The truth about Cobalt. The demand for colbalt is on the rise as we transition to electric vehicles is at an all time high.
Taken from JRE #1914 w/Siddharth Kara:
The truth about Cobalt. The demand for colbalt is on the rise as we transition to electric vehicles is at an all time high.
Taken from JRE #1914 w/Siddharth Kara:
Computer, car etc also created lots of new jobs.
A new report from the World Economic Forum projects that machines will handle half of the workplace tasks by 2025.
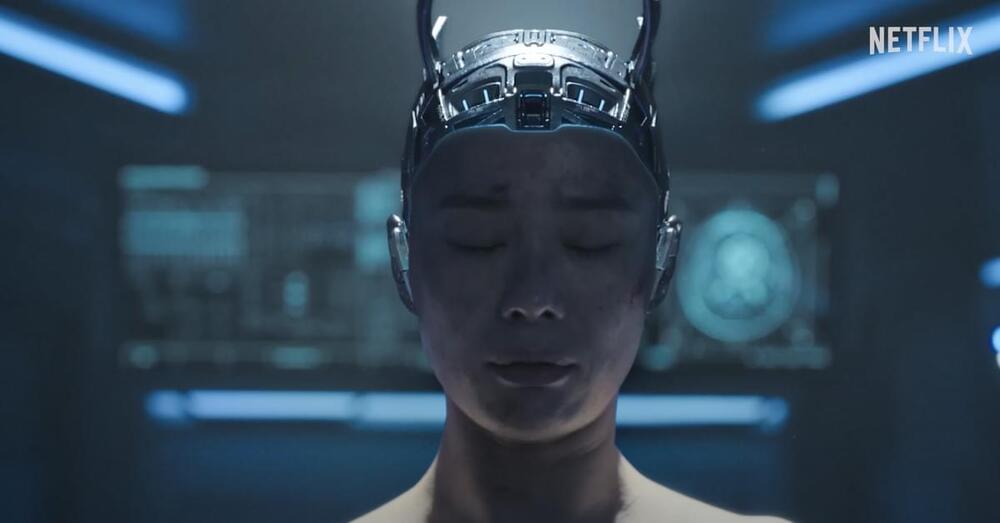


Year 2019 face_with_colon_three
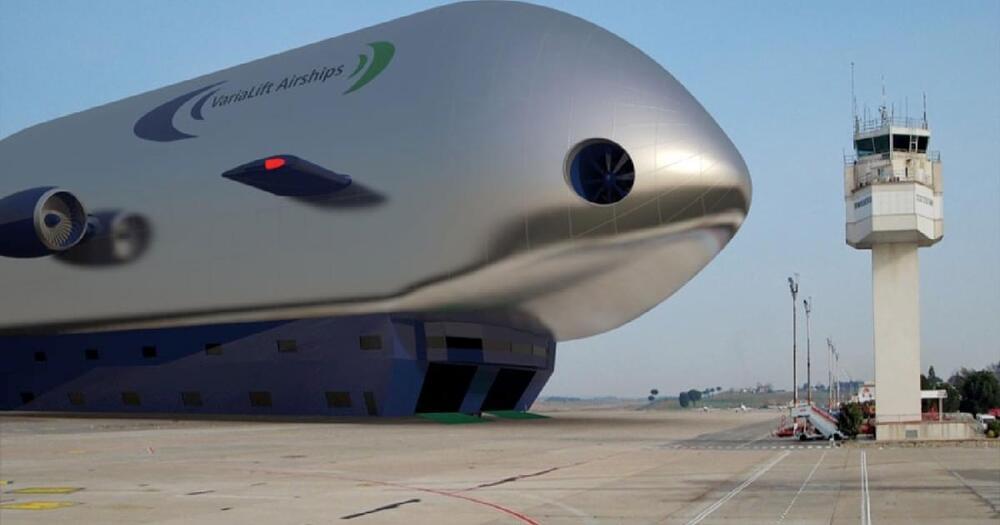
Zeppelins, the rigid airships most famously epitomized by the Hindenburg, now seem kind of retro, rather than the image of futurity they represented in the 1930s. But they could be about to make a comeback in a big way — courtesy of a new aluminum-shelled, solar-powered airship that’s being built by the U.K.-based company Varialift Airships.
According to the company’s CEO Alan Handley, the airship will be capable of making a transatlantic flight from the United Kingdom to the United States, consuming just 8% of the fuel of a regular airplane. It will be powered by a pair of solar-powered engines and two conventional jet engines.
While its lack of onboard battery would limit travel to daylight hours, and its speed will only be approximately half that of a Boeing 747, the Varialift airship does promise to be a useful cargo carrier. Its creators claim that it will be able to carry loads ranging from 50 to 250 tons. Larger models with payloads up to 3,000 tons aren’t out of the question either. Bulky cargo such as electricity pylons, wind turbine blades, and towers, or even prefabricated structures such as oil rigs could be carried underneath using cables. That means that cargo will have a weight limit, but no practical size limit.

Topic:10 incredible concepts of the future technology.
Channel Link ➡➡ #https://youtube.com/
Facebook ➡➡ #https://www.facebook.com/
Tiktok ➡➡ # https://www.tiktok.com/
Instagram ➡➡ # https://www.instagram.com/
Links✅
Virtual Space Tourism Flight.
As artificial intelligence and automation technologies continue to improve, they will become more important in driving the growth of new industries that are based on data.
Artificial intelligence is the development of computer systems that are able to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and problem-solving. AI systems are typically designed to be able to learn from experience, adapt to new inputs, and improve their performance over time.
Automation, on the other hand, refers to the use of technology to automate tasks that were previously performed by humans. This can include everything from simple tasks like data entry to more complex tasks like driving a car or managing a supply chain. Automation can be powered by a variety of technologies, including AI, robotics, and machine learning.
In 2100,the world will be totally different for us.
Many new technologies will appear and change the future of humans. Fastest transportation systems, prettier planes, safer and prettier cities will be the norm in this future. We will live longer too.
Our current technologies are ridiculous in comparison to the technology of the future. This is the World’s Future.
Now, there are many problems that are unsolved. Issues like traffics jams, pollution, or lack of affordable housing make our cities difficult to live. But in the future, all these issues could be solved. So the world in the future can be more beautiful. But if these problems aren’t solved the future can be worse for humans.
So we made a realistic impression of the world in 2100.
This future will be exciting and amazing.
Please enjoy the video and like it!
Don’t forget to subscribe for more video of this kind.
Thanks for watching!
In some ways, the world in 2090 may resemble the world we live in today. Yet, two key areas will almost certainly change: the natural world and technology. Will our thirst for consumption ultimately deplete the world’s most critical natural resources? Or will technology help us persevere? And how will innovation change the way we move, work, and explore? Today, we’ll take a deep dive into these captivating questions.
Sources:
Population.
https://www.un.org/en/sections/issues-depth/population/
The Map of the World in 2090 Suggest We Have a Huge Problem.
https://www.indy100.com/discover/world-map-2090-population-d…ca-7665711
Vacuum Trains: a high-speed pipe dream?
https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20120601-high-speed-pipedreams.
Melting Ice Sheets will Add over 15 inches to Global Sea Level.
Go to https://www.ExpressVPN.com/UniverseInsideYou and find out how you can get 3 months free.
Watch our Nikola Tesla playlist with many interesting videos on Tesla: https://bit.ly/3DNdl65
While there is still much mystery surrounding the life and death of Nikola Tesla, perhaps the most intriguing of mysteries lay in his inventions that never fully saw the light of day. Inventions such as the Death Ray, the Earthquake machine, his flying vehicles, and much more. With the intellect and creative prowess he possessed, we can only begin to imagine the thoughts and ideas he had but never shared.
What we do have, is a small fraction, a record of the incredible inventions that he either discussed, began building, or had actual working prototypes. These were never fully developed or deployed, at least not to the public knowledge, but had the potential to be world-changing… some for better and some for worse… Narration: Petra Ortiz — http://petraortiz.com Scences from History Channel were used under Fair Use. Help my channel here: https://www.patreon.com/universeinsid… here: http://bit.ly/2COJqdM T-Shirts: https://teespring.com/stores/universe… All lost robot-voiced videos can be found here: https://subscribestar.com/universe-in… 💜 Subscribe and like if you enjoyed the video. Thank you 💜 Join us on: 🌺 Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/universe.in… 🌺 Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/universalloving 🌺 Twitter: https://twitter.com/universeinsideu For Spanish narrated videos, visit my Spanish channel: https://youtube.com/watch?v=TXG5GXHaMqk&feature=share You can also help by translating or adding CC to the videos: https://www.youtube.com/timedtext_cs_p… #universeinsideyou #nikolatesla.
Narration: Petra Ortiz — http://petraortiz.com.
Scences from History Channel were used under Fair Use.
Help my channel here: https://www.patreon.com/universeinsideyou.