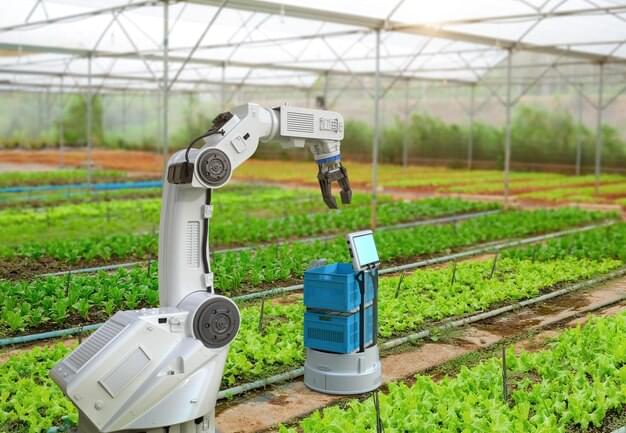
The agricultural sector in South Africa is undergoing a transformation with the introduction of AI-powered harvesting robots. These advanced machines are set to revolutionize farming by increasing efficiency, reducing labor costs, and ensuring better crop yields. With the growing challenges of climate change, labor shortages, and the need for sustainable farming, AI-driven technology is emerging as a critical solution for modern agriculture.
Artificial intelligence has become a vital tool in various industries, and agriculture is no exception. AI-powered robots are designed to perform labor-intensive tasks such as planting, watering, monitoring crop health, and harvesting. These machines utilize machine learning, computer vision, and sensor technology to identify ripe crops, pick them with precision, and minimize waste.
In South Africa, where agricultural labor shortages and rising costs have posed challenges to farmers, AI-driven automation is proving to be a game-changer. With an estimated 8.5% of the country’s workforce employed in agriculture, technological advancements can significantly improve productivity while alleviating labor constraints.