Two other international teams are planning Mars launches in July. NASA plans to deploy a rover named Perseverance, and the United Arab Emirates will send a probe called Hope. The European and Russian space agencies were planning to send a probe to Mars this year, but announced on Thursday that the launch will be delayed by two years so they can finish important tests, and partly because of the coronavirus pandemic.
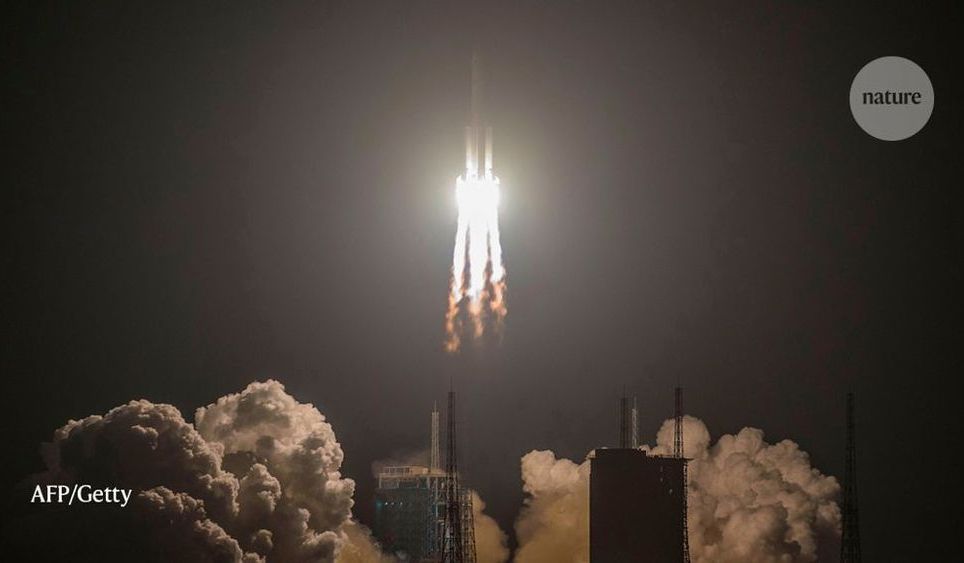
China’s first journey to Mars is one of the most anticipated space missions of the year. But with parts of the country in some form of lockdown because of the coronavirus, the mission teams have had to find creative ways to continue their work.
Researchers involved in the mission remain tight-lipped about its key aspects, but several reports from Chinese state media say that the outbreak will not affect the July launch — the only window for another two years.
“The launch is so important politically that they will make it happen,” says Raymond Arvidson, a planetary geologist at Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri, who has been involved with several US Mars missions.