such speeding waves could actually be possible. We know that when light is travelling through a medium (such as gas or plasma), its phase velocity is slightly slower than c — the speed of light in a vacuum, and, as far as we know, the ultimate speed limit of the Universe.
At our 2019 Ending Age-related Diseases conference in New York City, we had the pleasure of speaking with Dr. Michael West, the CEO of AgeX Therapeutics.
Dr. West can rightfully be called a pioneer in his field with a substantial background in biomedical and biotechnology corporations. After completing his PhD at Baylor College of Medicine, he founded Geron Corporation in 1990, where he launched and directed programs in telomere biology as it relates to cancer, aging, and human embryonic stem cell technology. He subsequently established the research group that went on to isolate human embryonic stem cells for the first time.
After his time at Geron, Dr. West was chairman and CEO of Advanced Cell Technology, which was acquired by the Japanese company Astellas Pharma in 2016 for $379 Million. Following his success with Advanced Cell Technology and Geron, Dr. West served as the CEO/co-CEO of BioTime Inc. for ten years.