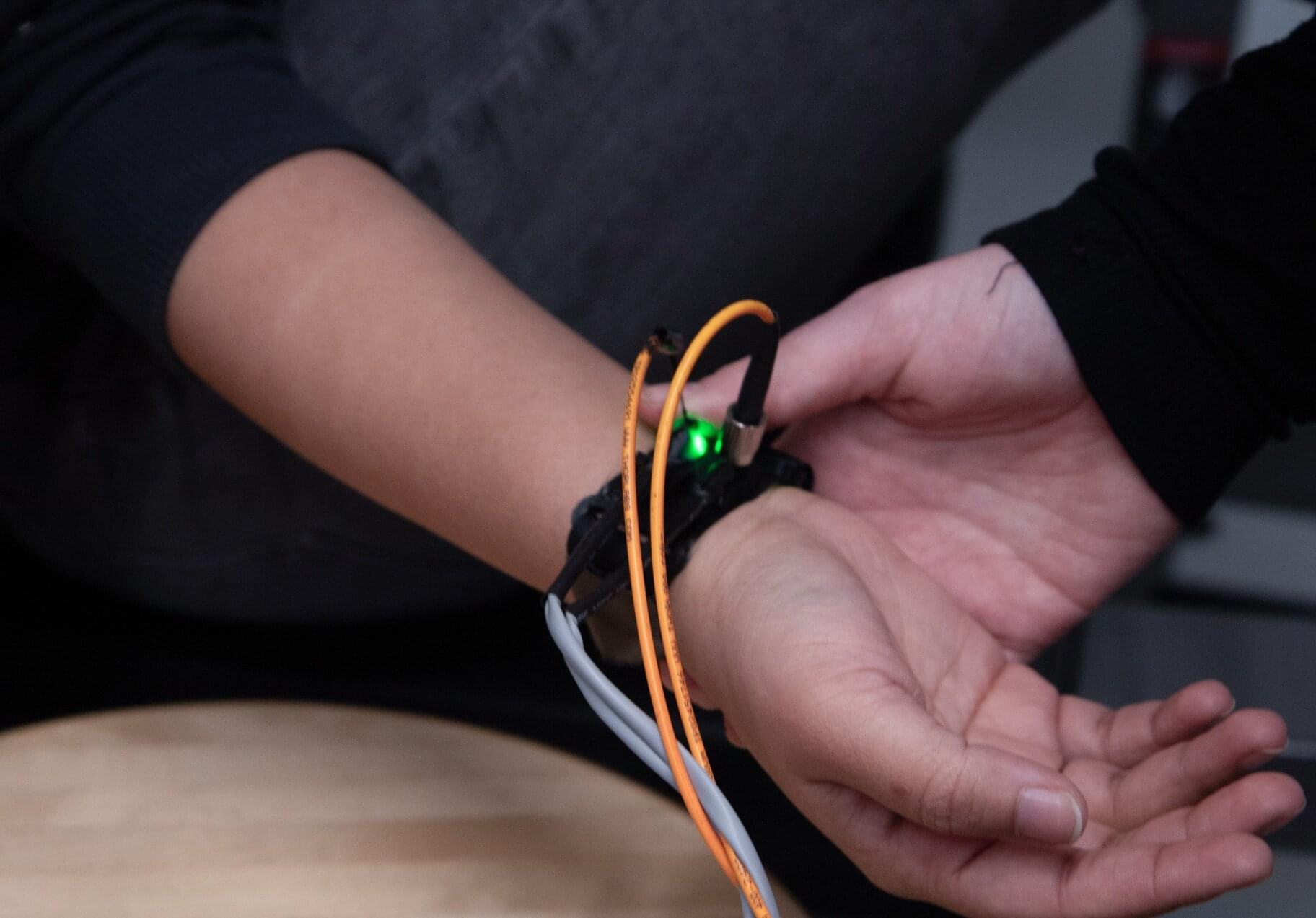
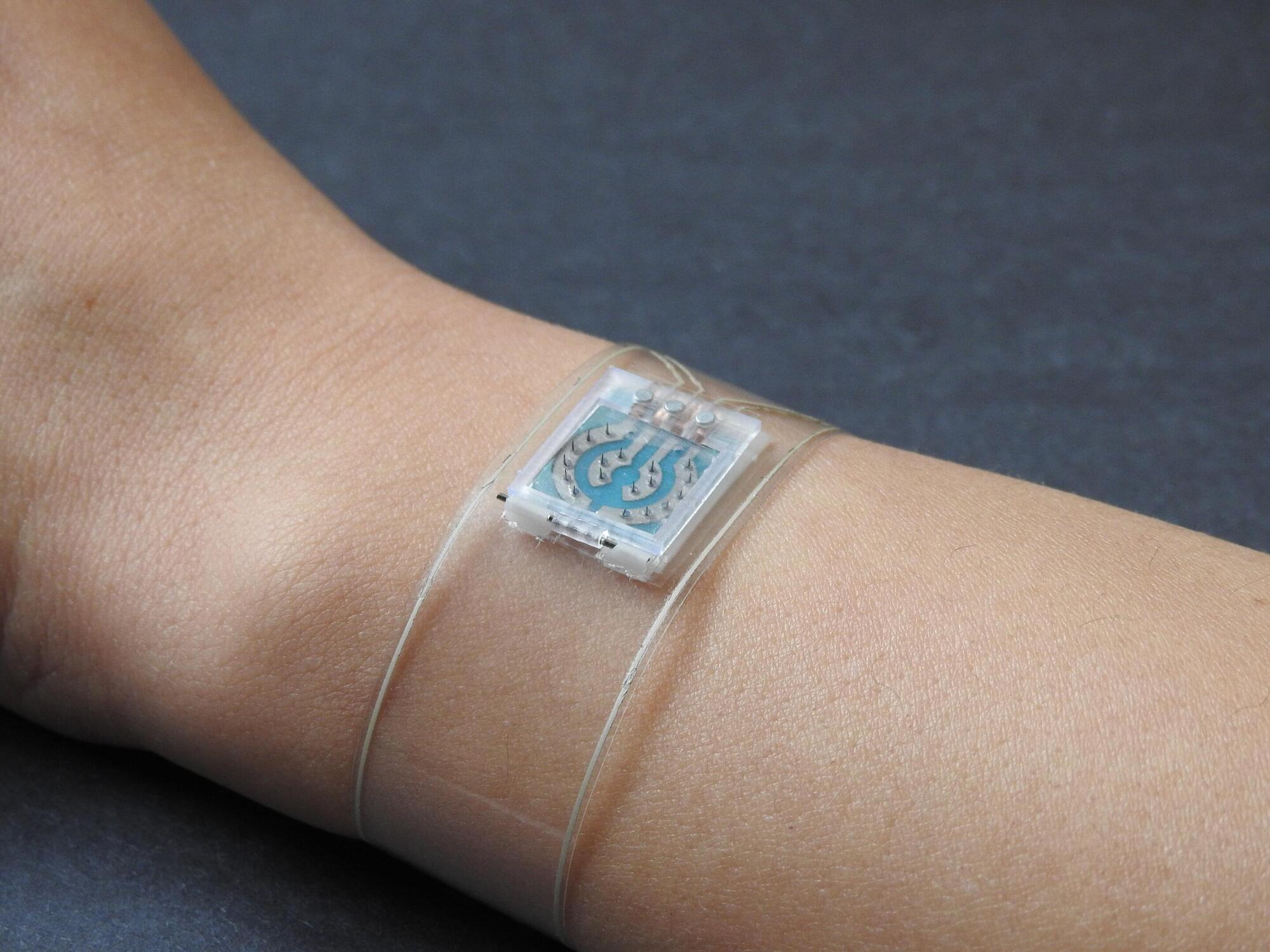
A new wearable wristband could significantly improve diabetes management by continuously tracking not only glucose but also other chemical and cardiovascular signals that influence disease progression and overall health. The technology was published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
The flexible wristband consists of a microneedle array that painlessly samples interstitial fluid under the skin to measure glucose, lactate and alcohol in real time using three different enzymes embedded within the tiny needles. Designed for easy replacement, the microneedle array can be swapped out to tailor wear periods. This reduces the risk of allergic reactions or infection while supporting longer-term use.
Simultaneously, the wristband uses an ultrasonic sensor array to measure blood pressure and arterial stiffness, while ECG sensors measure heart rate directly from wrist pulses. These physiological signals are key indicators of cardiovascular risk, which is often elevated in people with diabetes but is rarely monitored continuously outside of a clinical setting.