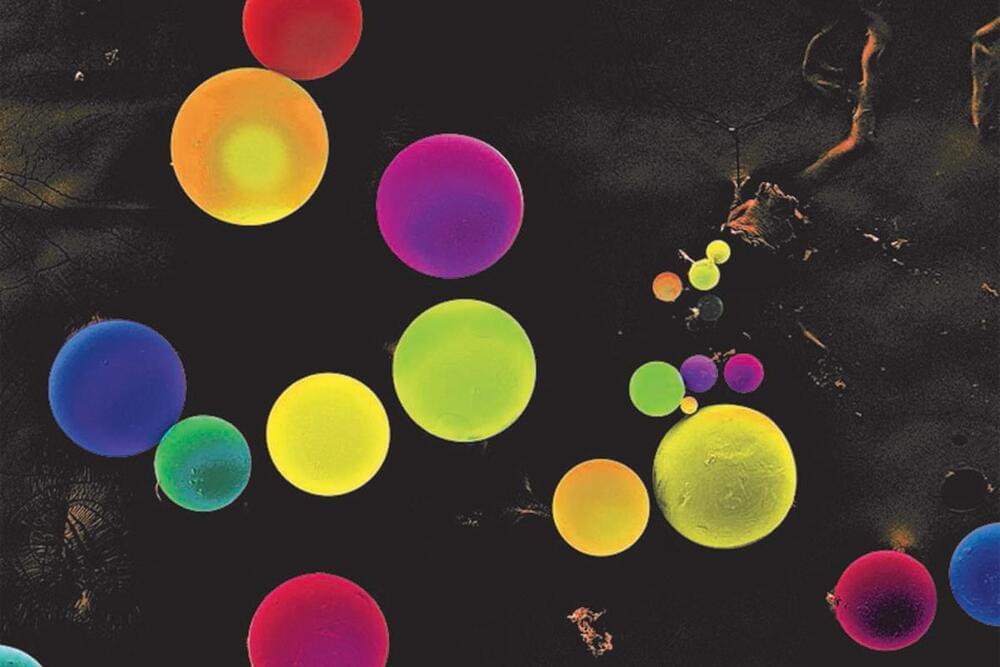Microplastics are an environmental hazard found nearly everywhere on Earth, released by the breakdown of tires, clothing, and plastic packaging. Another significant source of microplastics is tiny beads that are added to some cleansers, cosmetics, and other beauty products.
In an effort to cut off some of these microplastics at their source, MIT researchers have developed a class of biodegradable materials that could replace the plastic beads now used in beauty products. These polymers break down into harmless sugars and amino acids.
MIT researchers developed biodegradable materials that could replace the plastic microbeads now used in beauty products. The materials could also be used to encapsulate nutrients for food fortification.