New cities are currently being planned to ease the strain on existing ones. In an ideal world, they should provide work and housing, and be sustainable and climate-neutral at the same time. Is this a realistic objective?


A zero-soil vertical farm is growing fresh greens stacked over 30 feet high.
Make sure to follow Focal Point for more stories like this!

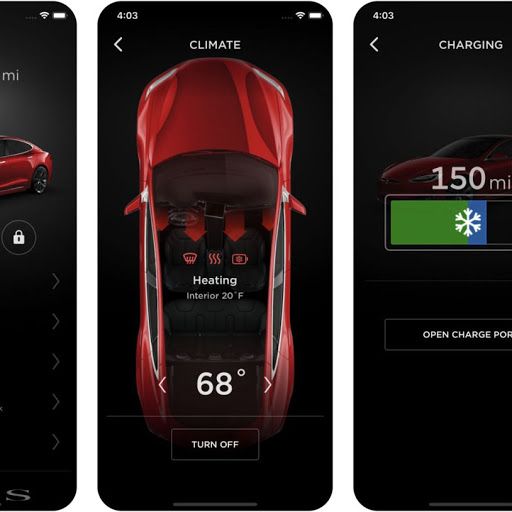

Elon Musk has agreed to build what is being hailed the “world’s largest virtual power plant”, by rolling out solar panels and Tesla batteries to 50,000 homes in South Australia. The scheme, which will be completed over the next four years, will see any excess energy stored in each battery fed back into the grid to provide power to the rest of the state whenever required. The South Australian government claims participating households will generate a total of 250MW of electricity – about half as much energy produced by a typical coal-fired power station. Read more — Elon Musk about to launch…
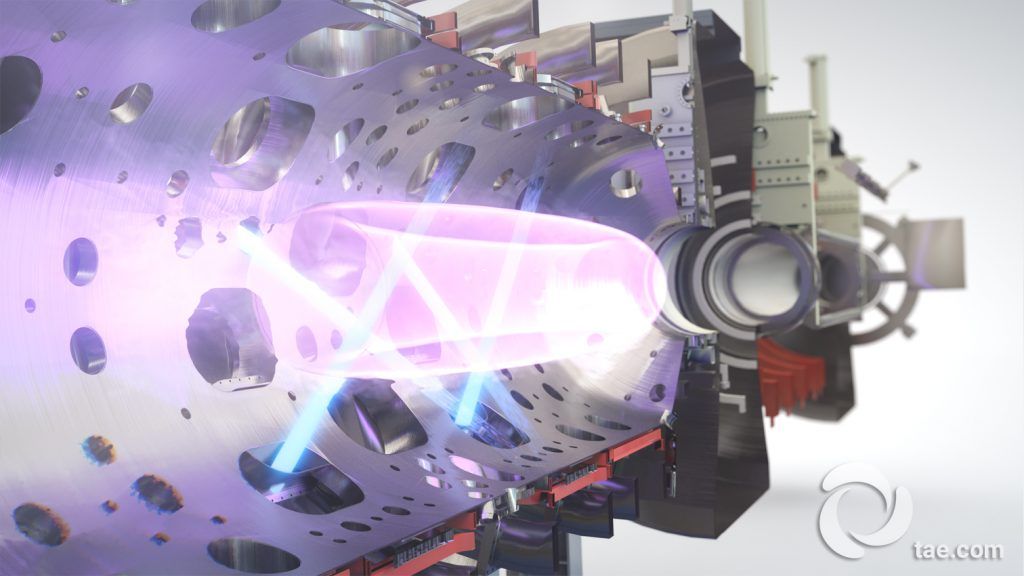
TAE Technologies, Inc. (formerly Tri Alpha Energy), the world’s largest and most advanced private fusion company, has announced that its proprietary beam-driven field-reversed configuration (FRC) plasma generator, “Norman,” surpassed a new technical milestone, bringing the company closer to the reality of commercial fusion power. This latest achievement marks a significant step in the company’s mission to create a global energy revolution with clean, safe, sustainable fusion energy.
Norman, the $100MM National Laboratory-scale device named for company founder Dr. Norman Rostoker, was unveiled in May 2017 and quickly reached first plasma in June 2017. After over 4,000 experiments to date, Norman has now exceeded the capabilities and performance of the company’s previous FRC plasma generator, C-2U, and sets a new company record for plasma temperature.
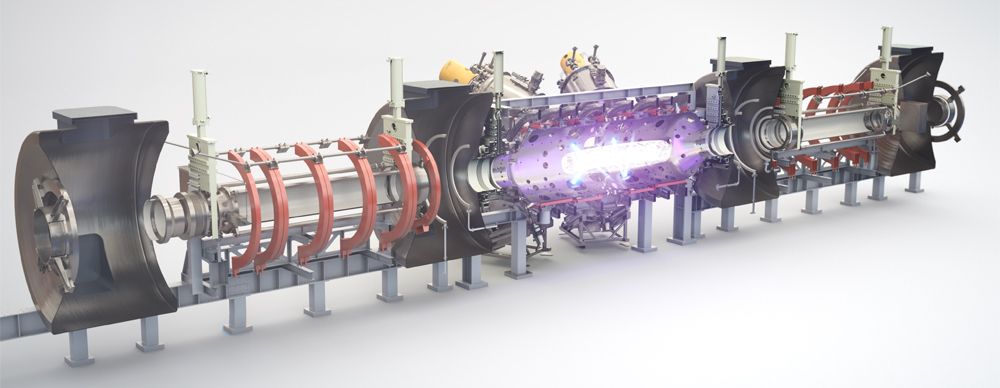
TAE Technologies, the California-based fusion company backed by Microsoft co-founder Paul Allen, said its latest and greatest plasma generator has exceeded the headline-grabbing performance of its previous machine.
“This announcement is an important milestone on our quest to deliver world-changing, clean fusion energy to help combat climate change and improve the quality of life for people globally,” Michl Binderbauer, the company’s president and chief technology officer, said in a news release. “This achievement further validates the robustness of TAE’s underlying science and unique pathway.”

The successful launch of the new rocket, the Falcon Heavy, by SpaceX from the Kennedy Space Centre in Florida into a Mars orbit around the Sun, has captured the world’s imagination and attention mainly because of its power but also because of its payload.
Famously aboard the spacecraft is a Tesla Roadster, owned by SpaceX CEO Elon Musk, but joining the bright red sports car on its journey around our solar system is the Arch Library, created using 5D optical storage technology developed by Professor Peter Kazansky and his team at the University of Southampton’s Optoelectronics Research Centre.
This first Arch library (pronounced Ark) – known as the Solar Library — contains the Foundation Trilogy of science fiction books written by Elon Musk’s favourite American author, Isaac Asimov… Archs are the vision of the Arch Mission Foundation which wants to permanently preserve and disseminate human knowledge as part of an ‘Encyclopedia Galactica’ across time and space for the benefit of future generations.