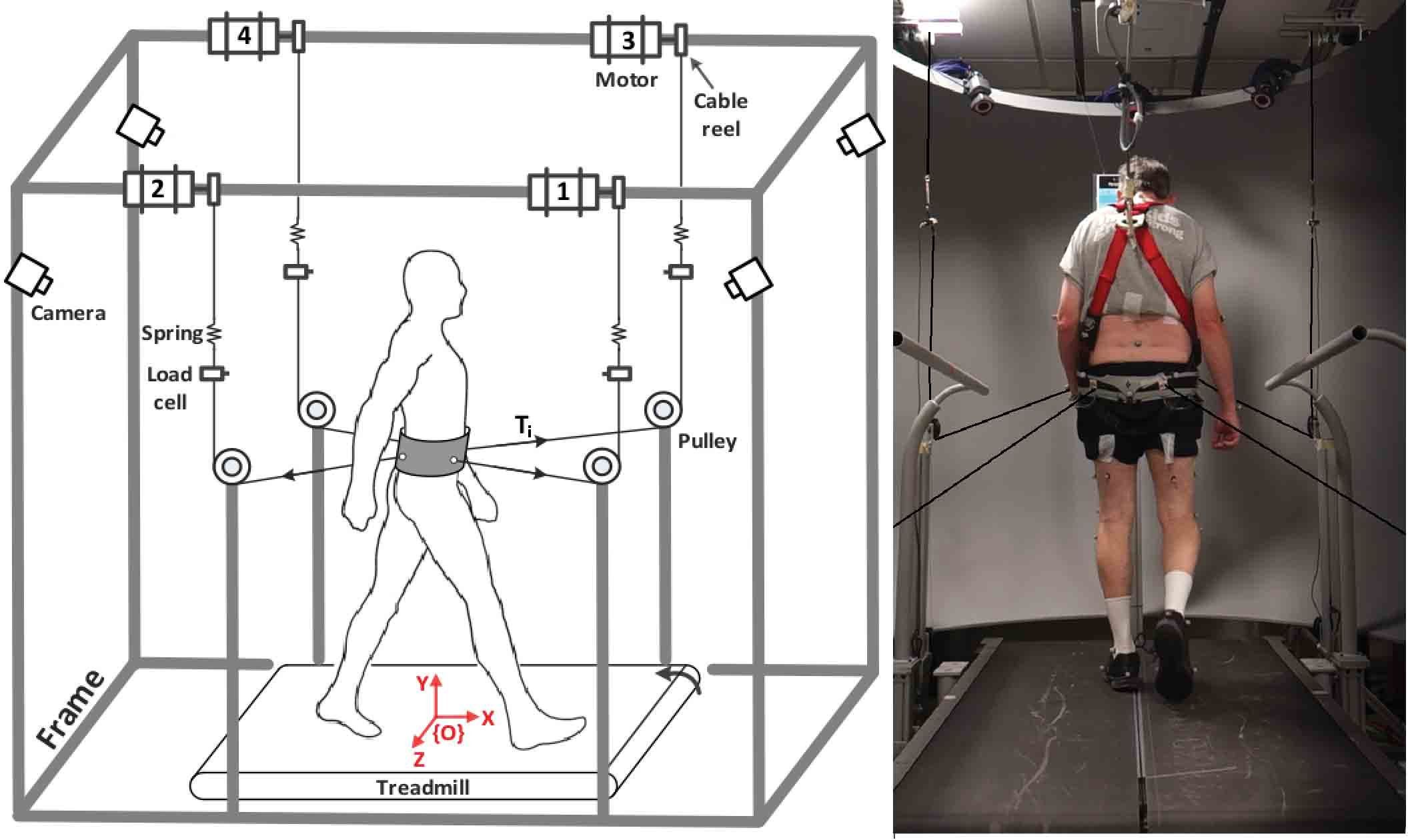
Some 50,000 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease (PD) every year. The American Institute of Neurology estimates there are one million people affected with this neurodegenerative disorder, with 60 years as average age of onset. Falls and fall-related injuries are a major issue for people with Parkinson’s?up to 70 percent of advanced PD patients fall at least once a year and two-thirds suffer recurring falls. These fall rates are twice as high as those of adults of comparable age, so improving balance in patients with Parkinson’s would provide a major health advantage.
Sunil Agrawal, professor of mechanical engineering and of rehabilitation and regenerative medicine at Columbia Engineering, along with Dario Martelli, a post-doctoral researcher in his group, have been working on this issue with Movement Disorders faculty from the department of neurology at Columbia University Medical Center?Stanley Fahn, a leading expert in Parkinson’s, and Un Jung Kang, division director, and Movement Disorder Fellow Lan Luo. In their latest study, published today in Scientific Reports, the team looked at whether or not Parkinson’s disease affects patients’ balance and diminishes their ability to react and adapt to walking with perturbations. The researchers found that the ability to adapt to multiple perturbations or to modify responses to changing amplitudes or directions was not affected by PD; both the Parkinson’s and the healthy subjects controlled their reactive strategies in the same way.