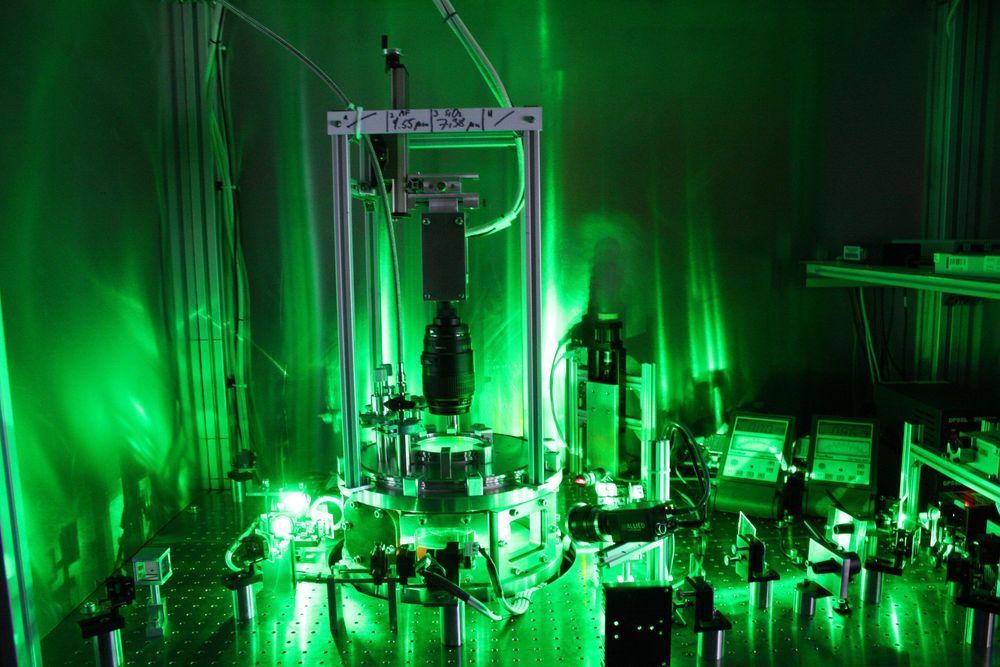
Since the end of the 19th century, physicists have known that the transfer of energy from one body to another is associated with entropy. It quickly became clear that this quantity is of fundamental importance, and so began its triumphant rise as a useful theoretical quantity in physics, chemistry and engineering. However, it is often very difficult to measure. Professor Dietmar Block and Frank Wieben of Kiel University (CAU) have now succeeded in measuring entropy in complex plasmas, as they reported recently in the renowned scientific journal Physical Review Letters. In a system of charged microparticles within this ionized gas, the researchers were able to measure all positions and velocities of the particles simultaneously. In this way, they were able to determine the entropy, as it was already described theoretically by the physicist Ludwig Boltzmann around 1880.
Surprising thermodynamic equilibrium in plasma
“With our experiments, we were able to prove that in the important model system of complex plasma, the thermodynamic fundamentals are fulfilled. What is surprising is that this applies to microparticles in a plasma, which is far away from thermodynamic equilibrium,” explains Ph.D. student Frank Wieben. In his experiments, he is able to adjust the thermal motion of the microparticles by means of a laser beam. Using video microscopy, he can observe the dynamic behaviour of the particles in real time, and determine the entropy from the information collected.