An international team of scientists has developed a semi-transparent solar cell with 12.3% efficiency and 30% transparency.
Category: sustainability – Page 70


Carbon-negative construction: New method turns CO₂ into strong, fire-resistant building materials
A new method inspired by coral reefs can capture carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and transform it into durable, fire-resistant building materials, offering a promising solution for carbon-negative construction.
The approach, developed by USC researchers and detailed in a study published in npj Advanced Manufacturing, draws inspiration from the ocean’s coral reefs’ natural ability to create robust structures by sequestering carbon dioxide. The resulting mineral-polymer composites demonstrate extraordinary mechanical strength, fracture toughness and fire-resistance capabilities.
“This is a pivotal step in the evolution of converting carbon dioxide,” said Qiming Wang, associate professor of civil and environmental engineering at the USC Viterbi School of Engineering. “Unlike traditional carbon capture technologies that focus on storing carbon dioxide or converting it into liquid substances, we found this new electrochemical manufacturing process converts the chemical compound into calcium carbonate minerals in 3D-printed polymer scaffolds.”

Biodiesel wastewater treatment: Capturing carbon and valuable chemicals
While biodiesel provides a cleaner-burning alternative to petroleum diesel, it produces CO2 and hazardous wastewater during manufacturing, requiring extra steps to achieve sustainability. A diagnostic study led by University of Michigan researchers works to improve a process that captures CO2 while treating biodiesel wastewater and produces valuable co-products like fuels and green chemicals.
During biodiesel production, fats—like vegetable oils, animal fats or recycled restaurant grease—are transformed into fuel through a process called transesterification. With the help of a catalyst, an alcohol (typically methanol) breaks the bonds in the fat molecules to create glycerol and long, chain-like molecules called fatty acid esters.
The fatty acid esters, which resemble petroleum diesel’s molecular structure, become biodiesel while the glycerol goes into the wastewater as a byproduct. If left untreated, glycerol can pollute natural water resources by depleting oxygen levels, suffocating fish and other organisms.
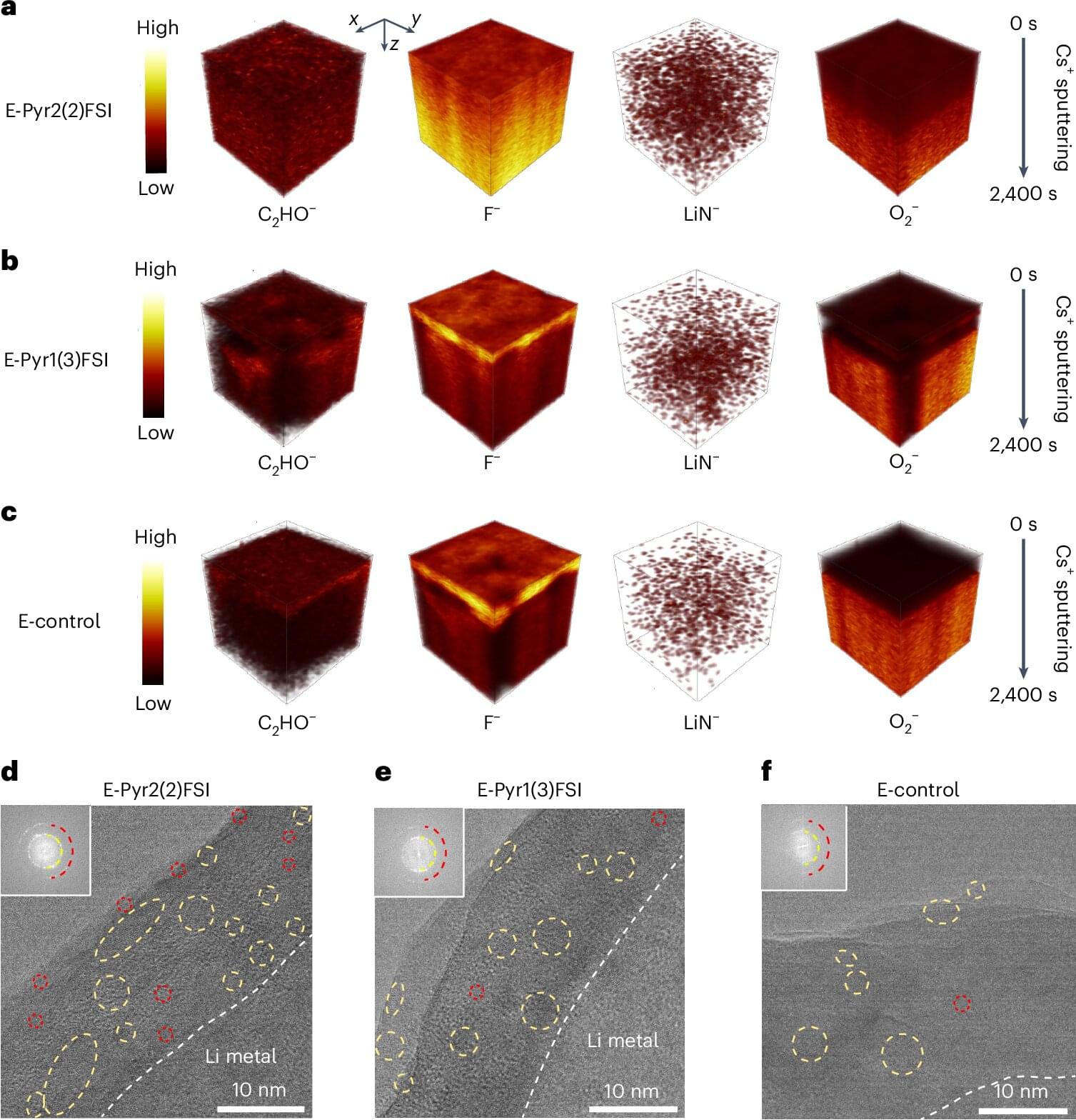
New electrolytes enable safe, stable and fast-charging lithium-metal batteries
In recent years, researchers have been trying to develop increasingly advanced battery technologies that can be charged faster and store more energy, while also remaining safe and stable over time. Lithium-metal batteries (LMBs), which contain a lithium-metal-based anode, have been found to be promising alternatives to lithium-ion batteries (LiBs), which are currently the most widely used rechargeable batteries.
A key advantage of LMBs is that they can store significantly more energy than LiBs, which could be advantageous for electric vehicles and other large or advanced electronics. Despite their potential, these batteries have so far proved to be less stable and safe than LiBs, while also charging relatively slowly; limitations that have so far prevented their widespread adoption.
A research team at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and other institutes recently designed new electrolytes based on symmetric organic salts, which could help to boost the performance of LMBs. Their newly designed electrolytes, introduced in a paper in Nature Energy, were found to improve the stability and charging speed of LMBs, preventing the formation of dendrites (lithium deposits that cause a battery’s performance to decline over time).
Elon Musk Drops BOMBSHELLS About Optimus Robots
Tesla is advancing towards a sustainable future through innovations in energy solutions, autonomous vehicles, and humanoid robots, while fostering a culture of safety and continuous improvement. ## Questions to inspire discussion s Future Production and Impact ” + 🚗 Q: How many vehicles does Tesla aim to produce by 2025? A: Tesla plans to produce over 10 million vehicles in 2025, up from just 20 in 2010, enabled by their compact, high-output factories.
S vision for Optimus humanoid robots? ” +A: Tesla envisions Optimus robots creating a future of abundance for all, producing goods and services with no limit when combined with solar energy and batteries.
🚕 Q: When will autonomous Teslas become widespread? A: Tesla expects autonomous vehicles to dominate roads within 5 years, with a software update enabling 10-100x more usefulness through robotaxi services. s Service and Energy Solutions ” + s approach to customer service? ” +s service team aims to provide a loveable experience, recognizing that future sales depend on service reputation and word-of-mouth marketing. ” + 🔋 Q: How do Megapack and Powerwall 3 benefit homeowners? A: Megapack and Powerwall 3 enable off-grid living and energy assurance, with Powerwall 3 and solar making homes self-sufficient during outages.
S unique about Teslas Supercharger network allows convenient road trips across the US, Mexico, Europe, and China, with charging speeds faster than a restroom break. ” +s AI and Manufacturing Innovations ” + s role in Teslas most powerful AI training systems. ” + s AI hardware compare to others? ” +s AI4 hardware is the most powerful and efficient AI inference computer, operating at very low power in all vehicles. ” + s innovative about TeslaA: The Cybertruck line aims to produce cars in under 5 seconds, using rapid liquid metal casting and automation, resembling a high-speed electronics line. ## Future of Transportation and Energy.
S full self-driving cars? ” +s self-driving cars achieve 10x human safety, never getting tired or distracted, and free up 10–12 hours per week for drivers. ” + s batteries contribute to grid stability? ” +A: Powerwall and Megapack batteries stabilize the grid by absorbing power spikes and filling drops, acting as a virtual grid in neighborhoods.
🚖 Q: How will the role of Uber and taxi drivers change? A: In the future, Uber and taxi drivers will manage fleets of self-driving cars instead of driving individually. ## Investment and Future Technologies.
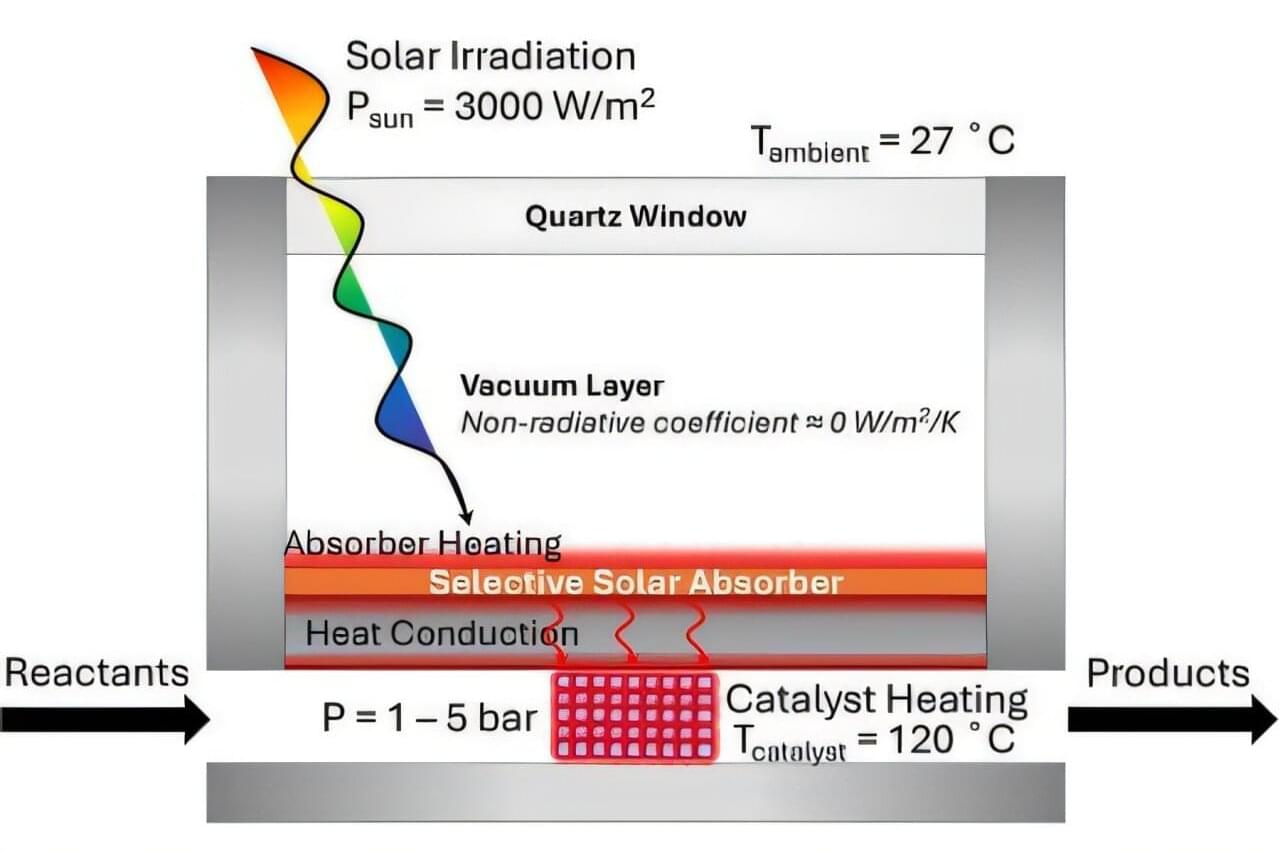
Solar-powered reactor shows potential for creating jet fuel with net-zero carbon emissions
Increasing energy demands and problems associated with burning fossil fuels have heightened interest in more sustainable energy sources, such as sunlight. But there are still areas where carbon-based fuel remains the standard, such as in the aviation industry. To address this need, scientists have been working to devise a way to use sunlight to generate solar-thermal heating that could then drive the chemical reactions that are needed to make jet fuel with net-zero carbon emissions.
Now, a team at Caltech that is part of a Department of Energy (DOE) Energy Innovation Hub known as the Liquid Sunlight Alliance, or LiSA, has developed such a solar-thermal heating system on a small scale and demonstrated that it can successfully drive an important reaction for jet fuel production.
Completely powered by solar energy, the so-called photothermocatalytic reactor incorporates a spectrally selective solar absorber to maximize the generation of solar-thermal heating. The modular design of the reactor takes advantage of current fabrication technologies and existing silicon solar panel production infrastructure.

Machine learning uncovers hidden heat transport mechanisms in organic semiconductors
Complex materials such as organic semiconductors or the microporous metal-organic frameworks known as MOFs are already being used for numerous applications such as OLED displays, solar cells, gas storage and water extraction. Nevertheless, they still harbor a few secrets. One of these has so far been a detailed understanding of how they transport thermal energy.
Egbert Zojer’s research team at the Institute of Solid State Physics at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz), in collaboration with colleagues from TU Vienna and the University of Cambridge, has now cracked this secret using the example of organic semiconductors, opening up new perspectives for the development of innovative materials with customized thermal properties.
The team has published its findings in npj Computational Materials.
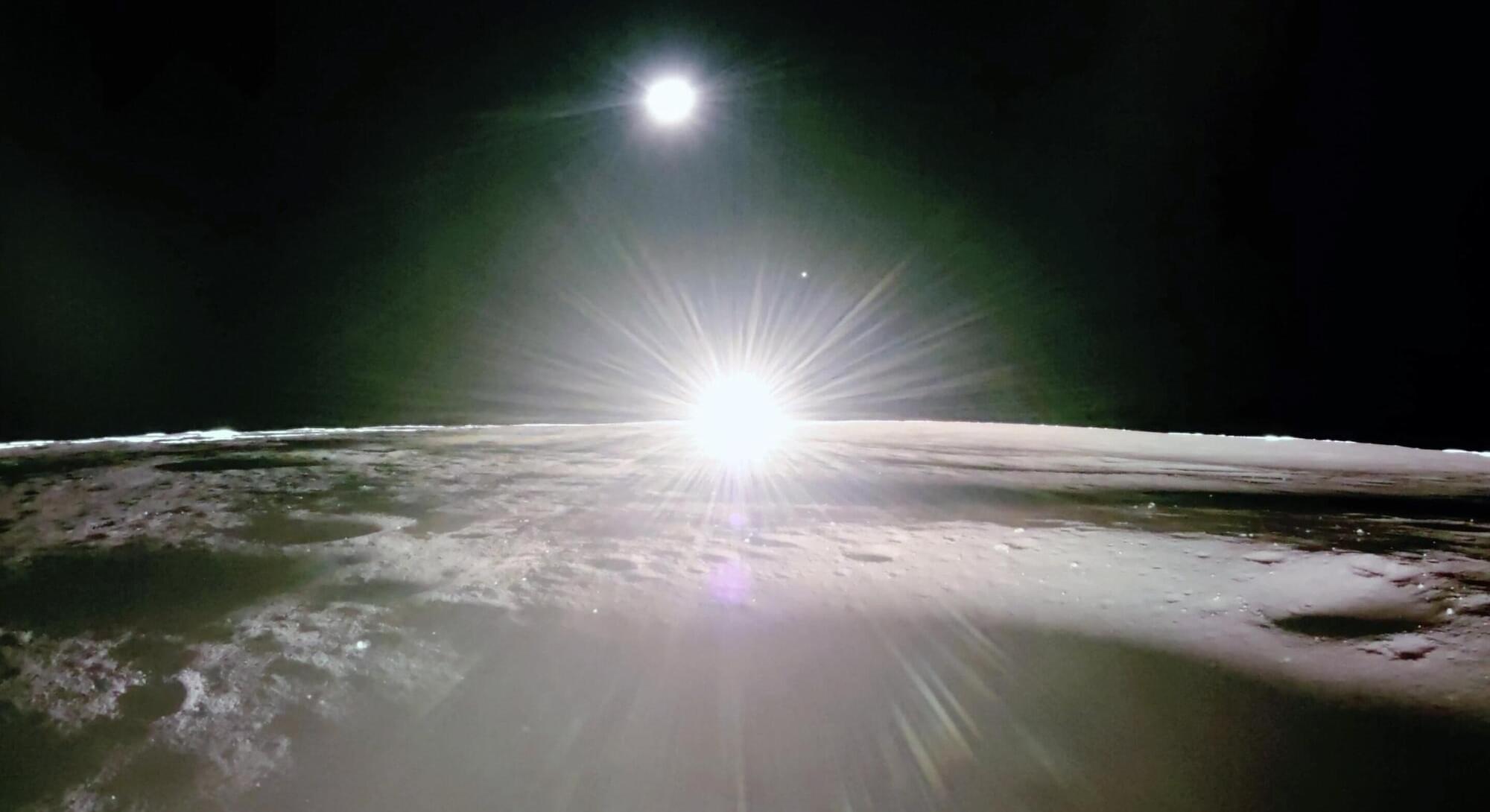

Blue Ghost lander captures stunning sunset shots on the moon before falling silent
A private lunar lander has captured the first high-definition sunset pictures from the moon.
Firefly Aerospace and NASA released the stunning photos Tuesday, taken before the Blue Ghost lander fell silent over the weekend. One shot included Venus in the distance.
Firefly’s Blue Ghost landed on the moon on March 2, the first private spacecraft to touch down upright and perform its entire mission. It kept taking pictures and collecting science data five hours into the lunar night before it died for lack of solar energy.
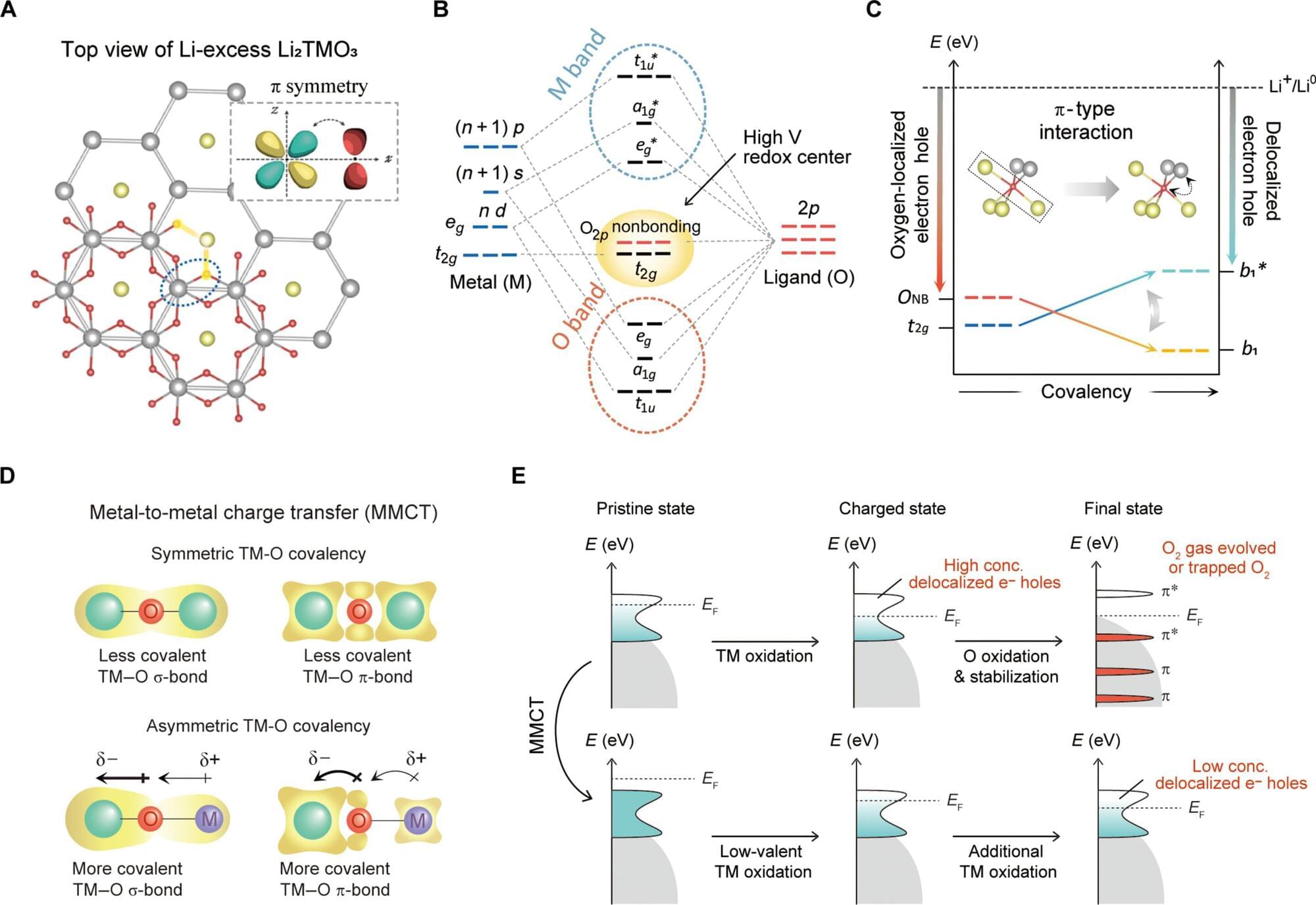
Electrode design could prevent explosions in next-gen batteries, allowing 1,000 km on a single charge
A research team at UNIST has identified the causes of oxygen generation in a novel cathode material called quasi-lithium and proposed a material design principle to address this issue.
Quasi-lithium materials theoretically enable batteries to store 30% to 70% more energy compared to existing technologies through high-voltage charging of over 4.5V. This advancement could allow electric vehicles to achieve a driving range of up to 1,000 km on a single charge. However, during the high-voltage charging process, oxygen trapped inside the material can oxidize and be released as gas, posing a significant explosion risk.
The research team, led by Professor Hyun-Wook Lee in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering, discovered that oxygen oxidizes near 4.25V, causing partial structural deformation and gas release.