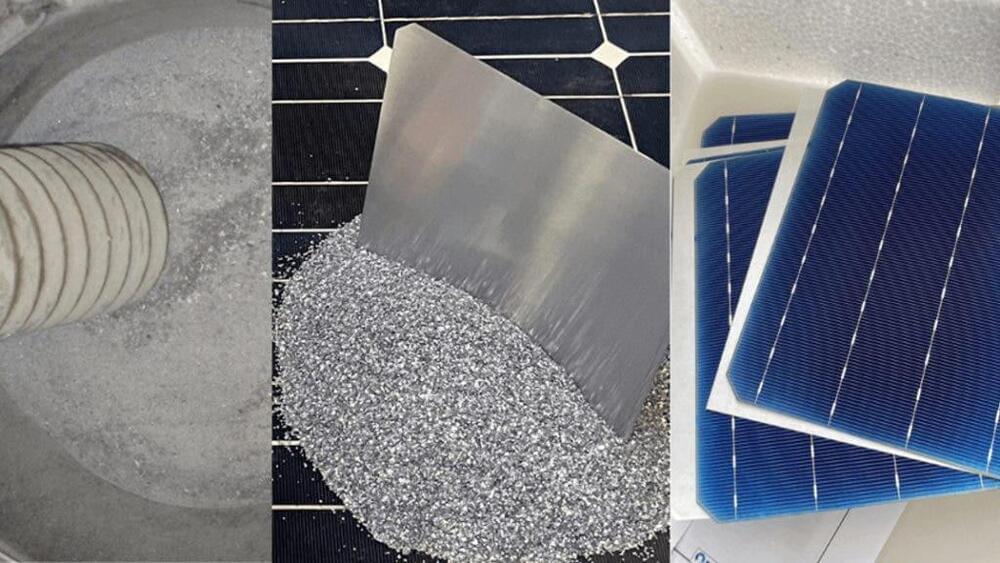
Fraunhofer ISE has developed a process for recycling the silicon in old solar panels.
The big knock on new technology like electric cars and solar panels is that they are not recyclable. People haven’t cared a flying fig leaf about recycling stuff for the past 100 years. If they did, citizens would be at the gates of the corporate headquarters of Nestlé, Coca Cola, and Pepsi with flaming torches and pitchforks demanding they stop inundating the Earth with their endless profusion of waste products.
But suddenly, people are all atwitter about what will happen to the batteries of electric cars. Fearmongers on the internet are telling people they will have to drive their old electric cars into lakes and rivers when they stop working. The amazing thing is, people believe that codswallop and repeat it to their friends as if it were carved on the stone tablets Moses brought down with him when he descended the mountain. So much for public education making people smarter.
Another cry you hear from the anti-technology crowd is that millions of old solar panels will be dumped into landfills to fester for centuries. Horse-puckey! Do we need a way to recycle solar panels? Yes, we do. And are responsible adults working on such systems as we speak? Yes, they are. Calm down, people. Everything you read on Twitter or Facebook is not gospel. And let’s not get started on the deliberate misinformation spewed by the talking heads on Faux News 24 hours a day.