Plans to produce a €25,000 car in Berlin Gigafactory are afoot.



It was inevitable. Amazon, which got its start selling books, is getting into the car business.
The e-commerce giant along with new partner Hyundai announced Thursday at the 2023 LA Auto Show that it will start selling vehicles on its website in the second half of 2024. Hyundai vehicles will be the first vehicles sold on Amazon.com’s U.S. store with other brands following later in the year.
The Amazon car sales section will allow customers to shop for vehicles in their area based on a range of preferences, including model, trim, color, and features, choose their preferred car, and then check out online with their chosen payment and financing options. Customers will be able to buy a vehicle online and then pick it up or have it delivered by their local dealership, according to Amazon.
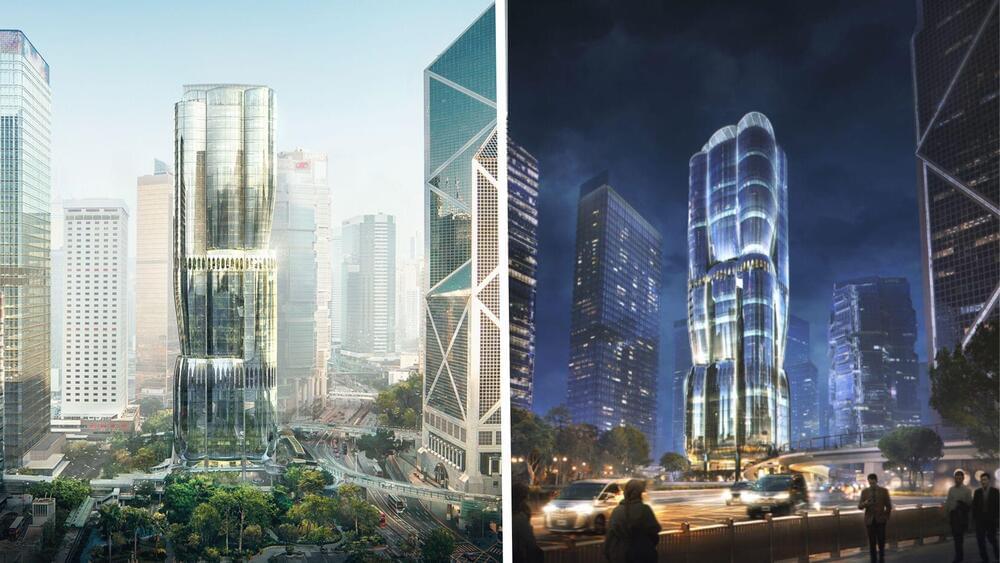

A Zaha Hadid-designed property in Hong Kong will have AI-powered lifts that generate their own energy.
An urban oasis with next-gen elevators
The new structure replaces an old car park to create an urban oasis filled with gardens boasting many plants and trees. Getting to these gardens requires taking Henderson’s next-generation AI-powered lifts.
An official from Henderson properties told Baba that in the future there will be an AI-powered lift assigned to each user so they no longer have to wait for long periods on the ground or on a specific floor. The AI system will be able to appropriately coordinate the lifts to travel according to the number of people waiting for them and their final destinations.
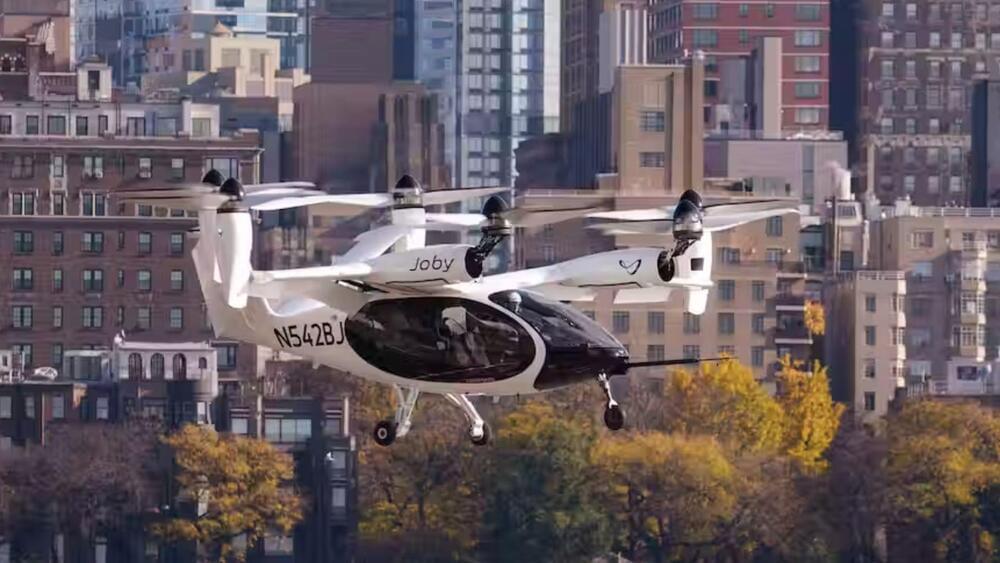

Joby Aviation achieves a historic milestone with the first manned eVTOL air taxi flight in New York City, showcasing its commitment to quiet, emissions-free urban air travel.
Joby Aviation.
The demonstration at the Downtown Heliport in Manhattan showcased Joby’s commitment to revolutionizing urban air travel.

Scientists from the UK and South Korea have discovered a way to create laser pulses 1,000 times stronger than currently possible. Using computer simulations, they have discovered that a new way of compressing the light can drastically increase its intensity to such an extent that it can extract particles from a vacuum. This new technique could open up doors for important discoveries into the very nature of matter.
Uncover the nature of matter
Researchers from the University of Strathclyde, Ulsan National Institute of Science & Technology (UNIST), and Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) have proposed a simple idea to revolutionize the next generation of lasers. They suggest using the gradient in the density of plasma, which is fully ionized matter, to cause photons to bunch together. This is similar to the way a group of cars bunches up as they encounter a steep hill. If this technique is successful, it could increase the power of lasers by more than one million times from what is currently achievable.
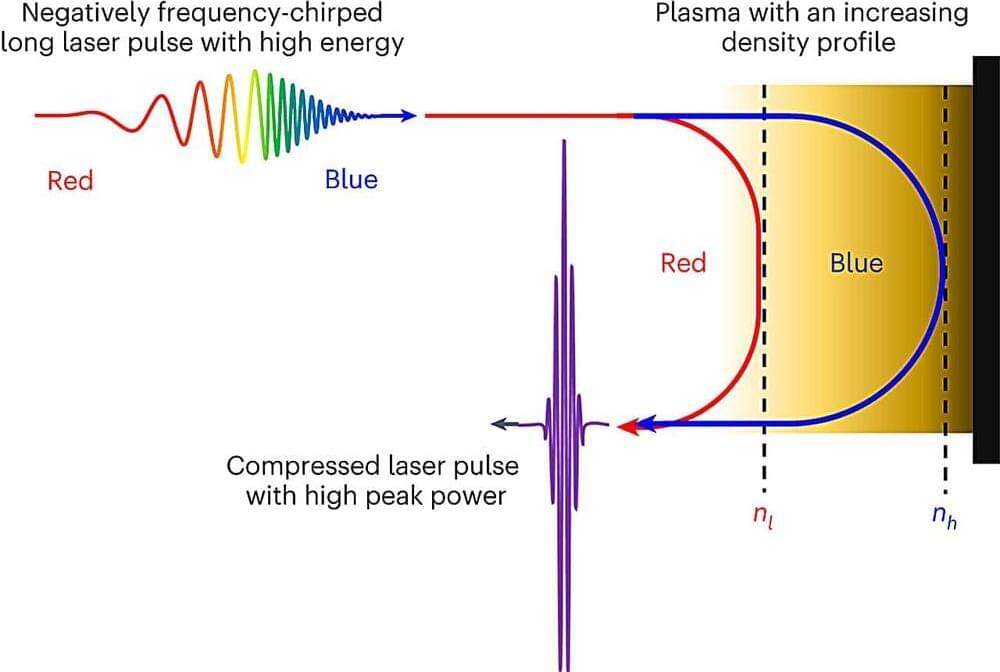
A new method of creating laser pulses, more than 1,000 times as powerful as those currently in existence, has been proposed by scientists in the UK and South Korea.
The scientists have used computer simulations in joint research to demonstrate a new way of compressing light to increase its intensity sufficiently to extract particles from vacuum and study the nature of matter. To achieve this the three groups have come together to produce a very special type of mirror—one that not only reflects pulses of light but compresses them in time by a factor of more than two hundred times, with further compression possible.
The groups from the University of Strathclyde, UNIST and GIST propose a simple idea—to use the gradient in the density of plasma, which is fully ionized matter, to cause photons to “bunch,” analogous to the way a stretched-out group of cars bunch up as they encounter a steep hill. This could revolutionize the next generation of lasers to enable their powers to increase by more than one million times from what is achievable now.


NEW YORK, Nov 13 (Reuters) — Electric air taxis could be transporting passengers from JFK Airport to downtown Manhattan by 2025 — on quiet, emissions-free journeys that take around seven minutes.
Manufacturer Joby Aviation (JOBY.N) carried out an exhibition flight at the Downtown Manhattan Heliport in New York on Sunday, the city’s first-ever electric air taxi flight and the first time Joby has flown in an urban setting.
The craft can recharge in about five minutes, while passengers are unloading and boarding, said CEO JoeBen Bevirt. The idea is that travelers will book their trip, similar to a rideshare app.

As cars become computers on wheels, the former BlackBerry and Dyson executive is approaching Volvo’s EV transformation with a consumer electronics mindset.
Today, I’m talking to Jim Rowan, the CEO of Volvo Cars.
Volvo’s Jim Rowan, now more than 18 months on the job, has strong opinions on EVs, car software, and autonomy.