“Why would anybody place the front end of a Nissan Skyline GT-R on a Tesla Model 3, even as a rendering?” one might rightfully ask. We’ll, let’s try to answer that.
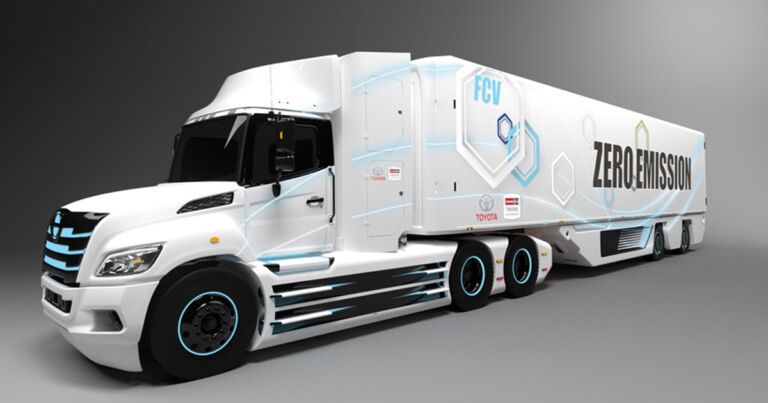



The Japanese carmaker’s North America division will be partnering with Hino USA, a commercial vehicles manufacturer, to produce the “heavy” Class 8 fuel cell truck specifically for the North American market.
The truck itself will be based on the existing Hino XL Series chassis and powered by Toyota’s fuel cell technology.
Toyota is planning to show off the first demonstration vehicle in the first half of 2021, but we still know little about it. The prototype of a prior initiative called Project Portal 2.0 may provide some clues: revealed in 2018, the prototype was a 670 horsepower semi with 1,325 pound-feet of torque and a towing capacity of 80,000 pounds. Its fuel cells gave it a reported range of 300 miles, CNET reports.
Mercedes-Benz teased two new electric vehicle variants, the EQS and EQE, which will both come in sedan and SUV models. The automaker plans to release six new electric vehicles over the next two years.

Tesla apparently has a new strategy for dealing with journalists: Don’t deal with them at all.
The electric car giant has dissolved its global public relations team, leaving the press with no formal point of contact at the world’s most valuable automaker, a new report says.
Essentially every staffer who used to work in Tesla’s PR office has either moved to a different position at the company or left altogether, according to electric vehicle industry blog Electrek, which said the move to disband the department was confirmed “at the highest level at Tesla.”
The next decade is going to be a transforming decade as many many technologies (some of which we all like to share in this group) are converging and maturing enough to rearrange our society in almost any aspect we can conceive.
I’m calling to those who are interested in creating and implementing an alternative model for the current social and governance systems, let’s build an open state that we can all support and trust regardless of our age, sex, geographical location, or belief system.
In the next 10 years, key technologies will converge to completely disrupt the five foundational sectors—information, energy, food, transportation, and materials—that underpin our global economy. We need to make sure the disruption benefits everyone.

Tesla CEO Elon Musk in July urged miners to produce more nickel, a key ingredient in the batteries that power the company’s electric cars. Musk offered a “giant contract” if supplies could be produced in an environmentally sensitive way.
While EVs are expected to help reduce global carbon emission, environmentalists are concerned that production of EV parts and increased mining may damage the environment.
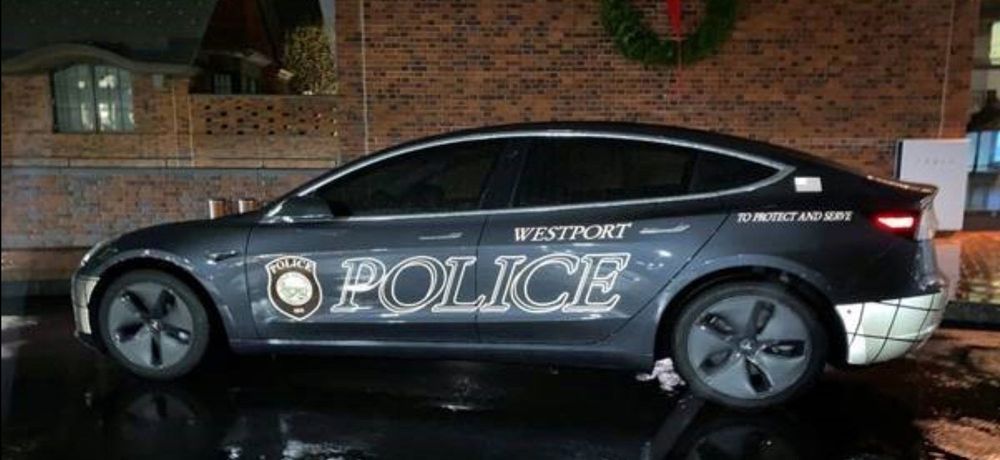

Tesla Model 3 is crushing Dodge Charger as a police car when it comes to the cost of ownership as the Bargersville Police Chief who pushed to electrify his fleet shares a 1-year review of the cost of operation.
Last year, we reported on the Bargersville, Indiana, police department updating their fleet with Tesla Model 3 vehicles.
Bargersville Police Chief Todd Bertram commented at the time:
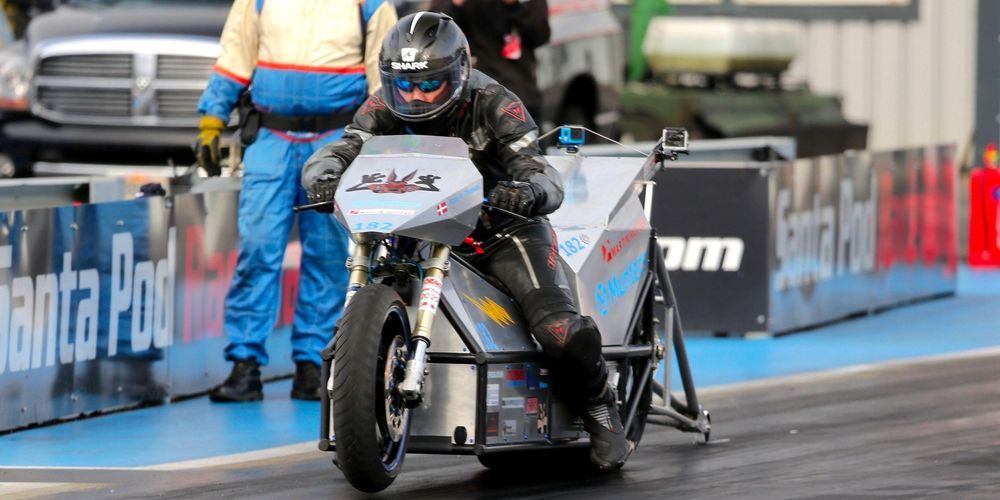

When Danish racing team True Cousins got started with electric motorcycle racing, their first attempt was rather modest. But twelve years after fielding their first custom 12 kW electric motorcycle, the team returned to set a new world record with a new bike featuring 100x the power.
The Silver Lightning is a custom built electric drag racing motorcycle featuring up to 1,200 kW of power.
Last week it laid rubber down on the strip at the Santa Pod Raceway in Bedfordshire, England during the event dubbed “NOT the Euro Finals”.
No daily driver needs a car with crazy acceleration or incredible top speed. However, torque and agility can definitely come in handy at times.

On a blustery winter day last December, a car carrying radioactive material approached one of the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey’s major transportation hubs. As the car got closer, an alarm flashed and sounded on a large monitor in the police operations center, identifying on a digital map the exact location of the vehicle and the specific radioactive isotope radiating from the car – Cesium-137. Within minutes, officers in the Port Authority Police Department – equipped with vehicle-mounted and pocket-sized radiation sensors displaying the same real-time digital map – tracked the vehicle and apprehended the suspects in a parking lot. Thankfully, the potential terrorists and radiation-emitting isotope were not a threat, as the scenario was only a drill.
The December exercise marked the capstone for DARPA’s SIGMA program, culminating a five-year effort to develop and deploy an automated, high-performance, networked radiation detection capability for counterterrorism and continuous city-to-region scale radiological and nuclear threat monitoring. The transition of the radiation-detection system took place prior to the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. In the eight months since the SIGMA transition, DARPA has been developing and testing additional sensors under its SIGMA+ effort to detect chemical, biological and explosive threats as well.
“We want to thank the Port Authority for their outstanding support throughout the SIGMA program and their continued support as we test SIGMA+ sensors,” said Mark Wrobel, DARPA program manager in the Defense Sciences Office. “Being able to test and refine the system in the country’s largest metropolitan region was invaluable in taking SIGMA from a research project to an operationally deployed system in just five years.”