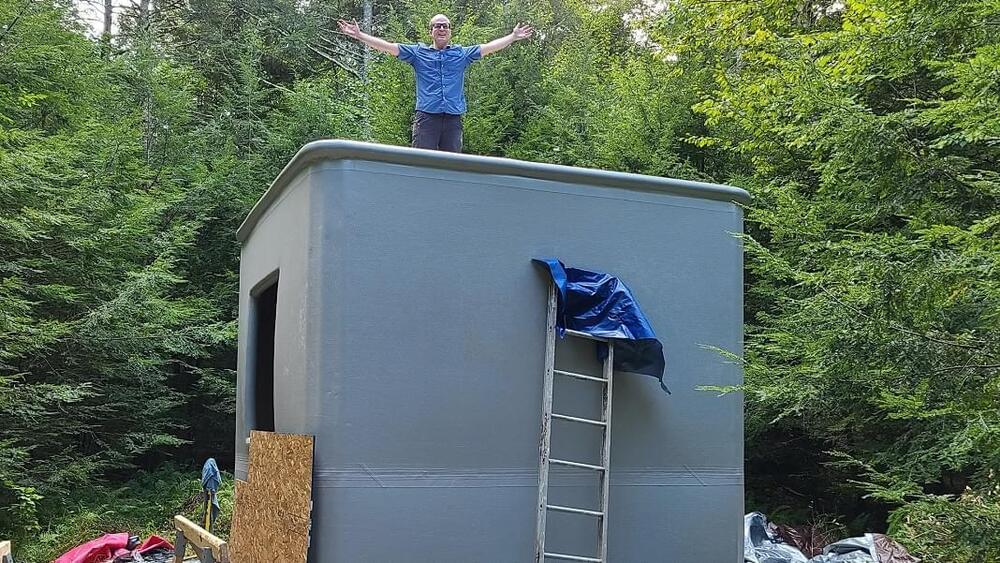
The form gets rolled out on a concrete slab or other foundation, then inflated with an air pump; at this point, it may look a little like one of those bouncy houses you see at children’s parties. Then a ready mix truck shows up—these trucks can mix concrete on their way to a site or at the site itself—and pumps concrete into the form. The company’s website says they can use local ready mix concrete, aircrete (a lightweight version of concrete that incorporates air bubbles instead of traditional aggregate), sustainable cement, and other “pumpable building materials.”
The concrete-pumping step is a bit like 3D printing, though 3D printed homes use concrete as printer “ink” to put walls down layer by layer rather than spitting all the concrete into a form at once. This is even faster; Bell told New Atlas, “For our 100-square-foot and 200-square-foot prototypes, the inflation took 7 to 10 minutes with air. Then the concrete pump filled them in 1.5 hours.”
Once the concrete has dried, the form isn’t stripped away; it stays right where it is, serving as an airtight barrier for waterproofing and insulation. The final step is to add all the things that make a house look and function like a house rather than a giant clay art project, that is, a facade, windows, doors, drywall, HVAC, and plumbing.