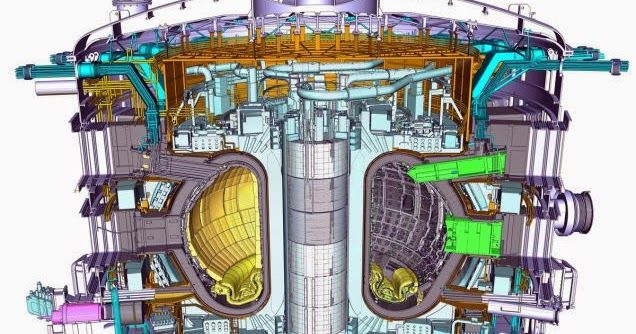
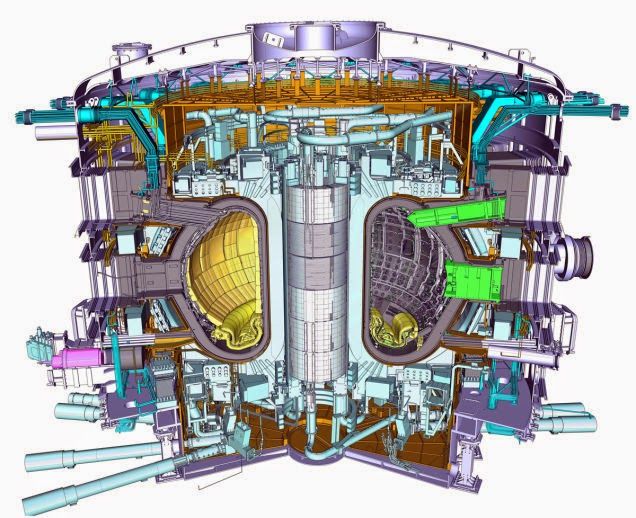
This is an invention that might possibly modify the civilization as we know it: A compact fusion reactor presented by Skunk Works, the stealth experimental technology section of Lockheed Martin. It’s about the size of a jet engine and it can power airplanes, most likely spaceships, and cities. Skunk Works state that it will be operational in 10 years.
Aviation Week had complete access to their stealthy workshops and spoke to Dr. Thomas McGuire, the leader of Skunk Work’s Revolutionary Technology section. And ground-breaking it is, certainly: Instead of utilizing the similar strategy that everyone else is using— the Soviet-derived tokamak, a torus in which magnetic fields limit the fusion reaction with an enormous energy cost and thus tiny energy production abilities—Skunk Works’ Compact Fusion Reactor has a fundamentally different methodology to anything people have tried before. Here are the two of those techniques for contrast: